熔盐堆是第四代反应堆中唯一采用液态燃料的堆型,其易裂变核素溶于高温氟化物或氯化物熔盐中,各种裂变产物也释放到熔盐中。高温、高辐照和高复杂化学环境熔盐的严苛服役环境,对熔盐堆结构材料提出了特殊性能要求[1~5]。基于此,美国橡树岭实验室在上世纪50年代开发出了具有优异高温力学、耐辐照和耐熔盐腐蚀性能的Hastelloy N合金。国内在其基础上对Si、C含量进一步优化,开发出了国产GH3535合金,在高温力学强度和耐熔盐腐蚀性能等关键性能上与Hastelloy N合金基本一致,部分性能优于Hastelloy N合金,目前是我国钍基熔盐堆的首选结构材料[6]。然而,Hastelloy N合金与GH3535合金均存在裂变产物碲致晶间腐蚀开裂问题,研究表明裂变产物Te会沿着合金晶界向内扩散,在晶界上形成多种脆性碲化物(如Ni3Te2、CrTe等),这些脆性碲化物会弱化晶界结合力,导致合金沿晶间开裂,降低合金力学性能和使用寿命,威胁反应堆服役安全[7~11]。本研究通过高温Te气氛环境下的腐蚀实验,研究了Te在合金中扩散行为与Te致合金晶间开裂机理。
1 实验方法
本研究所用的GH3535合金化学成分(质量分数)为:Ni-16.9Mo-7.0Cr-4.0Fe-0.5Mn-0.3Si-0.2Al-0.05C。通过电火花线切割将合金锭切成10 mm × 10 mm × 2 mm大小的试样,将试样在砂纸上磨至2000目,然后用氧化铝抛光膏抛光至镜面,最后依次在丙酮和无水乙醇里超声清洗10 min,冷风吹干后备用。碲源选择Te单质粉末,Te浓度根据试样总表面积计算,分别为:1、6和10 mg/cm2。将试样与Te粉真空密封在石英管内,放入管式炉中升温至700℃后保温150 h。
腐蚀结束后取出试样,用天平称量确定腐蚀增重,使用配置有Cu靶的X射线衍射仪(XRD,Bruker D8 Advance)鉴定表面腐蚀产物的物相,使用扫描电镜(SEM,ZEISS GeminiSEM 500)表征试样腐蚀后产物形貌,并用配置的能谱仪(EDS)进行微区元素定量分析,使用电子探针微区分析(EPMA,JXA-iHP200F)表征Te扩散深度与Te在晶界的分布,使用透射电镜(TEM,Thermo Scientific Talos F200X)研究晶界富碲相的成分与结构。
2 结果与讨论
腐蚀后试样增重与加入的碲粉质量一样,说明碲完全沉积在了合金试样上。腐蚀后试样表面形貌如图1所示,表面腐蚀产物呈层状,部分腐蚀层出现了剥落,EDS结果显示外层腐蚀层主要是Ni、Cr与Te。1和6 mg/cm2 浓度下的试样晶界处出现了明显的裂缝,10 mg/cm2 浓度下的试样并未明显的晶界开裂现象。另外,表面的球状颗粒为合金中的一次碳化物M6C (M = Mo, Ni, Cr),在晶内和晶界均有分布。试样腐蚀后表面XRD如图2所示,腐蚀产物均为Ni3Te2、Ni3Te2.07和Cr2Te3,但不同浓度样品这3种腐蚀产物比例有区别。1 mg/cm2 浓度下的试样腐蚀产物主要是Ni3Te2,10 mg/cm2 浓度下的试样XRD中Ni3Te2.07的衍射峰最强,说明在高浓度碲环境形成了富碲的碲化镍金属间化合物。3种试样的XRD中均有很强的合金基体衍射峰,这应是局部反应层剥落导致的。
图1
图1
GH3535合金试样在Te气氛中腐蚀后的表面形貌
Fig.1
Surface morphologies of GH3535 Ni-based alloy samples after exposure in 1 mg/cm2 (a), 6 mg/cm2 (b), and 10 mg/cm2 (c) Te vapor at 700oC for 150 h
