1 实验方法
将Q235钢加工成20.0 mm长的钢丝 (
为了研究南海热带环境下藤壶自然附着对金属的腐蚀行为影响,选择在藤壶生长繁殖最旺盛的夏季,于湛江调顺岛进行挂样实验。挂样地点水深约为15 m,潮差较大,海水电导率为36000 μS·cm-1,盐度为24.5,pH为7.86。将阵列电极牢牢固定在浮岛上,确保其工作面完全浸泡在海水中。
在实验的15和30 d取回样品,使用Nikon D800E单反相机记录电极表面宏观腐蚀形貌,并利用CS350电化学工作站进行电化学测试。线性极化和交流阻抗测试以2 cm
2 结果与讨论
2.1 碳钢在海水浸泡15和30 d的腐蚀规律
图1
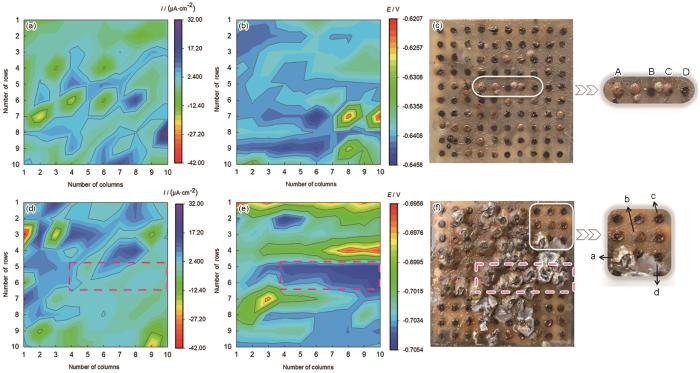
图1
Q235钢电极浸泡不同周期的电偶电流和偶接电位分布图及其对应表面形貌图
Fig.1
Galvanic current and coupling potential distribution maps (a, b, d, e) and surface topography maps (c, f) for 15 d (a-c) and 30 d (d-f)
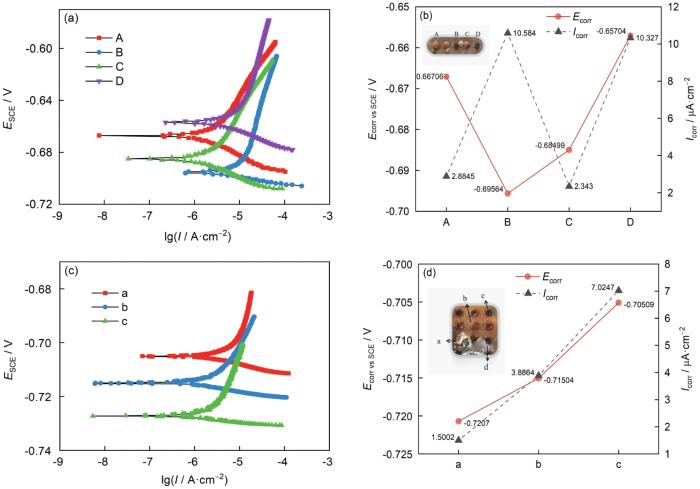
浸泡15 d,根据图1c可知,金属表面生成黄褐色腐蚀产物,表面有少数小藤壶附着。对距藤壶不同距离的4个微电极进行线性极化测试,极化曲线见图2a。图2b为距藤壶不同距离微电极的Icorr和Ecorr对比图,B和D微电极金属表面都直接暴露在海水中,二者Icorr相近,数值约为10 μA·cm-2,而B比D微电极更靠近藤壶附着位置,B微电极的Ecorr 更低,两者相差38 mV。A和C微电极表面都有腐蚀产物堆积,二者Icorr均小于仅有少量腐蚀产物覆盖的B、D微电极,腐蚀产物一定程度上会抑制金属腐蚀,而C微电极更靠近藤壶附着位置,C微电极Ecorr低于A微电极的Ecorr。由此推断藤壶附着会造成周围区域金属的腐蚀电位降低。
图2
图2
藤壶附着及周围区域的线性极化曲线
Fig.2
Linear polarization plots of barnacle attachment and surrounding area on 15 d (a, b) and 30 d (c, d)
浸泡30 d,根据图1f可知,电极表面50%以上的区域被藤壶覆盖,a微电极表面被藤壶覆盖,其Icorr为1.5 μA·cm-2,Ecorr为-0.7207 V,皆明显低于周围区域,且随距藤壶距离的增加,微电极Icorr和Ecorr皆呈增大趋势。b微电极表面被较厚腐蚀产物覆盖,其Icorr为3.9 μA·cm-2,明显低于仅有少量腐蚀产物的c微电极的Icorr,高于被藤壶覆盖的a微电极的Icorr,由此推断,虽然大型污损生物层和锈层下均含有大量的异养菌、铁细菌和中性硫氧化菌[13, 14],但藤壶石灰质底壳比碳钢表面腐蚀产物层更致密,底壳抑制营养物质传输和氧气扩散作用更强,使得下方细菌活性减弱,a微电极Icorr低于b微电极Icorr。同时,更为致密的藤壶底壳抑制溶解氧的传输,造成壳下微生物群落逐渐转变为厌氧菌和兼性厌氧菌,细菌通过分解有机体,产生酸性和有机活性物质[15~18],导致pH值下降、Ecorr低于未被藤壶附着的微电极。藤壶分泌的石灰质或摄食、代谢过程中分泌的有机物,使碳钢腐蚀产物的粘附性增加,结合更为牢固。因此,临近藤壶区域的电极表面腐蚀产物多于远离藤壶区域的腐蚀产物,腐蚀产物的累积继而影响物质的传输。
2.2 藤壶对金属腐蚀行为的影响
为了进一步阐明藤壶对金属表面的电化学行为的影响,选取图1f中有藤壶附着的a微电极、无藤壶附着的c微电极和表面有残余壳体的d微电极进行电化学阻抗测试。图3a和b为对应的Nyquist图和Bode图。从Bode曲线中可知,在|Z|0.01 Hz 频率下有藤壶附着微电极阻抗模值最大,为378.3 Ω·cm2,而无藤壶附着的微电极阻抗模值为237.8 Ω·cm2,有残余壳体的电极阻抗模值低于无藤壶附着的电极,仅为156.2 Ω·cm2。活体藤壶的阻隔性高于碳钢腐蚀产物的阻隔性,碳钢腐蚀产物的阻隔性高于藤壶残余壳体的阻隔性。藤壶附着对金属腐蚀起抑制作用,藤壶底壳主要成分为碳酸钙,导电性差,同时藤壶分泌的藤壶胶具有较大的内聚强度[19, 20],能将基体表面和其钙质底盘通过几微米的胶层连接起来,并通过粘腺导管网络系统运输液态胶到附着部位,液态胶又能通过流动和扩散作用,使基底与基体间的接触更为紧密[21,22],阻止海水直接与基体发生接触,限制溶解氧等成分的传输。藤壶因种内竞争导致脱落后,残余底壳中的有机质被细菌和微生物降解后其致密性大幅下降,其阻隔性大幅下降。
