微合金化是抑制SASS中析出相析出的有效方法,主要用于稳定其奥氏体组织[7]。Ni可以稳定奥氏体,延缓第二相形成,降低其析出敏感温度[8]。SASS中固溶N含量约为0.2% (质量分数),可以稳定奥氏体相,抑制第二相形成,且提高材料力学、热加工及耐蚀性能[9]。与其他元素相比,B在奥氏体中溶解度极小,容易向晶界偏析,可改善晶界稳定性能,对合金元素扩散和第二相析出产生影响[10~12]。B可抑制S31254超级奥氏体不锈钢在凝固过程中元素偏析和σ相形成,并减少晶界附近的贫Cr区,提高耐腐蚀性[13,14]。Li等[15]研究表明B可抑制钢中M23C6碳化物的生长和聚集,使其呈颗粒状分布在晶界,而非连续长条状;B在晶界上的偏聚降低晶界的界面能,提高晶界结合能力。Bai等[16]证实B对SASS变形过程中晶界上σ相的形成具有延缓作用,Yu等[17]研究表明B在晶界的偏析抑制了Mo偏析倾向,限制其向晶界扩散和偏析,抑制σ相的析出,促进塑性变形,有利于动态再结晶,在一定程度上改善材料的热塑性。在超级奥氏体不锈钢中添加适量Ce可以使得凝固组织中铁素体数量增加,在一定程度上减少Mo偏析和σ相析出[18~20]。
B对于SASS中析出相的抑制作用,主要源于对晶界的析出相产生影响,但是现有检测手段难以分析B在晶界的作用。为了进一步理解B的作用,本文选取固溶处理后S31254钢试样,借助低温扩散处理,促进B晶界扩散,通过高温时效处理,分析晶界析出相的析出规律,来阐明B对奥氏体晶界Cr、Mo的偏聚行为及析出相形成影响。为更好发挥B在SASS中的作用提供参考。
1 实验方法
本实验所用S31254钢由太原钢铁集团技术中心冶炼并热轧成28 mm厚板材,其化学成分(质量分数,%)为:C 0.013,Si 0.17,Mn 1.75,P 0.007,S 0.002,Cr 19.75,Ni 17.52,Mo 5.85,Cu 0.98,N 0.21,B 0.004,余量为Fe。热轧板的热处理工艺为:1180 ℃保温40 min进行固溶处理后水冷,固溶后的试样在300 ℃分别保温0、20、40和60 min扩散处理,之后在900 ℃进行保温2 h的时效处理,热处理工艺曲线如图1所示。为了便于分析,将300 ℃分别保温0、20、40和60 min扩散处理,并经900 ℃保温2 h的试样,分别对应标记为:300-0 min、300-20 min、300-40 min和300-60 min。
图1
用线切割机加工试样成10 mm × 10mm × 3 mm,在KSL-1200X型高温管式炉进行固溶处理、扩散处理、时效处理。随后试样用120#砂纸逐渐磨到3000#,用1.5 μm金刚石抛光膏在抛光机上机械抛光,用FeCl3盐酸饱和溶液进行浸蚀。金相组织析出相、腐蚀形貌用Zeiss Sigma 300型扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察,配合Oxford Ultim Max 40型能谱分析仪(EDS)分析析出相成分、元素分布。
采用改进的双环电化学动电位再活化(DL-EPR)方法来探索热处理工艺对S31254耐蚀性能的影响。DL-EPR测试使用PARSTAT 2273型电化学工作站,采用三电极体系,参比电极(饱和甘汞电极,SCE)、对电极(铂箔)和工作电极(老化样品)。将抛光后的10 mm × 10 mm × 3 mm标准试样在电化学工作站进行点蚀性能测试,腐蚀介质为25 ℃的10% (质量分数) NaCl溶液。电化学动电位极化曲线实验参数为:初始电位为-0.4 V (相对于开路电位),扫描速率为0.5 mV·s-1,终止电位是1.6 V (相对于开路电位)。电化学阻抗测试参数为:频率范围105~10-2 Hz,正弦波(AC)的交流幅值为10 mV。在电化学测试过程中每个样品至少测试3次,以确保数据的可靠性[21]。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 低温扩散与时效析出相
