因其卓越的力学、耐腐蚀及生物相容等特性,钛合金已广泛应用于骨科植入物领域[1,2]。其中,Ti-6Al-4V合金尤甚,作为目前最常见的钛合金,因其高强度、良好的生物相容性及较长的使用寿命,已被广泛应用于人工关节、骨折固定器等生物医用植入物。然而,Ti-6Al-4V合金的弹性模量约为110 GPa,远高于人体骨骼(约10~30 GPa)[3],导致其在植入后常常出现应力屏蔽效应,即植入物与周围骨组织的力学匹配不良[4]。此外,Ti-6Al-4V合金中的Al和V具有一定的生物毒性,这些元素在体内可能引发慢性毒性反应,增加患者的健康风险[5]。因此,开发具有低弹性模量且无毒的钛合金,成为生物医用材料研究中的关键目标之一。
当前,许多研究者着重研究低模量钛合金的设计[6,7]。β钛合金因其较低的弹性模量和良好的机械性能,成为潜在的替代材料。β钛合金通常以其较低的弹性模量(约40~50 GPa)和较高的韧性,能够有效减少应力屏蔽效应,较好地匹配人体骨骼的力学特性[8]。此外,β钛合金的合金成分具有更大的调整空间,可以通过合金元素的选择与比例来进一步优化其力学性能、耐腐蚀性以及生物相容性[9]。例如,Ji等[10]通过引入Zr和Nb,设计出了一种Ti-34Nb-6Zr合金,该合金具有低的弹性模量,同时又展现出较好的抗腐蚀性,适于用作骨科植入物。尽管β钛合金在减少弹性模量方面具有明显优势,但其耐腐蚀性及生物相容性仍受到其合金成分、微观结构及表面处理等因素的制约,如何在确保其较低弹性模量的同时,进一步优化其腐蚀性能和生物相容性,依然是一个亟待解决的课题。针对β钛合金的生产工艺,传统的加工方法,如铣削、铸造和热处理,虽然可以在一定程度上改善其力学性能,然而在制造形状复杂或精度要求较高的植入物时,传统加工方法存在很大的局限性[11]。因此,近年来,增材制造(AM)技术,成为了高熵合金[12]、哈氏合金[13]、铝合金[14]、钛合金[15]等高性能金属制造领域的重要发展方向。电子束增材制造(EBM)技术作为一种新型的增材制造方法,通过利用高能电子束直接熔化金属粉末,在较高的温度下进行逐层成形,能够精确控制材料的微观结构,具有高成形精度和较大的自由度,这使得其在制造复杂形状和高精度钛合金植入物时展现出独特的优势[16]。
虽然,在钛合金的加工中EBM技术展现了巨大潜力,但如何通过该技术实现低模量β钛合金的设计和优化,仍面临诸多挑战。特别是在腐蚀性能和生物相容性方面,现有的研究主要聚焦常规钛合金(如Ti-6Al-4V),而对新型β钛合金在模拟体液中的腐蚀行为和与细胞相互作用的机制研究较为薄弱。已有研究表明,β钛合金的腐蚀行为受合金成分、微观组织以及表面处理等多重因素的影响。例如,Sherif等[20]研究表明,合金中添加不同的合金化组元会影响其在模拟体液中的腐蚀速率,而不同的微观组织则可能导致不同的腐蚀产物形成,从而影响合金的抗腐蚀性能。因此,如何通过精确控制不同合金体系的微观结构和表面特性,提高其在体液环境中的耐腐蚀性,仍是一个关键问题。本研究选用了新型β钛合金Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn,采用EBM技术制作低弹性模量的钛合金,研究其在模拟体液中的腐蚀机制及生物相容性规律。通过电化学测试和细胞实验,探究Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金的腐蚀行为、生物相容性特征及其与细胞的相互作用,为设计具有优异腐蚀性能和生物相容性的低模量钛合金植入物提供理论依据和实验数据支持。
1 实验方法
1.1 材料制备
Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金名义成分(原子分数,%)为Ti-15Nb-2.5Zr-4Sn,经真空自耗熔炼,锻造,气雾化制粉(EIGA法)制备球形粉末,再经EBM成型制备测试样品。对比材料为锻造制备的Ti-6Al-4V (TC4)合金。
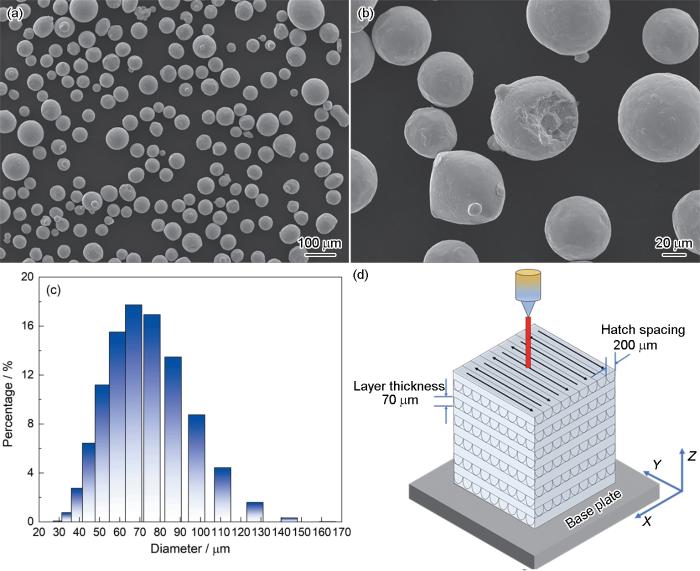
图1
图1
金属粉末的形貌特征、粒径分布及激光粉末床熔融(L-PBF)增材制造工艺示意图
Fig.1
Morphology, particle size distribution of metal powders, and schematic illustration of EBM additive manufacturing process: (a) low-magnification SEM image of metal powders; (b) high-magnification SEM image of metal powders; (c) particle size distribution histogram of powders, and (d) schematic diagram of the EBM process
图1d示,通过EBM技术将Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金粉末加工成测试样品。EBM成形采用了Arcam A1设备,具体工艺参数设置如下,加工参数设定为自动模式,其中速度函数为25,焦点偏移量为22。采用经电子束加热至450~500 ℃的纯钛基板,层厚为70 μm,束流电压为60 kV。为获得沿构建方向的<100>织构,逐层将填充图案沿X轴和Y轴旋转90°,填充间距为0.2 mm。加工完成后,样品在腔室内冷却至室温。这一参数设置有助于获得较高的成形精度和较好的微观组织结构。EBM技术的优势在于其可以通过精确控制激光的能量和扫描路径来优化材料的微观结构,从而在钛合金材料中实现更好的力学性能和抗腐蚀性。
作为对比材料,本文选用市面上广泛应用的TC4合金,该合金通过传统的锻造方法制备,具有良好的力学性能和生物相容性,广泛用于骨科植入物。
1.2 微观组织表征
使用X射线衍射仪(XRD,Bruker D8A)对两种材料样品进行物相分析,扫描角度范围为10°~90°,扫描速度10 (°)/min,使用铜靶Kα射线源。测试前各样品表面经过2000#SiC砂纸打磨,平整且无氧化层。
利用电子背散射衍射技术(EBSD,Quattro s.)测试增材制造样品与传统方法制造的样品的取向差异。样品需要先经过机械磨抛,之后进行电解抛光将表面打平并去除表面应力层。电解抛光使用90%酒精+10%高氯酸溶液作为电解液,保持电压恒定64 V,等待电流回升至设定电流时,取出样品并进行清洗。为了对比传统方法和增材制造生产的样品的取向差别,本文对TC4钛合金与EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn钛合金进行了测试,TC4合金回升电流值为0.7 A,Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金回升电流值为0.5 A,在1000倍倍数0.15 μm步长条件下进行EBSD测试。
1.3 力学性能测试
