近年来随着我国石油及能源工业的快速发展,埋地管线里程越来越长,油气管道建设稳步推进,高压、大管径、高钢级管线钢是石油和天然气输送管道发展的必然趋势[1,2,3]。我国70%的石油和99%的天然气运输全部依赖埋地管道进行输送,管道运输关系经济命脉,同时也关系到公共安全[4,5,6,7]。截止2018年,我国长输管线已达1.3×105 km,预计到2025年将完成2.4×105 km的铺设,其中西气东输一、二、三线和中俄东线为代表的高钢级管道就有4×104 km[8,9,10]。国家重大工程“西气东输”工程是目前世界上X80管线钢用量最大、铺设里程最长的管线工程[3,11],该工程几乎途经我国全部地形、地貌和气象单元,这些因素对管线钢的长周期安全运行将带来极大影响。因此,迫切需要对油气输送管道外腐蚀实施控制,尤其应该开展X80管线钢在我国西气东输工程沿线各种典型土壤环境下的服役安全性研究和数据积累工作。
土壤介质引起的应力腐蚀 (SCC) 是长输管道服役过程中最大的安全隐患之一[12,13]。随着服役时间的增加,埋地管道普遍存在外部涂层破损和剥离缺陷,在外加电位和土壤介质的共同作用下,将会发生不同pH值土壤环境下的SCC,导致高强管线钢存在严重的SCC风险[14]。目前,国内外学者已经对管线钢在高pH值含高浓度CO32-/HCO3-的涂层下滞留液 (pH=8.0~12.5) 和近中性pH值 (pH=5.5~8.0) 模拟溶液中的SCC进行了大量的研究[1,15,16,17],还有一些国内学者研究了管线钢在我国实际土壤模拟溶液中的SCC敏感性[18,19,20]。轮南作为“西气东输”工程的起点,这里蒸发强烈,土壤次生盐渍化严重,以粗砂为主且含盐量较高,是我国西部地区典型的内陆盐土,对材料的腐蚀作用很大。然而,目前尚未系统开展X80管线钢在我国西部盐渍土壤环境下的研究工作。
本文以我国新疆轮南土壤模拟溶液为实验介质,研究了外加电位对X80钢母材及焊缝在轮南土壤中SCC行为与敏感性的影响,探究其腐蚀机理和规律,为管线的运行和管理提供理论及数据支持。
1 实验方法
实验所用试样是从X80螺旋缝埋弧焊管上线切割而来,X80钢的具体化学成分 (质量分数,%) 为:C 0.047,Mn 1.81,Si 0.19,P 0.01,S 0.0021,Cr 0.35,Mo 0.11,Nb 0.066,Ni 0.14,V 0.003,Ti 0.015,Cu 0.17,Fe余量。X80钢在室温下的力学性能为:屈服强度604 MPa,抗拉强度727 MPa。断后伸长率38%。
选取新疆轮南地区土壤环境为模拟研究介质,依据轮南土壤的主要理化数据配制的模拟溶液成分 (质量分数,%) 为:Cl- 0.336,SO42- 0.155,HCO3- 0.028,溶液pH值为7.28,用分析纯NaCl,Na2SO4、NaHCO3及去离子水配制,整个实验过程中,持续向溶液中通入95%N2+5%CO2 (体积分数) 以维持近中性pH值环境,实验温度为10 ℃。
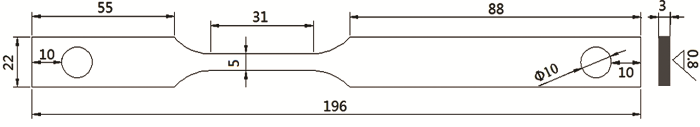
使用MFDL100型慢应变速率应力腐蚀试验机进行慢应变速率拉伸实验 (SSRT),拉伸应变速率是1×10-6 s-1。依据GB/T 15970制作试样,具体的试样尺寸与形状如图1所示。为了确保试样主受力方向在拉伸时与实际受力方向一致,X80母材试样是沿着实际管道的环向进行取材的;X80焊接试样从螺旋缝埋弧焊管上截取,其中焊缝区处于焊接试样标距中间位置。每个试样测试面经SiC水磨砂纸逐级打磨至1000#,然后使用丙酮除油、蒸馏水清洗、无水酒精脱水,冷风吹干后放入干燥器中备用。外加电位的SSRT实验施加的电位分别为:-1500,-1000,-850和-500 mV,均相对于饱和甘汞电极 (SCE)。实验温度为10 ℃。采用扫描电子显微镜 (SEM,JSM-6390A) 观察试样断口横截面及侧面的形貌。