图2
腐蚀后试样截面SEM形貌及EDS元素面分布如图3所示,所有试样腐蚀层均为内外两层。外层是碲与合金元素反应生成的碲化物,主要是Ni、Cr与Te,其中Ni与Cr间隔分布,Te近似均匀分布。EDS点分析结果表明,反应层中富Ni区的Ni∶Te原子比约为3∶2,富Cr区的Cr∶Te原子比约为2∶3,结合XRD结果,腐蚀产物主要是Ni3Te2与Cr2Te3。Cr2Te3相近似呈条状,整体上靠近合金基体,且与Ni3Te2相间隔分布。
图3
图3
GH3535合金试样在1, 6和10 mg/cm2 Te条件下高温暴露后截面SEM像及EDS元素面分布图
Fig.3
SEM image and EDS element mappings of GH3535 Ni-based alloy after corrosion in 1 mg/cm2 (a), 6 mg/cm2 (b) and 10 mg/cm2 (c) Te at 700oC
700℃时,Ni3Te2、Cr2Te3、Mo3Te4和MoTe2的标准摩尔生成Gibbs自由能(kJ/mol Te)分别为-59.125[12]、-55.483[13]、-30.897[14]和-28.570[14],可以看出Ni3Te2和Cr2Te3在热力学上更容易形成,实验现象与热力学数据是相符的。1、6和10 mg/cm2 浓度下的外腐蚀层厚度分别为1.8(±1.0)、12.1(±1.9)和19.5(±2.2) μm,随着Te浓度增加,反应层厚度接近线性增加,说明外层的碲化层不具有任何保护性。1 mg/cm2浓度下的试样反应层很薄,这会导致X射线穿透进基体,XRD结果中出现很强的基体峰。有Te扩散进了基体中,形成内扩散层,扩散层中的Te主要以长条状富Te相的形式富集,这些富Te相向基体延伸,在晶内普遍存在;扩散层深度分别为1~2、3~4和6~8 μm。10 mg/cm2浓度下试样的扩散层最厚,较厚的扩散层破坏了合金原有的晶界,这导致了在试样表面未观察到明显的晶间裂纹。所有试样的外层与内层腐蚀层之间开裂剥离了,这说明内外腐蚀层间结合力较差。
10 mg/cm2浓度下试样截面的EPMA元素面分布如图4所示,扩散层中的富Te相更加清晰,呈条状向基体内部延伸,富碲区同时有Ni、Cr、Fe的贫化与Mo的富集,这似乎与热力学理论是矛盾的,因为热力学上碲化钼(MoTe2、Mo3Te4)更难形成。由于波谱仪对微量元素的检测灵敏度更高,EPMA检测出了合金表面40 µm以下晶界上的Te富集,说明Te沿晶界扩散的更深。同时,晶界也出现了Ni、Cr、Fe的贫化与Mo的富集,深度比Te扩散深度更深。另外,表面的一次碳化物处没有出现Te的富集,Te也没有扩散进碳化物内部,这表明一次碳化物在Te环境非常稳定。
图4
图4
GH3535合金试样在10 mg/cm2 Te条件下高温暴露后截面EPMA-WDS元素面分布图
Fig.4
EPMA element mappings of GH3535 alloy after corrosion in 10 mg/cm2 Te at 700oC
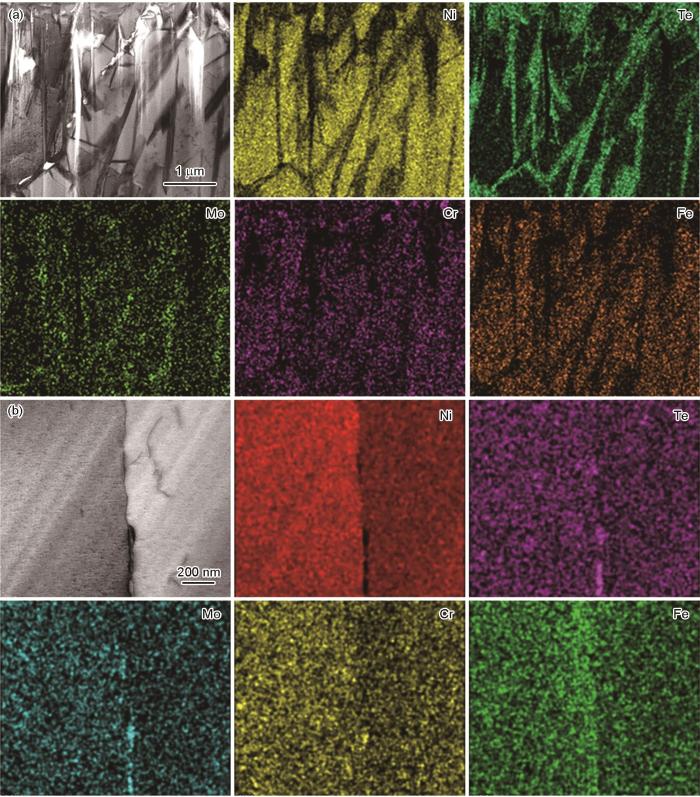
图5
图5
GH3535合金试样在10和1 mg/cm2 Te条件下高温暴露后TEM图像及EDS元素面分布图
Fig.5
TEM image and EDS element mappings of GH3535 alloy after corrosion in 10 mg/cm2 (a) and 1 mg/cm2 (b) Te at 700oC