采用Instron E10000电子万能试验机对EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金进行室温拉伸测试。试样沿成形方向加工为标准拉伸棒状样品,参考GB/T 228.1-2010标准,标距为10 mm。测试在室温下(25 ± 2) ℃进行,拉伸速率设定为0.5 mm/min。每组材料至少测试3个样品以确保数据可靠性,最终结果取平均值。样品的弹性模量测试采用自由共振弹性模量仪(JE-RT)进行。测试所用棒状样品尺寸为ϕ6 mm × 55 mm。样品加工过程中,确保两端面平行且与轴向垂直,表面粗糙度和尺寸精度符合测试要求。每个样品进行3次测试,最终的模量值取3次测试的平均值,以确保数据的准确性和可靠性。
1.4 腐蚀电化学测试
电化学测试试样的尺寸均为10 mm × 10 mm × 2 mm。在测试前,在试样背面焊接铜导线,以便进行电化学测试,并将暴露的工作面积设定为10 mm × 10 mm,其余非工作面则使用环氧树脂进行封装处理。测试采用三电极体系,使用电化学工作站(Gamry Instrument Reference 600+)测试。其中钛合金样品作为工作电极(Working Electrode,WE),大面积铂片作为对电极(CE),饱和甘汞电极(SCE)作为参比电极(RE)。测试溶液为模拟人体体液(Simulated Body Fluid,SBF)溶液;溶液成分为:NaCl 8.035 g/L,NaHCO3 0.355 g/L,KCl 0.225 g/L,K2HPO4·3H2O 0.231 g/L,MgCl2·6H2O 0.311 g/L,1.0 mol/L HCl 39 mL/L,CaCl2 0.292 g/L,Tris (三羟甲基氨基甲烷) 6.118 g/L,并通过添加HCl (1.0 mol/L)调节模拟体液环境的pH至7.4。所有电化学测试均在恒温水浴37 ℃的条件下进行[21]。
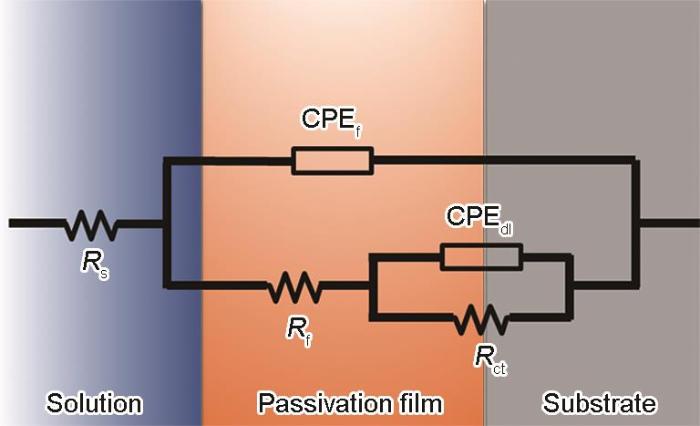
待开路电位稳定后进行电化学阻抗谱(EIS)测试,频率范围覆盖从105~10-2 Hz,以获取材料电极界面在宽频段下的阻抗特性,进一步反映其钝化膜的完整性和电荷传输阻力。所得EIS数据采用ZSimpWin 3.21软件进行拟合分析,以建立等效电路模型并提取相关电化学参数。为进一步评价合金的稳定性和腐蚀敏感性,采用动电位极化测试方法,扫描电位范围设定为-0.5 V至+1.8 V (vs. SCE),扫描速率为0.5 mV/s。通过Tafel外推法计算材料的腐蚀电流密度(Icorr)与自腐蚀电位(Ecorr),以比较其在SBF中的腐蚀倾向与速率。为验证材料在模拟体液中的钝化能力及其钝化膜的稳定性,设置了恒电位极化实验,在0.6 V (vs. SCE)恒定电位下持续极化7 h,考察两种钛基材料在钝化区内的长期腐蚀行为及钝化膜对腐蚀反应的阻碍效果。
1.5 X射线光电子能谱分析
钝化膜成分采用X射线光电子能谱(XPS,AXIS SUPRA+)进行分析。测试采用Al Kα辐射源(光子能量1486.6 eV)。样品表面经过预制备钝化膜后,使用XPS分析其元素组成及化学状态,重点分析Ti、Nb、Zr、Sn等元素的结合能变化。通过峰值拟合方法,结合已知数据,评估钝化膜的组成。所有数据以C 1s峰(284.8 eV)为校准标准,误差控制在±0.1 eV内。
1.6 生物相容性评价
将小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞MC3T3-E1 (每孔10000个细胞)接种至24孔培养板内,孔板内放置EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金样品,培养48 h。培养结束后,用预温的磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)轻柔冲洗细胞三次,再用4%多聚甲醛固定30 min。接着,使用0.1% Triton X-100/PBS溶液进行五分钟的渗透处理,之后用PBS溶液洗涤3次。然后,将细胞与异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)标记的笔鬼环肽(5 U/mL)在室温下孵育1 h。孵育后,用PBS冲洗细胞,并用DAPI (4',6-二脒基-2-苯基吲哚)染色液对细胞核进行染色,染色时间为5 min。最后,使用激光扫描共聚焦显微镜(CLSM,FV3000)采集荧光图像进行观察。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 微观组织分析
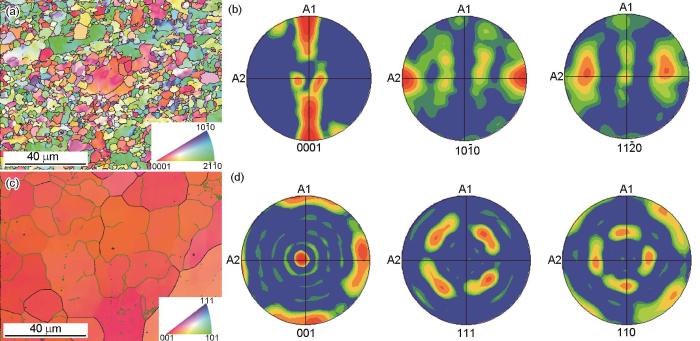
图2
图2
不同样品的晶粒取向图与晶体学织构极图对比
Fig.2
Comparison of grain orientation maps and pole figures for different samples: (a) Inverse pole figure (IPF) map of Ti-6Al-4V, (b) Pole figures of Ti-6Al-4V, (c) IPF map of EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn, (d) Pole figures of EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn
2.2 XRD分析
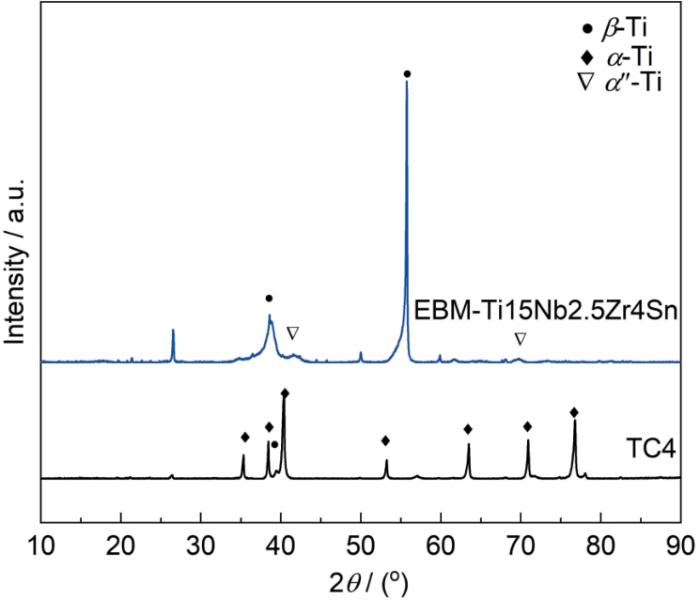
图3为EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金与TC4合金的XRD图谱。TC4合金主要由α-Ti相和少量β-Ti相组成,衍射峰锐利且强度高,表明其具有良好的晶体完整性和典型的α + β双相钛合金特征。相比之下,EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金的衍射峰明显不同,主要由β-Ti相构成,并伴有一定量的马氏体α″相析出,未观察到明显的α相峰,说明EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金为典型的亚稳β型钛合金。其α″相的存在可能与快速冷却或应变诱导马氏体转变有关[22,23]。整体上,EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金的XRD峰较宽,表明其晶粒较小或存在较高残余应力。这一结果揭示了两种合金在晶体结构和相组成上的本质差异。
图3
图3
EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn与TC4的合金XRD图谱
Fig.3
XRD patterns of EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn and TC4 Ti-alloys
2.3 力学性能与弹性模量
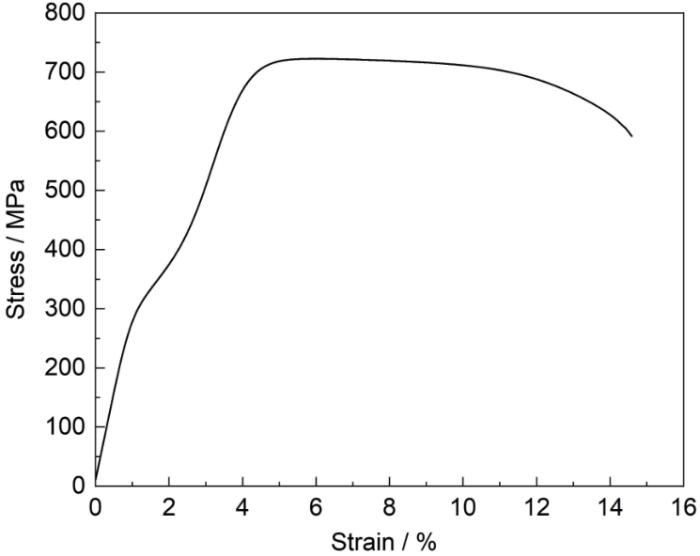
图4
图4
EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金在室温下的拉伸应力-应变曲线
Fig.4