图1
SCC敏感性可使用断面收缩率损失系数Iψ来表征,其表达式如下:
式中,ψ和ψ0分别表示试样在腐蚀介质与空气中的断面收缩率。通常情况下,材料-介质体系的SCC敏感性随Iψ增大而增强。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 SSRT拉伸实验
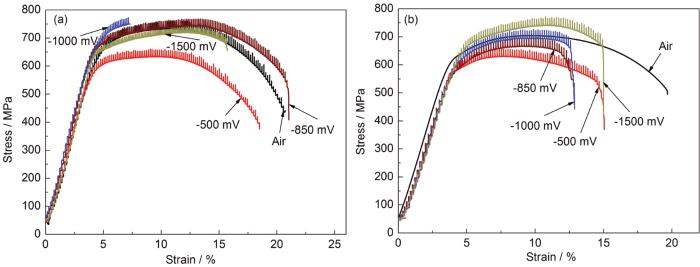
图2是X80管线钢母材及焊缝在空气中与轮南土壤模拟溶液中不同外加电位下的SSRT曲线。可见,X80管线钢焊缝的SSRT试样均在焊接热影响区发生断裂。除了X80钢母材在-850 mV电位下的延伸率高于空气中的,其他电位下的延伸率均明显低于空气中的,并且对比焊缝和母材的SSRT曲线可知,焊缝区域的延伸率较母材低,表明X80钢母材和焊缝在轮南土壤模拟溶液中具有一定的SCC敏感性。
图2
图2
X80管线钢母材及焊缝在轮南土壤模拟溶液中不同外加电位下的SSRT曲线
Fig.2
Strain-stress curves of X80 steel at different potential: (a) base metal, (b) weld joint
根据拉断后试样的测量数据,计算得到的X80管线钢母材及焊缝在轮南土壤模拟溶液中的Iψ如图3所示。可见,X80钢母材及焊缝基本上都具有较明显的SCC敏感性;且X80钢焊缝在不同电位下的SCC敏感性指标Iψ均高于母材的,说明X80钢焊缝的SCC敏感性高于母材,这可能与焊缝组织相变和冶金反应有关;X80钢母材的Iψ随外加电位的负移而逐渐增大,说明外加电位的降低可使X80母材的SCC敏感性增加;X80钢焊缝的Iψ随外加电位的负移先增加后降低,在-1000 mV时达到最高,其SCC敏感性排序为Iψ (-500 mV)<Iψ (-1500 mV)<Iψ (-850 mV)<Iψ (-1000 mV),说明外加电位保护并不能有效抑制X80钢的SCC。
图3
2.2 断口及裂纹形貌观察
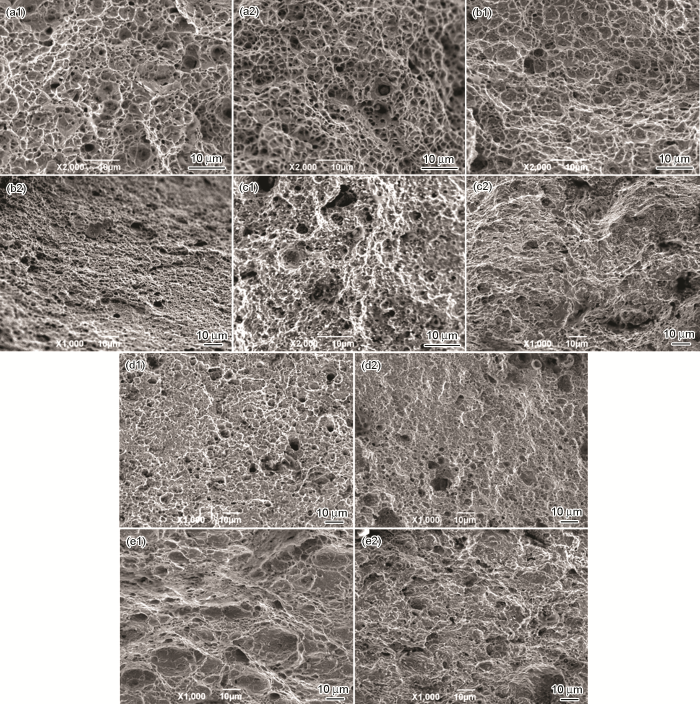
为了进一步研究不同外加电位对X80钢母材和焊缝SCC敏感性的影响,通过SEM观察了X80钢在不同电位下断口正面与侧面的微观形貌,见图4和5。X80钢宏观断口在空气中出现了显著的颈缩现象,从图4a1和a2可以看出,其微观断口表现为等轴韧窝与韧窝间微孔洞相间而生,表现为典型的韧窝微孔型的韧性断裂特征,这是由于X80钢在空气中的慢拉伸过程中产生了显著的塑性变形,当应力高于钢的屈服极限σs后,材料内部缺陷在相界、晶界、亚晶界和缺陷等部位形成位错塞积群,在应力集中处形成微孔洞,这些微孔洞随形变增加而相互吞并变大,最后导致颈缩和断裂的发生。X80钢母材和焊缝在不同电位下的宏观断口均发生了一定程度的颈缩,但其颈缩比例远低于空气中的,断口微观形貌主要由浅平小韧窝、微孔洞、撕裂棱和准解理面组成,表现为韧-脆混合断裂特征。在-500 mV电位下,X80钢母材和焊缝的断口形貌主要以浅平小韧窝为主,但韧窝特征不如空气中的明显,且断口中间区域出现了一些准解理小刻面,表明此时X80钢已表现出一定的SCC敏感性;在-850~-1500 mV电位下,X80钢母材和焊缝的断口形貌以准解理和解理特征为主,在脆性区之间存在少量的扁平小韧窝形貌,表明随外加阴保电位的负移,X80钢SCC敏感性进一步增加。断口形貌特征与SCC敏感性测试结果相一致。
图4
图4
X80管线钢母材及焊缝在空气中和不同外加电位下的断口SEM形貌