S31254钢试样经过1180 ℃固溶处理并水淬后,在300 ℃下分别保温0、20、40和60 min,并于900 ℃时效处理2 h,试样的显微组织如图2所示。可以看出析出相主要在晶界析出,这4种试样中的析出相数量存在明显差异。固溶后直接时效300-0 min试样,晶界析出相最多,在晶界几乎连成网状。300-20 min试样中晶界析出相数量明显减少,且呈间断性、断续状分布,和固溶后直接时效试样相比,经300 ℃保温时效的晶界析出相并非呈直线析出,呈现为锯齿状。300-40 min试样析出相比300-20 min试样,晶界析出相数量更少,间断性更大,晶界析出相锯齿形状明显。300-60 min试样中晶界析出相与300-40 min试样相近,断续的程度更为明显。
图2
图2
S31254钢在300 ℃保温不同时间后在900 ℃时效处理2 h的显微组织
Fig.2
Microstructures of S31254 steel after isothermal treatment at 300 oC for 0 min (a), 20 min (b), 40 min (c), 60 min (d) and then aging at 900 oC for 2 h
综上,300 ℃分别保温0、20、40、60 min不同时间,再900 ℃时效处理2 h后试样中析出相主要分布于晶界,随着扩散时间的延长,析出相的数量越来越少,在晶界呈现出锯齿状形态分布。
2.2 析出相各元素变化分析
S31254钢固溶处理试样经300 ℃分别保温0、40、60 min,再时效处理试样的EDS能谱分析结果见图3。可以看出,析出相主要含有Cr、Mo、B等元素,分为富含Cr、Mo的析出相和富含B、Mo的析出相两种类型。具体来看,固溶后直接时效300-0 min试样,晶界析出相最多,析出相中包括富含Cr、Mo的析出相和富含B、Mo的析出相,其中前者含量较多。300-40 min试样富含Cr、Mo的析出相很少,以富含B、Mo的析出相居多。300-60 min试样主要以富含B、Mo的析出相为主。由此可知,固溶试样经300 ℃扩散时间越长,越有利于含B、Mo的析出相的形成。
图3
图3
S31254钢在300 ℃保温不同时间后在900 ℃时效处理2 h后的EDS能谱分析
Fig.3
EDS composition analysis of S31254 steel after firstly isothermal treatment at 300 oC for 0 min (a), 40 min (b), 60 min (c) and then aging at 900 oC for 2 h
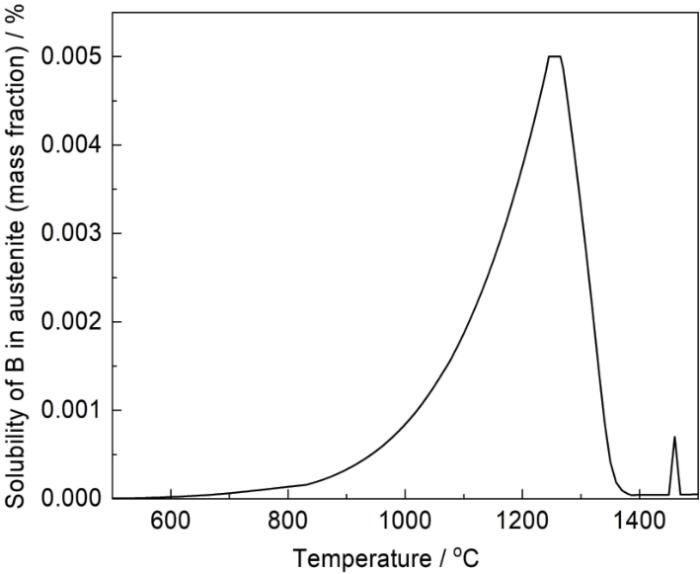
为了进一步分析低温扩散处理对晶界B的影响,采用Thermo-Calc计算软件,计算了B在fcc-Fe中不同温度的溶解度,图4给出了B在奥氏体钢中的溶解度曲线。可以看出1180 ℃固溶处理时,B在奥氏体基体中溶解度约为0.0031% (质量分数),由于不锈钢中B的添加量很低,为0.004%,应该1180 ℃固溶处理使得部分B溶在基体中。Xu等[22]利用微观组织表征和理论计算研究了B对σ相析出行为的影响,计算结果证实B优先偏聚于晶界,抑制Mo、Cr等的偏聚,从而抑制σ相的形成。Zhang等[23]研究表明B对析出相析出的机制以及对耐蚀性有影响,不仅抑制σ相的形成并可形成含B的Laves相,减少晶界附近的贫Cr区,提高SASS耐晶间腐蚀性能。结合SASS固溶处理后的淬水处理,固溶试样形成了过饱和固溶体,此时固溶态的试样中应该有部分B以过饱和形式溶于奥氏体基体或者缺陷中。由于B原子半径较小,为间隙原子,300 ℃下不同时间的扩散处理,B容易在保温过程中由奥氏体基体内向晶界扩散。扩散时间的长短对于B的扩散影响明显。从图2和3可见,300 ℃不同时间的扩散处理,影响了晶界析出相的析出,同时扩散时间不同晶界处B的能谱强弱也有差别,说明B扩散到晶界,影响时效过程中析出相的形成。
图4
2.3 低温扩散处理与时效组织耐蚀性能
S31254钢固溶处理试样,经300 ℃保温0、20、40、60 min,于900 ℃时效处理2 h后试样的电化学动电位极化曲线见图5。可见,析出相较少,300-40 min试样的耐蚀性和300-60 min试样接近,300-20 min试样的耐蚀性表现较弱,耐蚀性强弱依次是300-60 min > 300-40 min > 300-0 min > 300-20 min。
图5
图5
S31254钢经300 ℃保温处理不同时间后再经900 ℃时效处理2 h,在10%NaCl水溶液中的动电位极化曲线
Fig.5