Tensile stress-strain curve of EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn alloy at room temperature
综上所述,EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金在拉伸过程中展现出优良的强度–塑性协同特性。结合前述XRD及显微组织分析结果可以进一步推断,合金的相组成及亚稳组织在塑性响应中发挥了关键作用,特别是应力诱导形成与演化的α″相对变形机制具有重要影响。
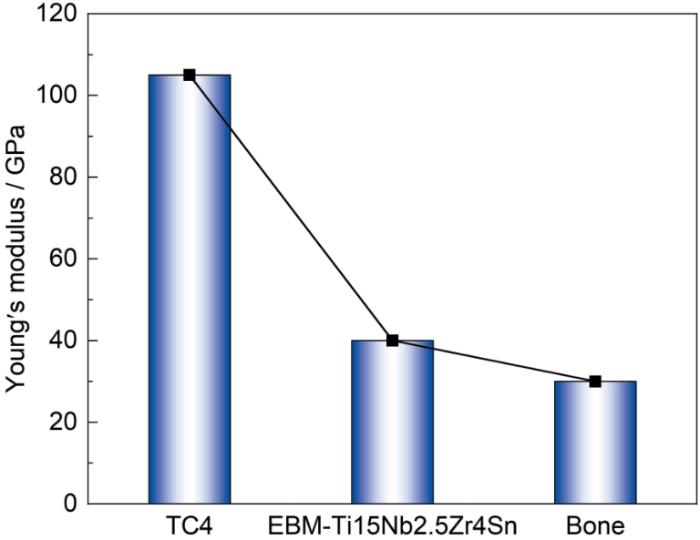
图5为所制备的EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金与其他常见生物医用金属材料的弹性模量。由图可见,EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金表现出显著降低的杨氏模量,其模量水平接近人体骨组织,会有助于缓解植入过程中的“应力遮挡效应”,从而提升植入体与骨组织之间的力学匹配性与服役稳定性。该低弹性模量的核心机制在于EBM成形过程中形成了高度择优取向的{100}织构。在β相中,<100>晶向为弹性模量最低的方向,因此强{100}织构会显著降低整体多晶材料的模量表现。与之相对应,合金中亚稳ω相已被有效抑制,避免了其对弹性模量提升的不利影响,进一步放大了织构调控的效果。与传统医用金属材料(如Ti-6Al-4V)相比,该合金在显著降低模量的同时仍保持优良强度,呈现了强度-模量双优的力学特性组合,更契合人体骨骼的力学要求。此外,引入了Nb、Ta、Zr等多种β稳定元素,不仅有助于稳定合金中的β相并抑制有害相的析出,还显著提高了材料的生物相容性。成分与织构的协同调控共同确保了合金在结构稳定性、生物安全性以及力学性能方面的综合优势。
图5
图5
EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金的力学性能对比分析:EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn和TC4合金的弹性模量图
Fig.5
Comparative mechanical properties of the EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn alloy: Bar chart of elastic modulus of the EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn and TC4 alloys
2.4 电化学行为
2.4.1 开路电位
图6为TC4与EBM-Ti15Nb2.5-Zr4Sn两种合金在模拟体液中168 h浸泡期间自腐蚀电位(Eocp)的演变趋势。由图可见,两种合金初始Eocp值均较低(约为-300 mV vs. SCE)。随腐蚀时间延长,Eocp逐渐正移,说明表面形成了钝化膜,对合金具有保护作用。TC4合金的Eocp在4 h后迅速趋于稳定,最终稳定在约-100 mV;而Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金的OCP提升速率略慢,最终稳定值约为-130 mV。总体而言,Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金OCP略低于TC4,但其仍表现出良好的钝化行为。
图6
图6
TC4与EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金在模拟体液中168 h浸泡期间的自腐蚀电位
Fig.6
Corrosion potential of TC4 and EBM-Ti15Nb2.5-Zr4Sn alloys during 168 h of immersion in simulated body fluids
2.4.2 电化学阻抗谱
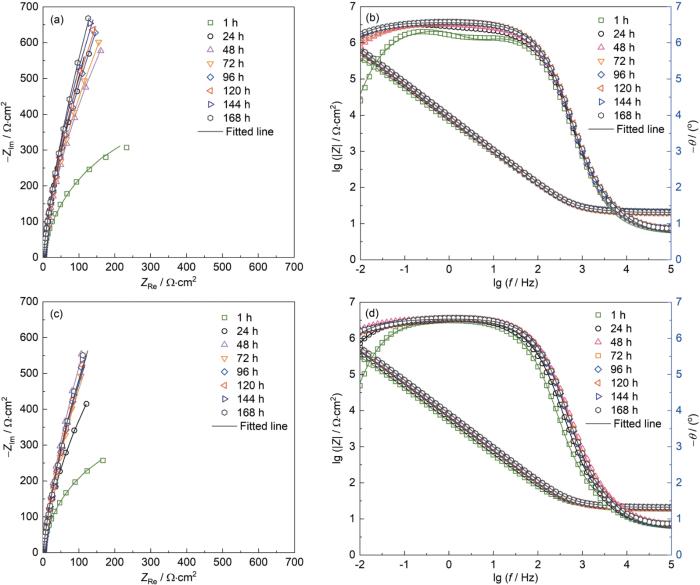
图7
图7
TC4合金和EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金在168 h浸泡过程中的Nyquist和Bode图
Fig.7
Nyquist plots (a, c) and Bode plots (b, d) of TC4 alloy after immersion in simulated body fluid for 168 h (a, b) and EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn alloy after immersion for the same duration (c, d)
图8
表1 EIS拟合结果
Table 1
| Type | Time / d | Rs / Ω·cm2 | Qf / 10-5 S·cm-2·S n | n1 | Rf / Ω·cm2 | Qdl / 10-5 S·cm-2·S n | n2 | Rct / 106 Ω·cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC4 alloy | 0 | 22.45 | 2.48 | 0.9 | 17.93 | 0.18 | 1.00 | 0.83 |
| 1 | 21.41 | 1.44 | 0.92 | 24.77 | 0.74 | 0.91 | 8.20 | |
| 2 | 20.93 | 1.31 | 0.93 | 22.23 | 0.76 | 0.91 | 4.07 | |
| 3 | 19.99 | 1.18 | 0.94 | 18.76 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 3.44 | |
| 4 | 20.78 | 1.17 | 0.94 | 21.10 | 0.78 | 0.92 | 3.99 | |
| 5 | 19.61 | 1.05 | 0.95 | 17.94 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 5.81 | |
| 6 | 20.93 | 1.04 | 0.95 | 18.53 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 6.93 | |
| 7 | 20.52 | 1.11 | 0.94 | 22.48 | 0.76 | 0.92 | 5.94 | |
| EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn | 0 | 20.74 | 2.02 | 0.93 | 23.30 | 1.62 | 0.92 | 0.71 |
| alloy | 1 | 20.1 | 1.49 | 0.94 | 17.81 | 1.41 | 0.91 | 2.65 |