Fig.4
Microfracture surface morphologies of X80 steel at different potential: (a1) base metal in air; (a2) weld joint in air; (b1) base metal, -500 mV; (b2) weld joint, -500 mV; (c1) base metal, -850 mV; (c2) weld joint, -850 mV; (d1) base metal, -1000 mV; (d2) weld joint, -1000 mV; (e1) base metal, -1500 mV; (e2) weld joint, -1500 mV
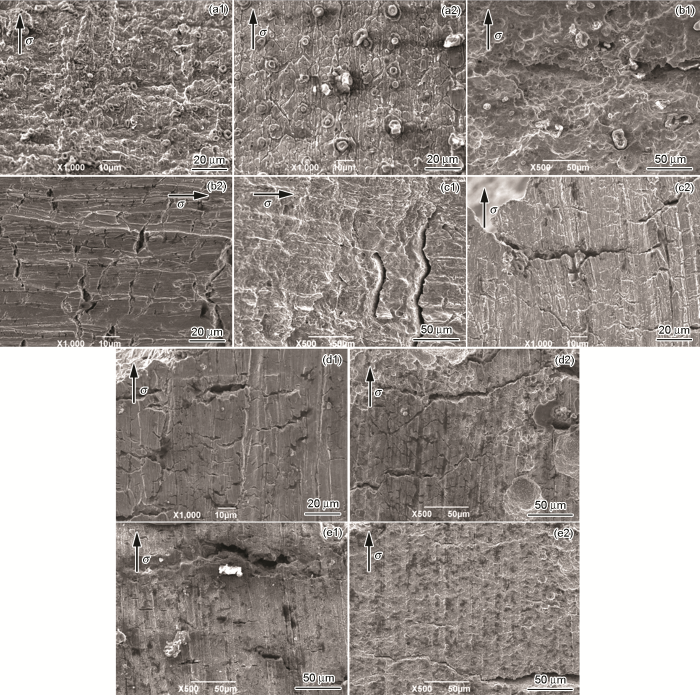
一般认为,在腐蚀性介质中拉伸试样断口侧面存在微裂纹 (二次裂纹),则表明该材料对SCC敏感[23]。图5是X80钢在空气中和不同外加电位下的断口侧面SEM形貌图。可见,X80钢母材与焊缝在空气中的SSRT断口侧面均发生了显著的塑性变形,并无二次裂纹产生,因此不具有SCC敏感性 (图5a1和a2)。在不同外加电位条件下,X80钢母材和焊缝断口侧面仅出现了少量的塑性变形,且侧表面上均出现了不同程度的二次裂纹,这些二次裂纹基本上均与拉伸载荷方向垂直。在-500 mV电位下,X80钢母材断口侧面二次裂纹较少,但出现大量溃疡状的点蚀坑,表明此种状态下SCC的萌生受阳极溶解 (AD) 过程的影响较大,X80钢焊缝断口侧面也出现了一些小的腐蚀坑,同时出现了大量细小的裂纹,表明X80钢在-500 mV电位下具有一定程度的SCC敏感性 (图5b1和b2)。在-850 mV电位下,X80钢母材和焊缝断口侧面腐蚀程度较轻微,但二次裂纹的长度和密度明显增加,表明此种情况下X80钢的SCC敏感性进一步增加 (图5c1和c2);在-1000和-1500 mV电位下,X80钢母材和焊缝断口侧面的二次裂纹长度/密度进一步增加,与-850 mV 时相比,该电位下试样表面的AD过程进一步被抑制,析氢作用增强,表明析氢作用可促进X80钢母材及焊缝的SCC过程,增加SCC敏感性 (图5d1,d2,e1和e2)。
图5
图5
X80管线钢母材及焊缝在空气中和不同外加电位下的断口侧面SEM形貌
Fig.5
Secondary cracks morphologies of X80 steel side surfaces at different potential: (a1) base metal in air; (a2) weld joint in air; (b1) base metal, -500 mV; (b2) weld joint, -500 mV; (c1) base metal, -850 mV; (c2) weld joint, -850 mV; (d1) base metal, -1000 mV; (d2) weld joint, -1000 mV; (e1) base metal, -1500 mV; (e2) weld joint, -1500 mV
2.3 极化曲线测量
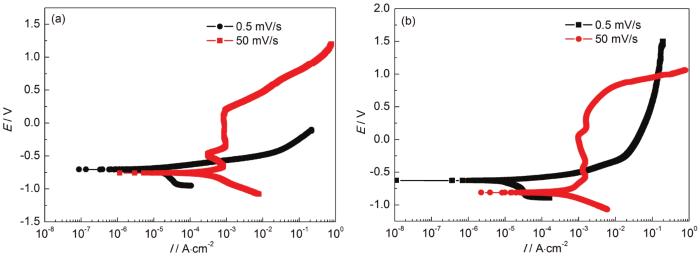