Potentiodynamic polarization curves of S31254 steel after firstly isothermal treatment at 300 oC for different time and then aging at 900 oC for 2 h in 10%NaCl solution
图6
图6
经300 ℃保温处理不同时间、再经900 ℃时效处理2 h后S31254钢的动电位再活化曲线
Fig.6
Potentiodynamic reactivation curves of S31254 steel with isothermal treatment at 300 oC for different time and then aging at 900 oC for 2 h in 10%NaCl solution
表1 图6中S31254钢动电位再活化曲线Ir与Ra拟合值
Table 1
| Sample | Ir / A·cm-2 | Ra (Ir/Ia) / % |
|---|---|---|
| 300-60 min | 0.001532 | 0.0880 |
| 300-40 min | 0.001876 | 0.1180 |
| 300-20 min | 0.006180 | 0.3394 |
| 300-0 min | 0.003789 | 0.2198 |
Ra代表再活化率,Ra越大,晶间腐蚀敏感性越强,根据检测结果对试样的晶间腐蚀敏感性进行分析。300-60 min试样为所有试样中耐晶间腐蚀敏感性最好,300-40 min试样的耐蚀性弱于300-60 min试样,但是总体来讲,300 ℃不同时间的保温处理有利于提升SASS的耐蚀性。Ir代表再活化电流,Ir值的大小表示合金元素的贫乏程度,由晶间腐蚀曲线知,300-20 min试样的Ir值最大,因为不锈钢中影响晶界耐蚀性的元素为Cr和Mo,析出相以高Cr高Mo为主,析出相与基体界面应该存在一定宽度的贫Cr贫Mo区,因而试样晶界表面析出相周边腐蚀区域很宽。300-60 min试样的Ir值最小,这也与析出相成分中Cr含量低,且析出相周围被腐蚀区域宽度小相对应。
S31254钢试样经过1180 ℃固溶处理40 min后水淬,经300 ℃分别保温0、20、40、60 min,并于900 ℃时效处理2 h后,再经电化学极化处理,表面腐蚀形貌如图7所示。可以看出,固溶后直接时效300-0 min试样表面晶界腐蚀严重,主要沿原有析出相发生腐蚀。300-20 min试样析出相减少,但相界面的腐蚀仍然很严重。300-40 min试样析出相明显减少,带有析出相的相界面的腐蚀程度也减弱。300-60 min试样析出相及腐蚀程度与300-40 min试样相近,较300-0 min、300-20 min试样相界面的耐蚀性明显提高。
图7
图7
经300 ℃保温处理不同时间后再经900 ℃时效处理2 h的S31254钢电化学极化腐蚀表面形貌
Fig.7
Surface corrosion morphologies of S31254 steel with isothermal treatment at 300 oC for 0 min (a), 20 min (b), 40 min (c), 60 min (d) and then aging at 900 oC for 2 h after electrochemical polarization
3 结论
固溶态含B超级奥氏体不锈钢S31254在300 ℃不同时间的扩散预处理,可以使B在奥氏体晶界发生再分布,保温时间越长,对于后续高温时效处理试样中析出相的析出影响越明显,有利于抑制时效过程中析出相的析出,同时由富Cr富Mo析出相转化为含B富Mo析出相。其中300 ℃保温40和60 min的试样抑制析出相析出效果明显。B参与析出相的析出,含B富Mo析出相的试样具有较佳的耐晶间腐蚀性能。
参考文献
Elucidating the passivation kinetics and surface film chemistry of 254SMO stainless steel for chimney construction in simulated desulfurized flue gas condensates
[J].