图3
图3
电化学阻抗图以及阻抗等效电路模型
Fig.3
Nyquist (a) and Bode (b) plot represents the fitted curve of the three samples, equivalent circuit diagram of attached by part of balanite or not attached by barnacle (c), and attached by barnacles (d)
利用Zview软件对阻抗谱进行拟合,图3c为藤壶脱落和无藤壶附着时的拟合等效电路,图3d为有藤壶附着时的拟合等效电路。为了消除非理想电容对拟合结果造成的影响,使用常相位角元件CPE,CPEf、CPEdl分别代表藤壶/碳钢之间的电容和双电层电容,Rs、Rf、Rct分别代表溶液电阻、藤壶/碳钢之间的孔隙或锈蚀电阻和电荷转移电阻,Warburg阻抗用于表明碳钢受扩散控制的腐蚀反应。表1为等效电路图中各等效电子元件的拟合数值。从表中可得,有藤壶附着区域Rct为19.81 Ω·cm2,无藤壶附着区域Rct为15.26 Ω·cm2,残余壳体区域Rct仅为1.629 Ω·cm2,因Rct与金属腐蚀速率负相关,可知藤壶附着下a微电极的腐蚀速率小于未被藤壶附着的c微电极,该结果与图2d极化曲线求得的瞬时腐蚀速率具有较好的一致性。因藤壶脱落区域残余的钙质底壳逐渐被细菌分解,金属重新暴露在海水中,使得d微电极的Rct远小于a、c微电极。a微电极的弥散指数CPEdl-P大于c、d微电极,电极表面被完整的生物底壳覆盖,耐蚀性更好。
表1 等效电路拟合值
Table 1
| Sample | Rs Ω·cm2 | CPEdl | RctΩ·cm2 | W | CPEf | Rf Ω·cm2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CPEdl-T S·sec n ·cm2 | CPEdl-P | R Ω·cm2 | T S0.5 | P | CPEf-T S·sec n ·cm2 | CPEf-P | ||||
| Attached by barnacles | 4.499 | 0.01280 | 0.72397 | 19.81 | 42.91 | 0.4261 | 0.4313 | 0.00077 | 0.24652 | 26.91 |
| Not attached by barnacles | 10.59 | 0.00483 | 0.51994 | 15.26 | 95.96 | 2.855 | 0.3167 | - | - | - |
| Attached by part of balanite | 10.85 | 0.00072 | 0.65406 | 1.629 | 34.99 | 2.742 | 0.4151 | - | - | - |
3 结论
(1) 藤壶附着造成碳钢的非均匀腐蚀,从浸泡15 d有小藤壶附着到30 d藤壶逐渐长大,碳钢微电极间偶接电位持续降低,电偶电流增加,最大偶接电位差从25 mV下降为9 mV,最大阳极区电偶电流从32 μA·cm-2降低为18.6 μA·cm-2,最大阴极区电偶电流增加到41.6 μA·cm-2。
(2) 随距藤壶附着位置距离的增加,碳钢腐蚀电位逐渐升高,腐蚀电流逐渐加大。藤壶底壳下碳钢的腐蚀电位比距藤壶附着点较远区域的腐蚀电位低25 mV,藤壶底壳下碳钢的腐蚀电流约为距藤壶附着点较远区域的腐蚀电流的21%。