图6是X80钢母材及焊缝在轮南土壤模拟溶液中分别进行快/慢速率扫描得到的电化学极化曲线。可见,X80钢母材及焊缝试样在非裂尖区域 (慢扫极化曲线) 和裂纹尖端 (快扫极化曲线) 的电化学行为相似,X80钢母材及焊缝在非裂尖区域一直处于活化状态,说明该区域的阴极和阳极均表现为活化控制特征;而X80钢母材及焊缝在裂尖区域的阳极曲线中出现了轻微的活化-钝化转变区和稳定钝化区,说明裂尖区域的阳极首先受活性溶解过程控制、接着发生了轻微钝化、最后钝化膜破裂导致裂尖进一步溶解,其开裂机理为裂尖阳极溶解-膜破裂机理;根据快扫极化曲线和慢扫极化曲线零电流电位的差异可将外加电位分为3个区域:(1) 在慢扫极化曲线的自腐蚀电位以上,快扫与慢扫的极化曲线均为阳极曲线,表明SCC裂纹萌生 (即非裂尖区域的电化学过程) 受阳极过程控制,其SCC机制为AD过程,而裂纹扩展 (即裂尖区域的电化学过程) 的SCC机制为裂尖AD-膜破裂过程。从该电化学特征判断,-500 mV测试条件处于AD-膜破裂机制电位区域。(2) 在快扫与慢扫极化曲线的自腐蚀电位之间,阴极吸氧反应和析氢反应的混合过程将发生在非裂纹尖端区域,而析氢过程将促进SCC微裂纹的成核与扩展,进一步强化非裂尖区域的氢脆 (HE) 机制,而裂尖区域产生的非稳态AD过程直接促进了裂尖的阳极溶解与扩展,说明该区域的SCC机制为AD+HE的混合机制[22]。(3) 在快扫极化曲线自腐蚀电位 (大约-800 mV) 以下,裂尖与非裂尖区域的电化学过程均为阴极析氢过程,表明SCC机制以HE过程为主,X80钢的HE敏感性在此电位范围内显著增强[23]。从该电化学特征判断,-850,-1000和-1500 mV这3种测试条件均处于HE机制电位区域。
图6
图6
X80管线钢母材及焊缝在轮南土壤模拟溶液中的快慢扫极化曲线
Fig.6
Polarization curve of X80 steel in simulated soil solution: (a) base metal; (b) weld joint
2.4 分析讨论
在外加阳极电位-500 mV下,因阳极溶解作用导致X80钢表面出现了大量的点蚀坑 (图5b)。这些蚀坑底部由于受到应力集中作用而成为潜在的裂纹形核处,进而影响X80钢的SCC过程[24]。然而,由于阳极溶解作用致使萌生的裂纹被溶解掉而不能产生有效的扩展,因此,-500 mV电位在一定程度上又降低了X80钢SCC敏感性。由图6可知,X80钢在-850,-1000和-1500 mV这3种阴极电位条件下电化学行为均受阴极析氢过程控制,因此,当外加阴极电位负移,X80钢表面析氢反应逐渐加强。高的阴极电流使进入钢中的H增加,从而降低了钢的韧性,进而促进氢致开裂 (HIC) 的发生。可见,在-800 mV电位以下,阴极反应产生的H增多,X80钢的SCC敏感性增大。
3 结论
(1) X80管线钢及其焊缝在轮南土壤模拟溶液中表现出了一定的SCC敏感性。在同一外加电位下,X80钢焊缝的SCC敏感性高于母材的,这可能与焊缝组织相变和冶金反应有关。
(2) 外加电位对X80管线钢在轮南土壤模拟溶液中的SCC敏感性与开裂机理具有显著影响。在-500 mV阳极电位范围内,X80钢的SCC机理为裂尖AD-膜破裂机制,在-800 mV电位以下 (-850,-1000和-1500 mV),由于HE作用在SCC过程中产生的影响更大,阴极析氢反应会促进钢的氢致开裂,X80钢SCC敏感性显著增加。
参考文献
EIS analysis on stress corrosion initiation of pipeline steel under disbonded coating in near-neutral pH simulated soil electrolyte
[J].
Effect of inclusions on initiation of stress corrosion cracks in X70 pipeline steel in an acidic soil environment
[J].
Significant technical progress in the West-East gas pipeline projects-line one and line two
[J].Increasing the steel strength grade and pressure of gas pipelines are a tendency of gas pipeline construction and an important symbol of progress in gas pipeline technologies. Companies and research institutes in China conducted coresearch projects and made a set of key technical achievements to make the design pressure and the pipe strength of the Line One and Two in the WestEast Gas Pipeline and other major arterial pipeline projects reached, even exceeded the international level in the corresponding period. The achievements include (1)the development of X70 and X80 grade pipeline steel, welded pipes, and fittings, (2)the breakthrough of the application limit of spirally submerge arc welded pipes, and the establishment of the technical route for alternative application of spirally and longitudinally submerge arc welded pipes with highstrength and largediameter in main pipelines, (3)the first investigation of dynamic fracture and crack arrest in China, which adopts the Battelle Two Curve method to predict the toughness requirement for the Line One and Line Two WestEast Gas Pipelines, (4)the investigation of strainbased design for oil & gas pipelines, which solves problems of the methodology and high strain pipe application in seismic and active faults areas, and (5)investigations of controlling the corrosion and strain aging of high strength pipes, and so on. These achievements have significance to the economy of pipeline construction and the safety of pipeline service.