为进一步分析晶界富碲相,使用FIB沿表面晶界切取截面试样,1 mg/cm2浓度下试样的TEM结果如图5b所示,晶界处存在Te的局部富集。部分Te在二次碳化物附近聚集,碳化物一定程度上阻碍了Te的沿晶扩散。由于晶界相对基体具有更高的能态和更低的扩散激活能,晶界是元素扩散的快速通道[18],因此Te沿晶界向内扩散,在晶界处富集。Cheng等[9]认为是碲化反应易于在晶界和合金基体-晶间二次碳化物界面处发生,导致Te在二次碳化物附近聚集。另外,扩散到晶界的Te与晶界的Ni、Cr反应,消耗了晶界基体附近的Ni、Cr,导致基体内Mo的过饱和,过饱和的基体γ相会分解生成碳化物和新的γ相[19]。这也是碲在碳化物附近富集的一种原因。
10 mg/cm2浓度下的试样TEM分析结果如图6所示,试样晶界存在连续的Te富集相,EDS与高分辨结果表明这些富Te相与扩散层中富Te相的成分和结构类似。这些相的TEM高分辨照片与Fourier转换结果表明,其晶体结构为单斜的Ni3Te2 相,空间群为P21/m(21),晶格常数为:a = 0.755 nm,b = 0.38 nm,c = 0.61 nm,α = γ = 90°,β = 91.22°。未看出明显的MoTe2相,这表明这些富Te相结构是Ni3Te2,但是有Mo掺杂。其形成机理与扩散层中的富Te相相似,因为表面只是一种特殊的晶界。除了晶界具有较低的扩散激活能,晶界上Te的偏析还会降低Fe、Cr在晶界的扩散势垒[20],Ni、Fe、Cr在晶界上向外扩散也更快,因此晶界出现了明显的Ni、Fe、Cr的贫化,合金晶界也出现去合金化,导致了晶间裂纹的产生。因为Fe、Cr在氟化物熔盐中的活性溶解,可以推测含Te氟盐环境下合金晶界处的Fe、Cr将会加速溶解。
图6
图6
GH3535合金试样在10 mg/cm2 Te 条件下高温暴露后的TEM像及EDS元素面分布与高分辨图
Fig.6
TEM image (a), EDS element mappings (b-f) of GH3535 alloy after corrosion in 10 mg/cm2 Te at 700oC, HRTEM image of the selective area marked by yellow square in Fig.6a (g), and the corresponding fast-Fourier transform pattern (h)
3 结论
Te气氛腐蚀后合金表面出现内外两层腐蚀层,外层为Te反应层,主要是Ni3Te2、Ni3Te2.07和Cr2Te3,反应层厚度与Te浓度成线性关系;内层为Te扩散进基体形成的扩散层。扩散层并非是均匀的,而是由基体和许多长条状富碲相组成。Te在合金近表面主要沿晶界向内扩散到更深处,同时晶界出现明显的Ni、Fe、Cr的贫化,导致了晶间裂纹的产生。
参考文献
Status of materials development for molten salt reactors
[R].
Thorium molten salt reactor nuclear energy system
[J].
钍基熔盐堆核能系统
[J].
Corrosion in the molten fluoride and chloride salts and materials development for nuclear applications
[J].
Corrosion of materials for molten salt reactor
[J].