(3) 活体藤壶壳体为碳酸钙和有机质的复合材料,具有较好的阻隔性,其抑制溶解氧的传输造成藤壶活体附着下碳钢的低腐蚀电位、低腐蚀电流的“双低”现象;藤壶脱落后,经微生物分解有机质后,残存壳体阻隔性大为降低,其阻隔性低于碳钢腐蚀产物阻隔性,促使碳钢快速腐蚀。藤壶生长过程中分泌的有机物与藤壶附着点周围碳钢的腐蚀产物混合,增大了腐蚀产物的粘附强度,促进腐蚀产物的累积,增大腐蚀产物的阻隔性。海洋环境中,藤壶对碳钢的附着会加剧碳钢时空二维的非均匀腐蚀。
参考文献
Research progress of biofouling and its control technology in marine underwater facilities
[J].
海洋水下设施生物污损及其控制技术研究进展
[J].
Molecular design of barnacle cement in comparison with those of mussel and tubeworm
[J].
Macrofouling induced localized corrosion of stainless steel in Singapore seawater
[J].
Mechanism for Barnacle-induced crevice corrosion in stainless steel
[J].
Effects of oyster as macrofouling organism on corrosion mechanisms of a high-strength low-alloy steel
[J].
Correlation between electrochemical impedance and current distribution of carbon steel under organic coating
[J].
Ecology of harbor fouling organisms on spot detectation and quantification of fouling organisms of Seagull floating dock
[J].
港湾污损生物生态研究—海鸥浮码头污损生物现场检测及其污损量化
[J].现场检测了坞修海鸥浮码头尾舵舱、船体和船头的污损生物,共检出8类30余种生物。优势种为紫贻贝Mytilus galloprovincialis,首次发现粗胞苔虫Scrupocellaria sp.,物种多样性顺序为船头>尾舵舱>船体。尾舵舱口污损最严重,此处重叠附着厚度达15 cm,硬壳类污损生物覆盖面积百分比达70%。讨论了季节因素、船体结构、海水流动状态和阳光照射对污损生物群落组成的影响;将检出的污损生物分成硬壳类群、被覆类群、直立类群和藻类群4类,根据硬壳类附着面积大小给出污损程度的量级并绘出了浮码头的生物污损图,对促进非生物专业科技人员的交流、防污标准的制定及污损生物生态数学建模具有一定的推动作用。
Simulating effects of marine fouling organisms on corrosion of Zn sacrificial anodes
[D].
模拟污损生物附着对Zn阳极腐蚀性能影响的研究
[D].
Corrosion behavior and regularities of two stainless steels in seawater environment of different harbors
[J].
两种不锈钢在港口海水环境中的腐蚀行为和规律研究
[J].
Influence of environmental factors in Yulin area of the South China Sea on localized corrosion of steels
[J].
南海榆林海域环境因素对钢局部腐蚀的影响
[J].采用典型钢宏观海生物实海验证腐蚀试验,测试分析钢样锈 层中主要腐蚀细菌、FeS和钙盐沉淀物.结果表明,由于南海榆林海域水温较高,海生物一年 四季生长旺盛,在钢样表面呈不均匀附着,使钢样表面电化学不均匀性增大;榆林站钢样锈 层中几种好氧菌及厌氧的硫酸盐还原菌比温度较低的青岛站的高几倍至3个数量级,并呈聚 集分布;几种钢样腐蚀产物中的FeS含量榆林比青岛高01~1倍左右,南海榆林海域细菌局 部腐蚀效应较大,这是加剧钢的局部腐蚀的两个重要因素.