| 2 | 18.94 | 1.08 | 0.95 | 18.60 | 1.18 | 0.91 | 7.07 | |
| 3 | 18.71 | 0.88 | 0.98 | 13.56 | 1.58 | 0.89 | 5.36 | |
| 4 | 20.38 | 0.85 | 0.98 | 15.02 | 1.51 | 0.89 | 5.82 | |
| 5 | 20.24 | 1.27 | 0.94 | 18.86 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 1.54 | |
| 6 | 21.15 | 0.80 | 0.98 | 15.12 | 1.45 | 0.89 | 6.16 | |
| 7 | 21.09 | 0.82 | 0.98 | 15.66 | 1.38 | 0.89 | 6.12 |
2.4.3 极化曲线测试
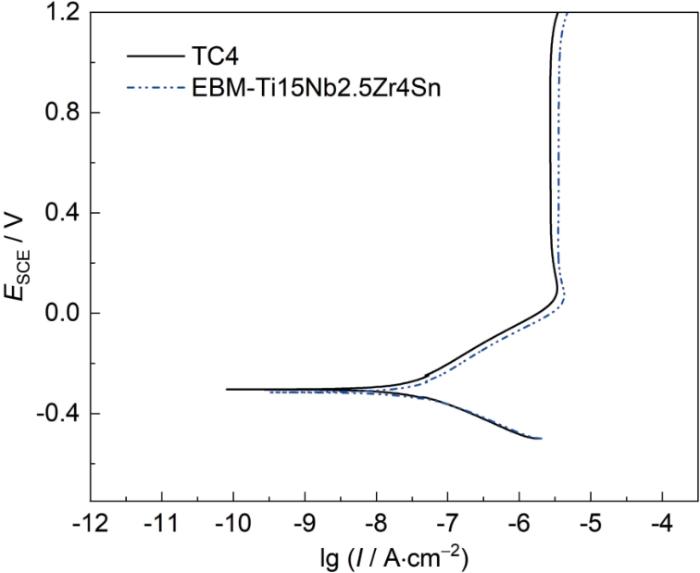
图9为TC4合金与EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金在模拟体液中浸泡168 h后的动电位极化行为。由图可见,两种合金均表现出典型的钝化行为,其极化曲线在约0 V附近迅速转折,进入稳定的钝化区。在整个测试电位范围内,Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金的腐蚀电流密与TC4合金的腐蚀电流密度相当。通过Tafel外推法得到腐蚀电流密度如表2所示,EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金的腐蚀电流密度(308 nA·cm-2)接近TC4合金的腐蚀电流密度(284 nA·cm-2)。该结果与前述EIS结果一致,进一步证实与TC4合金相比,EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金在生理环境中同样具有优异的耐蚀性。
图9
图9
TC4与EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金在模拟体液中腐蚀168 h后的动电位极化曲线
Fig.9
Potentiodynamic polarization curves of TC4 and EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn alloys in SBF after 168 h of corrosion
表2 TC4与EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金的动电位极化曲线拟合结果
Table 2
| Parameters | Icorr / nA·cm-2 | Ecorr/ mV | Epit/ V | βa/ mV·dec-1 | βc/ mV·dec-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC4 | 284 | -300.2 | 1.159 | 0.159 | 0.124 |
| EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn | 308 | -312.7 | 1.132 | 0.156 | 0.120 |
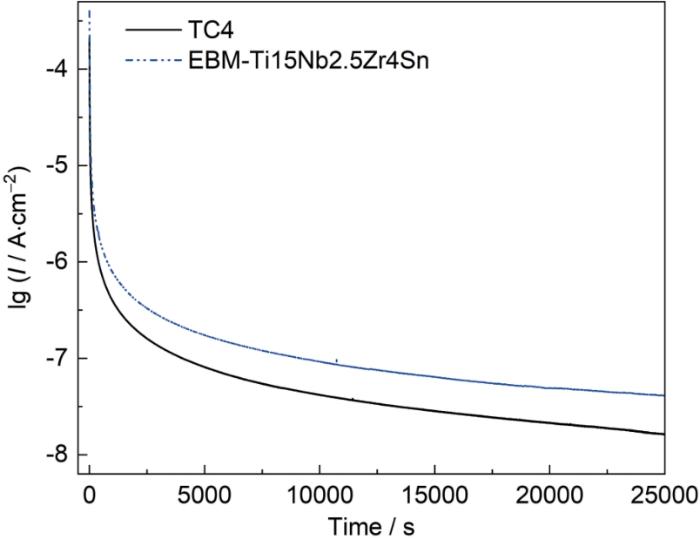
在电位为0.6 V vs. SCE的恒电位条件下,对两种材料进行了7 h的恒电位极化测试,以评估其表面钝化膜的稳定性,测试结果如图10所示。实验初期,所有材料的腐蚀电流密度均出现明显下降,并在短时间内迅速趋于稳定,说明在外加阳极极化条件下,各材料表面迅速形成了致密的钝化膜,有效抑制了金属的进一步溶解。在整个测试过程中,EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn与TC4合金的稳态电流密度均维持在10-8 A·cm-2数量级,且EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金的稳态电流略高于TC4合金,表明其具有优异的耐腐蚀性能与钝化膜稳定性。总体而言,两种材料在电位激励下均表现出高度的自钝化行为,形成的钝化膜能够长期保持稳定,有效屏蔽腐蚀介质,验证了其在生理环境中的腐蚀防护潜力。
图10
图10
TC4和Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金在恒电位(0.6 V vs. SCE)下的极化电流-时间曲线
Fig.10
Current-time curves of TC4 and Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn alloys under potentiostatic polarization at 0.6 V vs. SCE
2.5 表面钝化膜成分分析
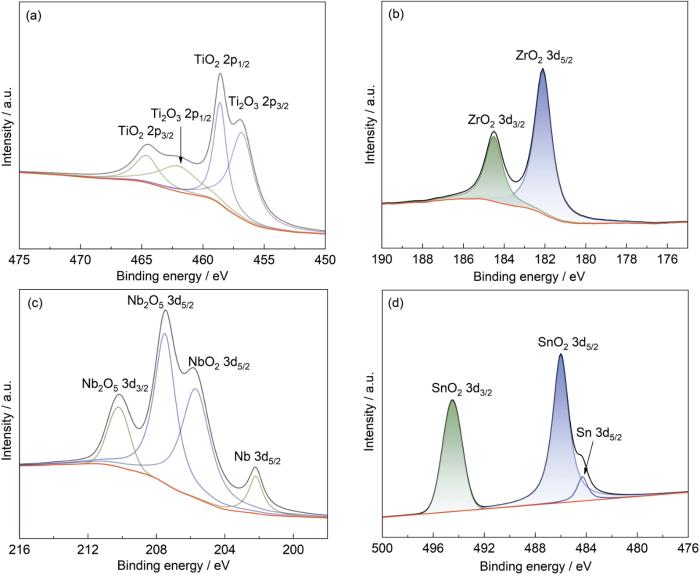
为进一步探究Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金在模拟体液中形成的钝化膜成分,对其在SBF中浸泡168 h后的表面膜层进行了XPS分析,结果如图11所示。高分辨率谱图显示了Ti 2p、Nb 3d、Zr 3d、Sn 3d以及Ca 2p等元素的化学态信息。在Ti 2p谱图中,位于458.6与464.6 eV的两个特征峰对应于TiO2,而456.8与462.0 eV处则为Ti2O3的特征峰[28],表明膜层中同时存在4价与3价Ti的氧化物,反映出膜结构中可能存在非晶相或多价态共存的亚稳态结构。Nb 3d谱图中,207.5和210.2 eV为Nb2O5的特征峰,205.7 eV对应NbO2,202.2 eV为单质Nb的峰位,说明在膜层中存在高价Nb的氧化物主导相,并可能伴随少量低价Nb或还原态Nb残留[29]。Zr 3d和Sn 3d的谱图中,分别检测到ZrO2 (182.1和184.5 eV)和SnO2 (486.0和494.5 eV)的特征峰,同时在Sn 3d谱图中还检测到单质Sn的峰位(484.3 eV),说明Sn也参与了氧化膜的形成。综上分析,Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金表面钝化膜主要由TiO2、Ti2O3、Nb2O5、ZrO2和SnO2构成。其中,TiO2和Nb2O5是钛基合金中最常见的稳定氧化物,它们被广泛报道具有良好的生物相容性,能够促进细胞黏附和细胞生长[30],为合金的骨整合性能提供了材料基础。
图11
图11
EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金表面钝化膜的XPS谱
Fig.11
XPS spectrum of the passivation film on the surface of EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn: (a) Ti 2p, (b) Zr 3d, (c) Nb 3d, (d) Sn 3d