熔盐电堆的材料腐蚀
[J].熔盐反应堆是一种以熔融盐为冷却剂和核燃料的反应堆。作为6种第四代核电站概念堆之一,熔盐堆正日益受到人们的关注。材料的腐蚀问题是熔盐堆发展过程中面临的一个技术挑战。为此,相关研究机构开展了大量研究,并取得了积极进展。本文对材料在熔融氟化物中的腐蚀机制、腐蚀行为以及抗蚀材料发展现状等方面的研究进行了综述。
Hot corrosion and protection of structural materials in molten salt reactor
[J].
熔盐堆用结构材料的热腐蚀及防护
[J].本文综述了结构材料在熔融氟化盐中的热腐蚀及其影响因素,以及表面防护涂层研究现状。
Corrosion behavior of GH3535 superalloy in FLiNaK molten salt
[J].As one of the most promising next generation reactors, the molten salt breeder reactor (MSBR) with excellent inherence security has attracted more and more attentions in recent years due to energy shortage and the security problem of traditional nuclear reactor. The most significant service characteristic of the structural material used in MSBR is the existence of FLiNaK molten salt compared with other nuclear reactors. FLiNaK molten salt is very corrosive to the structural material in the reactor, and affects the safety operation of nuclear power plants. A polycrystalline Ni-Mo-Cr-Fe superalloy was developed and used as an important structural material in MSBR at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), but the corrosion mechanism of the alloy in FLiNaK molten salt has not been determined since the study terminated in 1970' s as some politic reasons. Alloy served in harsh environments, often using protective coating to improve the corrosion properties. While few works about the coating corrosion resistance in FLiNaK molten salt were reported at present. Al2O3 and Cr2O3 coatings usually have excellent corrosion resistance in molten salt, such as sulphate, nitrate and halide molten salt. But, whether the oxide film has corrosion resistance in FLiNaK molten salt has not been determined. In this work, the corrosion mechanism of alloy in FLiNaK molten salt was studied by using immersion corrosion experiment through the method of SEM, EDS and XRD. The influence of Al2O3 coating on corrosion resistance in FLiNaK molten salt was also investigated. The results show that the Al2O3 coating does not affect the exsolution corrosion characteristics of Cr and Mo elements in FLiNaK molten salt at 700 ℃ for 400 h. The different is that naked alloy exhibits intergranular corrosion characteristic, and the alloy with Al2O3 coating exhibits spot corrosion characteristic. The Al2O3 coating cannot improve the corrosion resistance of the alloy in FLiNaK molten salt. The Al2O3 film dissolved in molten salt and resulted in the exposure of the alloy surface. The corrosion rate was increased since the formation of corrosion cell between oxide film and the exposed alloy surface.
GH3535合金在FLiNaK熔盐中的腐蚀行为
[J].
Status of tellurium-Hastelloy N studies in molten fluoride salts
[R].
Effect of temperature on diffusion behavior of Te into nickel
[J].
EPMA and TEM characterization of intergranular tellurium corrosion of Ni-16Mo-7Cr-4Fe superalloy
[J].
Effect of Cr contents on the diffusion behavior of Te in Ni-based alloy
[J].
Effect of grain boundary carbides on the diffusion behavior of Te in Ni-16Mo-7Cr base superalloy
[J].
Thermochemical data acquisition. Part II
[R].
Chromium activity in the Cr-Te system using a CaF2 EMF method
[J].
Diffusion of tellurium at nickel grain boundaries: a first-principles study
[J].
Diffusion of chromium in nickel
[J].
Experimental and computational study of diffusion mobilities for fcc Ni-Cr-Mo alloys
[J].
The effect of tellurium on intergranular cohesion in iron
[J].
Influence of grain size on tellurium corrosion behaviors of GH3535 alloy
[J].The effects of grain size on the tellurium corrosion behaviors have been investigated systematically in GH3535 alloy. After the exposure to Te vapor, the triple-layer scales, which consist of Ni3Te2, Cr3Te4, MnTe, M6C carbides and Fe-riched gamma phase, occur in both the fine-grained and coarse-grained specimens. The thicker outer layer, the more discrete inner layer, the shallower Te permeation and Cr3Te4 existence along grain boundaries can be observed in the fine-grained specimens. By comparing the Gibbs free energies and calculating the effective diffusion coefficients, the tellurization mechanism and the role of grain size were discussed.
Tellurium segregation-induced intergranular corrosion of GH3535 alloys in molten salt
[J].