西气东输一、二线管道工程的几项重大技术进步
[J].提高管线钢强度级别和管道输送压力是天然气输送管道的发展趋势,是输气管道技术进步的重要标志。近年来,我国管道企业和相关科研院所联合攻关,取得了一批关键技术成果,使西气东输(为便于区别,以下称为西气东输一线)和西气东输二线等国家重点管道工程的设计压力和钢管强度级别达到或领先于同时期的国际水平。这些成果包括:①研制了X70、X80钢级高性能管线钢及焊管、管件;②突破国际上螺旋缝埋弧焊管的使用禁区,确立了具有中国特色的“大口径高压输送主干线螺旋缝埋弧焊管与直缝埋弧焊管联合使用”的技术路线;③在国内首次研究了高压输气管道动态断裂与止裂问题,分别采用Battelle简化公式和Battelle双曲线法预测了西气东输一线和西气东输二线等管道延性断裂的止裂韧性;④在国内首次研究了油气管道基于应变的设计方法,解决了该设计方法及抗大变形管线钢管在强震区和活动断层管段应用的技术难题;⑤研究解决了高强度焊管的腐蚀控制和应变时效控制技术等。上述成果对降低输气管道建设成本、保障管道运行安全具有重要意义。
Investigation of the corrosion progress characteristics of offshore subsea oil well tubes
[J].
Hua Jianmin: By the end of the 12th Five Year Plan, the total mileage of our long oil and gas pipeline exceeded 100000 km
[DB/OL]. (
华建敏: 十二五末我长输油气管道总里程超10万公里
[DB/OL]. (
Influence of soil moisture on the residual corrosion rates of buried carbon steel structures under cathodic protection
[J].
Bayesian analysis of external corrosion data of non-piggable underground pipelines
[J].
Intelligent construction of oil and gas pipeline to be speeded up
[N].
油气管道智能化建设待提速
[N].
The current situation and development trend of China's Long distance natural gas pipeline
[J].
我国长输天然气管道现状及发展趋势
[J].
The scale of China's oil and gas pipeline network will reach 240000 km by the year of 2025
[DB/OL]. (
2025年我国油气管网规模将达到24万公里
[DB/OL]. (
X80 pipe for the second west east gas pipeline and its welding process
[J].
西气东输二线用X80管材及其焊接工艺
[J].
Role of Fe oxides in corrosion of pipeline steel in a red clay soil
[J].
Review of stress corrosion cracking of pipeline steels in "low" and "high" pH solutions
[J].
Effect of cathodic protection on corrosion of pipeline steel under disbonded coating
[J].
Investigating the mechanism of stress corrosion cracking in near-neutral and high pH environments for API 5L X52 steel
[J].
Stress corrosion cracking behavior of X80 pipeline steel with design factor of 0.8 in near-neutral pH value solutions
[J].
0.8设计系数用X80管线钢在近中性pH溶液中的应力腐蚀开裂行为
[J].
Effect of plastic deformation on the electrochemical and stress corrosion cracking behavior of X70 steel in near-neutral pH environment
[J].
Effect of SRB on stress corrosion cracking of X100 pipeline steel in northwest saline soil
[J].
SRB对X100管线钢在西北盐渍土壤中应力腐蚀开裂行为的影响
[J].
Stress corrosion cracking of X100 pipeline steel in acid soil medium with SRB
[J].
SRB作用下X100管线钢在酸性土壤环境中的应力腐蚀开裂行为
[J].-进入钢基体表面,致使X100钢的SCC敏感性减小。]]>
Effect of applied potentials on stress corrosion cracking of X80 pipeline steel in simulated YingTan soil solution
[J].Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of X80 pipeline steel in a simulated solution of the acidic soil environments in Yingtan China was studied by means of potentiodynamic polarization curves, slow strain rate test (SSRT) and corrosion morphologies characterized by SEM. The results show that X80 pipeline steel has high SCC susceptibility in the simulated solution and the failure mode is transgranular cracking. The SCC mechanism would vary with the applied cathodic potential. When the applied potential is positive to about -930 mV, the SCC behavior is controlled by the combined effect of anodic dissolution (AD) and hydrogen embrittlement (HE), i.e. the SCC mechanism is AD+HE. However, when the applied potentials are lower than -930 mV, such as -1000 and -1200 mV, the process of hydrogen evolution plays the dominant role in SCC occurrence, meaning that the SCC mechanism is HE under such applied potentials. Moreover, SCC susceptibility increases with decreasing applied cathodic potential. Compared with X70 pipeline steel in. acidic soil environments, HE plays a more important role in affecting SCC occurrence.