2.6 生物相容性
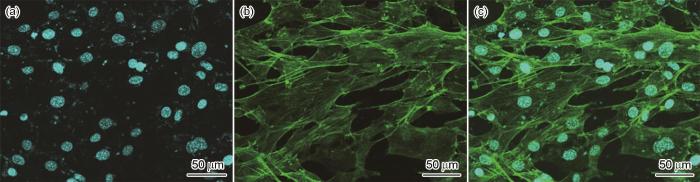
通过CLSM对Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金表面培养的MC3T3-E1成骨前体细胞进行荧光染色后的形貌图像如图12所示。DAPI染料发出蓝色荧光,可有效标记细胞核结构;而FITC标记的鬼笔环肽(Phalloidin)可特异性结合细胞内的肌动蛋白微丝,呈现绿色荧光信号,从而清晰揭示细胞骨架系统的空间分布特征。从图中可观察到,细胞核在材料表面呈均匀分布,未出现明显空缺或聚集现象,表明细胞在EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金表面具有良好的铺展与黏附行为。同时,肌动蛋白微丝组装形成的网状结构高度有序、连续性良好,表明细胞骨架系统结构完整,未受到材料界面的不良干扰。此外,实验过程中观察到细胞形态饱满、边界清晰,无明显变性或凋亡特征,进一步说明该材料表面对细胞增殖及黏附无毒害作用。这些结果共同验证了EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金具有优异的细胞相容性,能够支持成骨细胞的黏附、铺展与骨架重构,为其在骨科植入物等生物医用领域的应用提供了可靠的生物学基础。
图12
图12
MC3T3-E1细胞在EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金表面的CLSM像
Fig.12
CLSM images of MC3T3-E1 cells cultured on the surface of EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn alloy: (a) cell nuclei stained with DAPI (blue), (b) actin filaments labeled with FITC-phalloidin (green), (c) merged image
3 结论
(1) EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金成形后组织均匀,显微结构以β相为主,伴随部分应变诱导α″相析出。EBM-Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金的拉伸强度约为725 MPa,延伸率达到约14.6%,同时弹性模量仅为40 GPa左右,显著低于TC4合金(~110 GPa),更接近人体骨组织(10~30 GPa)。
(2) 在SBF中,Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金表现出低腐蚀电流密度、高电荷转移电阻以及稳定的钝化行为,腐蚀速率与TC4合金相当,说明其表面钝化能力强,电化学稳定性高。
(3) Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金表面钝化膜主要由TiO2、Ti2O3、Nb2O5、ZrO2和SnO2等氧化物组成,其中TiO2和Nb2O5具有良好的生物活性,可促进细胞黏附与成骨行为。
(4) 在Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金表面,MC3T3-E1细胞展现出良好的铺展状态,细胞核分布均匀,肌动蛋白微丝网络结构清晰完整,形态饱满,未见细胞中毒证候,表明Ti15Nb2.5Zr4Sn合金具备良好的细胞相容性。
参考文献
Research status of biomedical porous Ti and its alloy in China
[J].Porous Ti not only inherits the physical and chemical properties of titanium alloy, such as higher special stiffness, special strength, excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, but also its unique pore structure gives it the characteristic of ultra-low density and large surface area. It is an alternative material for human body with structural and functional integration. It has been widely used in the field of clinical medicien in recent years. Many research and applications show that the properties and functions of porous Ti strongly depend on the pore structure of porous Ti prepared by different methods. Surface activation technology can significantly improve the surface activity of porous Ti and shorten the healing period after implantation. In this paper the common preparation methods of porous Ti were introduced based on the structure and properties of porous Ti. The surface modification, biological activity, osteoinductive properties of porous Ti and their domestic research status were summrized. The development of biomedical porous Ti and titanium alloys was prospected.
医用多孔Ti及钛合金的国内研究现状
[J].多孔Ti继承了钛合金较高的比刚度、比强度等物理化学特性、优异的耐腐蚀性和生物相容性,其独特的孔隙结构又赋予其超低密度和大比表面积等特点,是结构功能一体化的人体替代材料,近年来在临床医学领域得到了非常广泛的应用。众多研究和应用表明,多孔Ti的性能和功能强烈依赖于不同方法制备多孔Ti的孔隙结构。表面活化技术可显著提高多孔Ti的表面活性,缩短植入人体后的愈合期。本文针对多孔Ti的结构和性能特点,介绍了多孔Ti的常见制备方法,对多孔Ti的表面改性、生物活性与骨诱导性及国内的研究现状进行了总结,展望了生物医用多孔Ti及钛合金的发展。
Metal additive manufacturing: A review
[J].