The influence of macrofouling on the corrosion behaviour of API 5L X65 carbon steel
[J].Seawater is a complex corrosive system, and biofouling is one of the factors that influences corrosion processes. The behaviour of corrosion associated with the development of macrofouling was investigated during the first 6 months of the successional process. Three treatments were compared: the 'Control' treatment (absence of macrofouling); 'Community' treatment, and 'Barnacle' treatment, where other macroorganisms were excluded. In the Community treatment, the dominant organisms were filamentous macroalgae (23.73%), barnacles (17.51%), hydroids (16.96%) and encrusting bryozoans (9.58%). In the Barnacle treatment, the cover varied between 39.38% and 62.50%. The corrosion potential ranged from -665.75 to -517.50 mV(Ag/AgC l((KCl))) and could not be associated with fouling development. The highest corrosion rate in the control suggests that macrofouling provides a protection against mass loss. The highest percentage of localised attacks was found in the Community treatment. This may indicate that not only barnacles, but also other organisms induce localised corrosion.
Effect of marine fouling creatures on corrosion of carbon steel
[J].
海洋污损生物对碳钢腐蚀的影响
[J].报道了国产碳钢(A3,3C)在我国黄海、东海、南海三个海上实验站八年实海试验的结果。从污损生物附着和碳钢腐蚀的结果看出,污损生物可降低碳钢平均腐蚀率,但促进局部腐蚀;在污损生物活跃的东海、南海近岸海域,一年后碳钢表面100%附着,腐蚀速率稳定在一定值。
Influence of oceanic biofouling on corrosion of carbon steel in seawater
[J].
生物污损对碳钢海水腐蚀的影响
[J].
A study on microbiologically influenced corrosion of a carbon steel in seawater
[J].
海水中碳钢内锈层中的微生物及其对腐蚀的影响
[J].
Research progress of nanomaterials in the prevention of biological fouling on ships
[J].
Progress in marine biologically influenced corrosion study
[J].
金属材料海洋环境生物污损腐蚀研究进展
[J].

海生物因素是影响海洋环境金属材料腐蚀行为的主要因素之 一.综述了金属材料海生物腐蚀研究领域中有关生物膜的结构与功能、海水环境微生物 腐蚀机理研究和宏观海生物附着引起的局部腐蚀等几个方面近年来的进展情况.并结合我国 开展海生物腐蚀研究的现状提出建议和讨论.
Stress corrosion cracking behavior of 2205 duplex stainless steel in 3.5% NaCl solution with sulfate reducing bacteria
[J].
硫酸盐还原菌作用下2205双相不锈钢在3.5%NaCl溶液中应力腐蚀开裂行为研究
[J].采用动电位极化技术、慢应变速率拉伸实验 (SSRT) 以及扫描电子显微镜 (SEM) 等方法研究了硫酸盐还原菌 (SRB) 新陈代谢对2205双相不锈钢 (DSS) 在3.5% (质量分数) NaCl溶液中的应力腐蚀开裂 (SCC) 行为的影响。结果表明,与无菌溶液中相比,SRB的存在促进了2205DSS的阳极溶解过程,诱发了点蚀,为SCC萌生提供了裂纹源。2205DSS的SCC敏感性与SRB活性浓度呈正相关,在稳定生长期SRB活性浓度最大,此时2205DSS的SCC敏感性最大。2205DSS在含SRB的3.5%NaCl溶液中发生的SCC机理为阳极溶解和氢脆混合控制机制。SRB作用下,2205DSS中铁素体相表现为穿晶解理特征,奥氏体相表现为韧性撕裂的特征,铁素体相具有更高的SCC敏感性。
Crevice corrosion behavior of Q345E steel in simulated seawater solution
[D].
Q345E钢在模拟海水溶液中缝隙腐蚀行为研究
[D].
The adhesion of marine organism and the influence on the surface and performance of cement-based materials
[D].
海洋生物附着及对水泥基材料表面及性能影响研究
[D].
Electrolyte conductivity through the shell of the eastern oyster using a four-electrode measurement
[J].
Barnacle cement proteins: importance of disulfide bonds in their insolubility
[J].Barnacles produce a cement that is a proteinaceous underwater adhesive for their secure attachment to the substratum. The biochemical properties of the cement have not previously been elucidated, because the insolubility of the cement proteins hampers their purification and characterization. We developed a non-hydrolytic method to render soluble most of the cement components, thereby allowing the proteins to be analyzed. Megabalanus rosa cement could be almost completely rendered soluble by its reduction with 0.5 m dithiothreitol at 60 degrees C in a 7 m guanidine hydrochloride solution, the high concentration of dithiothreitol being indispensable to achieve this. The effectiveness of this reduction treatment was confirmed by the detachment of the barnacle from the substratum. Three proteins comprising up to 94% of the whole cement were identified as the major cement components. The cDNA clone of one of these major proteins was isolated, and the site-specific expression of the gene in the basal portion of the adult barnacle, where the cement glands are located, was demonstrated. A sequence analysis revealed this cement component to be a novel protein of 993 amino acid residues, including a signal peptide. This is the first report of the major component of the barnacle cement protein complex.