σ-phase formation in super austenitic stainless steel during directional solidification and subsequent phase transformations
[J].
Effects of Cr and Mo on precipitation behavior and associated intergranular corrosion susceptibility of superaustenitic stainless steel S32654
[J].
Corrosion behavior of 904L super-austenitic stainless steel in simulated primary water in nuclear power plants
[J].
904L超级奥氏体不锈钢在模拟核电一回路环境中的腐蚀行为研究
[J].
Passivation behavior of super austenitic stainless steels in simulated flue gas desulfurization condensate
[J].
超级奥氏体不锈钢在模拟烟气脱硫冷凝液中的钝化行为研究
[J].
Corrosion behavior of three super austenitic stainless steels in a molten salts mixture at 650-750 oC
[J].
超级奥氏体不锈钢的热腐蚀行为及机理研究
[J].
Review on development and second phase regulation of super austenitic stainless steels
[J].
超级奥氏体不锈钢发展及第二相调控研究现状
[J].
Investigating the effect of Cu-rich phase on the corrosion behavior of super 304H austenitic stainless steel by TEM
[J].
Influence of N on precipitation behavior, associated corrosion and mechanical properties of super austenitic stainless steel S32654
[J].
Effect of B addition on the microstructure and corrosion resistance of S31254 super austenitic stainless steels after solid solution treatment
[J].
Corrosion resistance and passivation behavior of B-containing S31254 stainless steel in a low pH medium
[J].
Effect of a new heat treatment process on B elements distribution, second phase precipitation and corrosion resistance of S31254 super austenitic stainless steel
[J].
新热处理工艺调控B元素分布对S31254超级奥氏体不锈钢第二相析出和耐蚀性能的影响
[J].
The mechanism on the B addition to regulate phase precipitation and improve intergranular corrosion resistance in UNS S31254 superaustenitic stainless steels
[J].
Effect of compression deformation on precipitation phase behavior of B-containing S31254 super austenitic stainless steel
[J].
Impact of boron addition on the hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of S31254
[J].
Effect of boron addition on the precipitation behavior of S31254
[J].
Influence mechanism of boron segregation on the microstructure evolution and hot ductility of super austenitic stainless steel S32654
[J].
The influence of Ce micro-alloying on the precipitation of intermetallic sigma phase during solidification of super-austenitic stainless steels
[J].
Effect of B and Ce micro-alloying on secondary phase precipitation and corrosion resistance of S31254 super austenitic stainless steel
[J].
B、Ce微合金化对S31254超级奥氏体不锈钢析出相及耐蚀性能的影响
[J].
Precipitation of second phase and its effect on corrosion resistance of Ce-containing S31254 super austenitic stainless steel
[J].
含Ce S31254超级奥氏体不锈钢析出相析出行为及耐蚀性
[J].
Detection of susceptibility to intergranular corrosion of aged super austenitic stainless steel S32654 by a modified electrochemical potentiokinetic reactivation method
[J].
Effects of B segregation on Mo-rich phase precipitation in S31254 super-austenitic stainless steels: experimental and first-principles study
[J].
Improved corrosion resistance of super austenite stainless steel by B-induced nucleation of laves phase
[J].