Elastic properties of human cortical and trabecular lamellar bone measured by nanoindentation
[J].An experimental investigation was undertaken to measure the intrinsic elastic properties of several of the microstructural components of human vertebral trabecular bone and tibial cortical bone by the nanoindentation method. Specimens from two thoracic vertebrae (T-12) and two tibiae were obtained from frozen, unembalmed human male cadavers aged 57 and 61 years. After drying and mounting in epoxy resin nanoindentation tests were conducted to measure Young's modulus and the hardness of individual trabeculae in the vertebrae and single osteons, and interstitial lamellae in the tibiae. Measurements on the vertebral trabeculae were made in the transverse direction, and the average Young's modulus was found to be 13.5 +/- 2.0 GPa. The tibial specimens were tested in the longitudinal direction, yielding moduli of 22.5 +/- 1.3 GPa for the osteons and 25.8 +/- 0.7 GPa for the interstitial lamellae. Analysis of variance showed that the differences in the measured moduli are statistically significant. Hardness differences among the various microstructural components were also observed.
Elastic deformation behaviour of Ti-24Nb-4Zr-7.9Sn for biomedical applications
[J].In this paper, the elastic deformation behaviour of a recently developed beta-type titanium alloy Ti-24Nb-4Zr-7.9Sn (wt.%) that consists of non-toxic elements and is intended for biomedical applications is described. Tensile tests show that this alloy in the as hot-rolled state exhibits peculiar non-linear elastic behaviour with maximum recoverable strain up to 3.3% and incipient Young's modulus of 42GPa. Solution treatment at high temperature has trivial effect on super-elasticity but decreases strength and slightly increases the incipient Young's modulus. Ageing treatment in the (alpha+beta) two-phase field increases both strength and Young's modulus and results in a combination of high strength and relatively low elastic modulus. In spite of the formation of the alpha phase, short time ageing has no effect on super-elasticity, whereas the non-linear elastic behaviour transforms gradually to normal linear elasticity with the increase of ageing time. We suggest sluggish, partially reversible processes of stress-induced phase transformation and/or incipient kink bands as the origin of the above peculiar elastic behaviour.
Research progress of the surface modification of titanium and titanium alloys for biomedical application
[J].Titanium and titanium alloys have widely been used in biomedical applications as main substitutes for hard human tissues. To better meet the needs of safety, comfort, and durability of titanium and titanium alloys after implantation in the human body, the surface modification treatment of titanium and titanium alloys has become a research hotspot. In this review, based on the basic properties and existing problems of titanium and titanium alloys, the methods of surface modification for titanium and titanium alloys are introduced to improve their mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and bacteriostatic/antibacterial properties. Furthermore, the current challenges and prospects have been presented in this paper.
Ti及钛合金表面改性在生物医用领域的研究进展
[J].Ti及钛合金作为人体硬组织的主要替代物之一,在生物医用领域应用广泛。为了更好地满足Ti及钛合金在人体中植入后的安全、舒适、耐久等需求,Ti及钛合金表面改性处理成为了研究的热点。本文基于Ti及钛合金的基础性能和存在的问题,从表面改性提高其力学性能、生物相容性、抑菌/抗菌性能等方面综述了Ti及钛合金表面改性在生物医用领域的研究进展,并提出了面临的挑战以及发展方向的建议。
Achieving stable ultra-low elastic modulus in near-β titanium alloys through cold rolling and pre-strain
[J].
Cluster-formula-embedded machine learning for design of multicomponent β-Ti alloys with low Young'smodulus
[J].The present work formulated a materials design approach, a cluster-formula-embedded machine learning (ML) model, to search for body-centered-cubic (BCC) β-Ti alloys with low Young’s modulus (E) in the Ti–Mo–Nb–Zr–Sn–Ta system. The characteristic parameters, including the Mo equivalence and the cluster-formula approach, are implemented into the ML to ensure the accuracy of prediction, in which the former parameter represents the BCC-β structural stability, and the latter reflects the interactions among elements expressed with a composition formula. Both auxiliary gradient-boosting regression tree and genetic algorithm methods were adopted to deal with the optimization problem in the ML model. This cluster-formula-embedded ML can not only predict alloy property in the forward design, but also design and optimize alloy compositions with desired properties in multicomponent systems efficiently and accurately. By setting different objective functions, several new β-Ti alloys with either the lowest E (E = 48 GPa) or a specific E (E = 55 and 60 GPa) were predicted by ML and then validated by a series of experiments, including the microstructural characterization and mechanical measurements. It could be found that the experimentally obtained E of predicted alloys by ML could reach the desired objective E, which indicates that the cluster-formula-embedded ML model can make the prediction and optimization of composition and property more accurate, effective, and controllable.
Improving the strength and corrosion resistance of the biomedical Ti2448 alloy through the addition of trace interstitial nitrogen
[J].
Development and application of novel biomedical titanium alloy materials
[J].<p>Biomedical titanium alloy materials have become the main raw materials for orthopedic, dental and cardiovascular implants or devices, but their biological and mechanical compatibility remains to be improved to meet the long-term safety and function in services for clinical application. Whether developing the novel medical titanium alloys with high-strength, low-modulus and other finer comprehensive performance, or upgrading and optimizing the traditional medical titanium alloys, it is the foundation and key to ensuring the structure homogeneity, high performance, versatility and low cost of biomedical titanium alloy materials and expanding its clinical application. The design, physical metallurgy, materials process, microstructure and properties, surface modification, advanced manufacturing and the clinical application of biomedical titanium alloys were introduced, and their latest research progress was reviewed in this paper, together with the recent advances in the author's R & D team. Finally, the further research and development trend of biomedical titanium alloys are summarized.</p>
新型医用钛合金材料的研发和应用现状
[J].医用钛合金材料已成为骨科、齿科和心血管等植介入物或器械用主要原材料,但要满足患者临床治疗的长效安全性和功能性,医用钛合金材料的生物及力学相容性仍有待提高。无论是开发新型高强度、低模量等综合性能优良的新型医用钛合金材料,还是立足对传统医用钛合金材料性能的优化升级,确保医用钛合金材料的均质化、高性能、多功能和低成本是扩大其临床应用的基础和关键。本文从医用钛合金材料合金设计、物理冶金、材料加工、组织与性能、表面改性、先进制造及临床应用等诸方面进行综述,并介绍了作者研发团队的最新进展,展望了未来发展趋势及待解决的问题。
Study on the microstructure and properties of Ti-34Nb-6Zr alloy for biomedical applications
[D].
生物医用钛合金Ti-34Nb-6Zr的组织及性能研究
[D].
Electrochemical corrosion behavior of 3D-printed NiTi shape memory alloy in a simulated oral environment
[J].
3D打印NiTi形状记忆合金在模拟不同口腔环境中电化学腐蚀行为研究
[J].
High-temperature oxidation behavior of laser additively manufactured AlCoCrFeNiSi high entropy alloy
[J].