外加电位对X80管线钢在鹰潭土壤模拟溶液中应力腐蚀行为的影响
[J].采用电化学动电位极化技术、慢应变速率拉伸(SSRT)实验和SEM对X80管线钢在鹰潭土壤模拟溶液中的应力腐蚀行为进行了研究. 结果表明: X80管线钢在酸性土壤环境中具有较高的SCC敏感性, 其断口模式为穿晶SCC; SCC机制随外加电位的不同而改变, 在外加电位高于-930 mV时, 其SCC机制由阳极溶解和氢致腐蚀两种电极过程控制, 呈现阳极溶解和氢脆复合机制; 当电位低于该电位时, 其SCC为氢脆机制. 随着外加阴极电位的降低, X80管线钢的SCC敏感性不断增大; 与X70钢相比, 氢脆作用在X80管线钢SCC过程中发挥了更重要的作用.
Investigating a mechanism for transgranular stress corrosion cracking on buried pipelines in near-neutral pH environments
[J].
Influence of applied potential on the stress corrosion behavior of X90 pipeline steel and its weld joint in simulated solution of near neutral soil environment
[J].32-/HCO3- under the coating of liquid, the mechanism of cracking is widely regarded as membrane rupture, crack tip anodic dissolution mechanism; near neutral pH SCC occurred mainly in the coating containing low concentration of HCO3- resident fluid or groundwater environment. Due to pipe in the process of serving for a long time, pipeline external coating damage and strip defects are common, under the joint action of the applied potential and soil medium, SCC will generally occur in nearly neutral pH environment, which lead to a serious risk in nearly neutral pH SCC. As a new generation of high strength pipeline steel, the X90 steel probes into its SCC sensitivity at different applied potentials in a certain pH environment is of great significance. In this work, the SCC behavior as well as its mechanism of X90 pipeline steel and its weld joint in an simulated solution of the near neutral soil environment (NS4 solution) were studied by slow strain rate tensile tests (SSRT), potentiodynamic polarization tests and SEM observation of fracture surfaces. The results showed that both the as received X90 pipeline steel and its weld joint have obvious SCC susceptibilities, which initiated and extended in transgranular cracking mode under different applied potentials. Within the potential ranges from OCP to -1000 mV, the SCC mechanism of both X90 steel and its weld joint microstructures are a combined mechanisms of anodic dissolution (AD) and hydrogen embrittlement (HE), i.e. the AD+HE mechanism. The SCC susceptibility is apparent under the OCP due to a strong AD effect. At -800 mV, the SCC susceptibility comes to a minimum due to AD and HE being weaker, and it presents the highest SCC susceptibility at -900 mV because the HE effect was greatly enhanced. The SCC susceptibility of the weld organization is higher than that of the base metal, which may be related to organization phase transformation in the welds and metallurgical reaction.]]>
外加电位对X90钢及其焊缝在近中性土壤模拟溶液中应力腐蚀行为的影响
[J].采用慢应变速率拉伸(SSRT)实验、动电位极化技术和SEM观察等方法,研究了X90钢基体和焊缝在近中性土壤模拟溶液中不同阴极保护电位下的应力腐蚀行为。结果表明,X90管线钢及其焊缝组织在近中性土壤模拟溶液中均具有一定的应力腐蚀敏感性,裂纹扩展为穿晶腐蚀裂纹;应力腐蚀开裂(SCC)的裂纹萌生与扩展与外加保护电位有关。在开路电位(OCP)~-1000 mV的电位范围内,X90钢的SCC机制均为阳极溶解(AD)+氢脆(HE)的混合机制;在OCP下,由于AD作用较强,SCC敏感性较明显;在-800 mV下,由于AD和HE作用均较弱,导致SCC敏感性最低;而在-900 mV时,由于HE作用明显增强,具有最高的SCC敏感性;在相同电位条件下,焊缝的SCC敏感性高于母材。
Transgranular crack growth in the pipeline steels exposed to near-neutral pH soil aqueous solutions: Discontinuous crack growth mechanism
[J].
Mechanism for hydrogen evolution reaction on pipeline steel in near-neutral pH solution
[J].
Effect of electrolyte composition on crack growth rate in pipeline steel
[J].