激光增材制造AlCoCrFeNiSi高熵合金的氧化行为
[J].利用激光熔化沉积技术(LMD)增材制造了具有单相bcc结构的Al<sub>0.21</sub>Co<sub>0.17</sub>Cr<sub>0.13</sub>Fe<sub>0.11</sub>Ni<sub>0.18</sub>Si<sub>0.20</sub> (原子分数)高熵合金(HEA),其晶粒尺寸随着激光功率从900 W降低至700 W而逐步减小。在1100 ℃“干”空气和含10%H<sub>2</sub>O (体积分数)的“湿”空气的恒温氧化实验表明:该HEA能稳定生长单一的Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>膜;晶粒尺寸减小导致所生长Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>膜的氧化速度降低;H<sub>2</sub>O蒸气加快Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>膜生长速度。
Corrosion behavior in molten salts at 850 oC and its effect on mechanical properties of hastelloy X alloy fabricated by additive manufacturing
[J].
增材制造Hastelloy X合金在850 ℃混合硫酸盐中热腐蚀行为及其对力学性能的影响
[J].
Corrosion behavior of laser additive manufacturing AlSi10Mg Al-alloy in ethylene glycol coolant and detection of coolant degradation
[J].
乙二醇冷却液的劣化检测及增材制造AlSi10Mg铝合金在其中的腐蚀行为
[J].
Research progress on additive manufacturing of TiAl alloys
[J].
增材制造TiAl合金的研究进展
[J].轻质耐热的TiAl合金是航空航天和民用工业等领域最具潜力的高温结构材料之一。然而,由于其低的延展性和断裂韧性,制造TiAl零部件具有挑战性。目前,增材制造工艺被认为是制造TiAl零件具有前途的技术之一。本文在介绍增材制造技术原理和特点的基础上,综述了激光金属沉积(LMD)、选区激光熔化(SLM)和电子束熔化(EBM)制备TiAl合金的工艺-组织-性能关系,并对该技术未来的发展趋势进行了展望。
Research status and application of powder bed fusion additive manufactured titanium alloys
[J].
粉末床熔融式增材制造钛合金研究进展及应用
[J].
Effect of process parameters on the microstructure and high-temperature strengths of titanium aluminide alloy fabricated by electron beam melting
[J].
Influence of manufacturing parameters on the properties of electron beam melted Ti-Ni alloy
[J].Electron beam melting (EBM) is one of the additive manufacturing technologies which can be used to fabricate the complex structure and shape samples. Until now, there are few literatures published about the properties of Ti-Ni samples produced by EBM. In this work, the influence of two important manufacturing parameters of focus offset (FO) and speed function (SF) on the density, phase content and transformation behavior, microstructure and mechanical properties was investigated for the equiatomic Ti-Ni shape memory alloy fabricated by EBM used DSC, XRD, SEM, TEM and electronic universal testing machine. The results showed that all the Ti-Ni samples had a high relative density beyond than 97% for fabricated by different combinations of FO and SF in the selected range. The corresponding phase transformation temperatures for all the Ti-Ni samples fabricated by EBM were higher than the pre-alloyed Ti-Ni powder, due to the effect of evaporation of Ni element higher than that of the formation of Ni-rich Ti2Ni phase during the quickly melting and solidification process. On the other hand, the EBM manufacturing parameters of FO and SF had limited influence on the phase contents, phase transformation temperatures and Vickers hardness. Due to the feature of the EBM fabricating method, the different types of defects would be introduced in the Ti-Ni solid samples. Though all the samples had similar high relative density, the performance of the compression behavior were shown great difference, and the crack defect had the larger effect than the gas and lack-of fusion porosities on the compression fracture stress and strain.
打印参数对电子束增材制造Ti-Ni合金性能的影响
[J].利用SEM、XRD、DSC、TEM和等轴压缩等实验手段,研究和分析了打印参数焦距补偿(FO)和速度函数(SF)对电子束增材制造(EBM)制备的Ti-Ni合金显微组织、相组成、相变行为以及压缩性能的影响。结果表明:EBM打印参数FO和SF在一定范围内调节时均可制备出相对密度较高(97%以上)的Ti-Ni合金样品。由于EBM电子束的功率大,在预合金粉末快速受热熔化过程中,Ni元素的挥发效应大于富Ti相Ti<sub>2</sub>Ni析出效应对相变温度的影响,使得制备Ti-Ni块体的相变温度大于相应的预合金粉末,而打印参数FO和SF对制备样品的相变温度、相组成以及显微硬度的影响较小。EBM制备过程中在样品内部引入不同种类的缺陷类型,使得Ti-Ni合金样品在相对密度接近的情况下压缩性能表现出极大的差异,其中贯穿型裂纹缺陷对压缩性能的影响最大,使Ti-Ni合金的强度和塑性大幅度降低。
Elevated-temperature tensile properties of low-temperature HIP-treated EBM-built Ti-6Al-4V
[J].Evaluation of the high-temperature tensile properties of Ti-6Al-4V manufactured by electron beam melting (EBM) and subjected to a low-temperature hot isostatic pressing (HIP) treatment (800 °C) was performed in this study. The high-temperature tensile properties of as-built and standard HIP-treated (920 °C) materials were studied for comparison. Metallurgical characterization of the as-built, HIP-treated materials was carried out to understand the effect of temperature on the microstructure. As the HIP treatments were performed below the β-transus temperature (995 °C for Ti-6Al-4V), no significant difference was observed in β grain width between the as-built and HIP-treated samples. The standard HIP-treated material measured about 1.4×–1.7× wider α laths than those in the modified HIP (low-temperature HIP)-treated and as-built samples. The standard HIP-treated material showed about a 10–14% lower yield strength than other tested materials. At 350 °C, the yield strength decreased to about 65% compared to the room-temperature strength for all tested specimens. An increase in ductility was observed at 150 °C compared to that at room temperature, but the values decreased between 150 and 350 °C because of the activation of different slip systems.
Corrosion passivation in simulated body fluid of Ti-Zr-Ta-xSn alloys as biomedical materials
[J].The powder metallurgy method was used to manufacture three Ti-based alloys: Ti-15%Zr-2%Ta-4%Sn (Ti-Zr-Ta-4Sn), Ti-15%Zr-2%Ta-6%Sn (Ti-Zr-Ta-6Sn), and Ti-15%Zr-2%Ta-8%Sn (Ti-Zr-Ta-8Sn). Electrochemical measurements and surface analyses were used to determine the effect of Sn concentration on the corrosion of these alloys after exposure to a simulated body fluid (SBF) solution for 1 h and 72 h. It was found that the passivation of the alloy surface significantly increased when the Sn content increased from 4% to 6% and then to 8%, which led to a significant reduction in corrosion. The impedance spectra derived from the Nyquist graphs also explained how the addition of Sn significantly improved the alloys’ polarization resistances. According to the change in the chronoamperometric current at an applied anodic potential over time, the increase in Sn content within the alloy significantly reduced the currents over time, indicating that the uniform and pitting corrosion were greatly decreased. The formation of an oxide layer (TiO2), which was demonstrated by the surface morphology of the alloys after exposure to SBF solution for 72 h and corrosion at 400 mV (Ag/AgCl) for 60 min, was supported by the profile analysis obtained by an X-ray spectroscopy analyzer. It was clear from all of the findings that the tested alloys have a remarkable improvement in resistance to corrosivity when the Sn content was increased to 8%.
Effect of build-up direction and annealing on corrosion properties of selected laser melting Ti6Al4V alloy
[J].
成型方向及热处理对选区激光熔化Ti6Al4V合金腐蚀性能的影响
[J].研究选区激光熔化(Selective laser melting,SLM) Ti6Al4V合金的成型方向及热处理对其在Hanks体液中腐蚀性能的影响。针对不同状态SLM-Ti6Al4V合金的微观组织结构,借助电化学方法跟踪其在Hanks体液中的腐蚀钝化行为,从α/α′相含量、尺寸和取向分布等因素揭示不同状态合金在医用环境中耐腐蚀性能差异的机理。结果表明,成型方向和后续热处理对SLM-Ti6Al4V合金微观组织结构的影响导致了其腐蚀行为的差异。800 ℃以下热处理合金的XZ面耐腐蚀性优于XY面,表现出明显的各向异性,且随热处理温度的升高α/α′相尺寸增大,耐腐蚀性逐渐下降,各向异性减弱。800 ℃及以下热处理SLM-Ti6Al4V合金的腐蚀以点蚀为主,900 ℃及以上热处理合金的腐蚀机制为沿晶界腐蚀。800 ℃热处理合金的α/α′相尺寸及界面密度与成型态相当,表现出良好的耐腐蚀能力。
On the influence of thermal history on the martensitic transformation in Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn (wt%)
[J].Metastable β titanium alloys, such as Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn, have potential for application in vibration damping systems due to their ability to display superelastic behaviour. However, their use is currently limited due to large variations in the temperature range over which this behaviour is stable, which can additionally be shown to depend on the thermal history of the sample. This study demonstrates the sensitivity of the microstructure to thermal history and highlights a possible cause for this variability. Currently held theories of ω formation supressing the martensitic transformation have been called into question and an alternative mechanism based on a total stress approach has been suggested. Understanding this variability enables better design of alloys and processing routes in order to achieve materials with the desired properties required for industrial application.
Orthorhombic phase transformations in titanium alloys and their applications
[J].The link and difference between orthorhombic phase transformations in <em>β</em>-type titanium alloys and in Ti<sub>3</sub>Al containing high concentrations of transition metal elements such as Nb are first outlined in this paper. Recent investigations on these transformations conducted in the authors' group are reviewed followed by discussions of remaining problems. Three examples were presented to illustrate the applications of the orthorhombic phase transformations: design and development of superelastic titanium alloys for biomedical use, preparation of ultra-fine basketweave microstructure of titanium alloy wire for fastener manufacturing, and sheet and foil production of alloys based on Ti<sub>2</sub>AlNb.
钛合金中的正交相变及其应用
[J].
Stress-induced α″martensitic transformation mechanism in deformation twinning of metastable β-type Ti-27Nb-0.5Ge alloy under tension
[J].
Four-dimensional printing—The additive manufacturing technology of intelligent components
[J].
4D打印—智能构件的增材制造技术
[J].4D打印技术自2013年提出以来就引起了学术和工业界的广泛关注,它属于智能构件的增材制造技术,是在材料、机械、力学、信息等学科高度交叉融合基础上产生的颠覆性制造技术。讨论了4D打印的概念与内涵;介绍了4D打印在航空航天、汽车、生物医疗和软体机器人等领域的应用前景;阐述了4D打印在智能构件设计、模拟仿真、数据处理与工艺规划、材料、成形工艺与装备和智能构件的功能评测等方面的发展现状以及目前存在的一些问题;提出了关于4D打印的研究思考,最后指出了4D打印的未来发展方向和研究重点。
High temperature deformation behavior and microstructure evolution mechanism transformation in Ti2448 alloy
[J].
Ti2448合金高温变形行为及组织演变机制的转变
[J].研究了多功能亚稳β型Ti2448(Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn, 质量分数, %)合金在$\beta$单相区的高温变形行为. 结果表明,在低应变速率(-1</sup>)和高应变速率(>1 s<sup>-1</sup>)条件下, 真应力和应变速率的双对数关系可以通过2个线性关系分别表征, 平均应变速率敏感值(m<sub>avg</sub>)分别为0.265和0.032, 这不同于常规β钛合金随着应变速率的增大而逐渐降低的应变硬化规律, 即Sigmoidal曲线特征. 微观组织演化和动力学分析显示, 这种特殊的双线性关系与高应变速率导致的局域化非均匀塑性变形行为和动态再结晶(DRX) 相关联.尽管动态回复(DRV)是该合金高温塑性变形的主要组织演变机制, 高应变速率使得组织演变从DRV向DRX 转变, 并在交错的变形带内形成小于3 μm的细晶组织. 因此, 高应变速率条件下的DRX是实现Ti2448合金高温变形过程中细化组织的主要机制.
Coupling effect of pre-strain combined with isothermal ageing on mechanical properties in a multilayered Ti-10Mo-1Fe/3Fe alloy
[J].
预变形与等温时效耦合作用下Ti-10Mo-1Fe/3Fe层状合金的力学性能
[J].基于热锻/热轧工艺以及均匀化热处理制备了孪生与位错滑移耦合变形的Ti-10Mo-1Fe/3Fe层状合金,利用LSCM、XRD、SEM、SEM-EDS、EBSD、Vickers硬度计和拉伸试验机等研究了预变形与等温时效耦合作用对层状合金力学性能的影响。结果表明,经拉伸预变形和等温时效处理后,该合金具有{332}<113>孪晶和位错滑移带多层交替变形组织,且呈现出较高的屈服强度和较大的均匀伸长率。等温时效析出的ω相提高了β相稳定性,使得变形初期的塑性变形方式由位错滑移主导,这是其具有较高屈服强度的主要原因。预变形诱发的孪晶推迟了屈服之后颈缩的快速发生,而且后续变形过程中进一步激活的孪晶引起的动态晶粒细化效应及其与层界面的交互作用,使其具有较大的均匀伸长率。因此,在孪生与位错滑移耦合变形层状合金的基础上,进一步通过预变形诱发{332}<113>孪晶和等温时效析出ω相的双重耦合效应,可在较大范围内调控β型钛合金的强塑性匹配。
Cyclic oxidation behavior of TiAl alloy with electrodeposited SiO2 coating
[J].
TiAl合金表面电沉积SiO2涂层抗循环氧化性能研究
[J].针对TiAl合金在热循环环境中的抗氧化需求,本文采用电沉积方法在TiAl合金表面制备了SiO<sub>2</sub>涂层,并研究了涂层在900 ℃下的抗循环氧化性能,分析了电沉积SiO<sub>2</sub>涂层的失效机制。实验结果表明,电沉积SiO<sub>2</sub>涂层可有效提高TiAl合金的抗循环氧化性能。SiO<sub>2</sub>涂层可与TiAl基体发生反应生成 Ti<sub>5</sub>Si<sub>3</sub>,促进界面处选择性氧化生成Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>层,起到扩散阻挡作用。然而,由于SiO<sub>2</sub>涂层与TiAl合金存在热失配问题,会导致涂层内热应力集中,从而萌生裂纹。裂纹为氧的向内扩散和基体元素的向外扩散提供了通道,在氧化膜表面形成大量团簇,导致了SiO<sub>2</sub>涂层连续致密的结构遭到破坏,但SiO<sub>2</sub>涂层循环氧化200 h后仍未发生剥落,说明其仍保持一定的高温防护能力。
Electrochemical properties of Nb coating on TC4 substrate in simulated body solution [J] J
TC4表面沉积Nb涂层在模拟体液环境下的电化学性能研究
[J].利用双阴极等离子溅射技术在Ti-6Al-4V (TC4) 合金表面沉积Nb涂层,采用XRD、XPS和SEM研究涂层的组成及横截面形貌,并采用电化学工作站对涂层与基体的电化学性能及其钝化膜半导体特性进行研究。电化学测试均在模拟人体体液环境的Ringer's溶液中37 ℃下进行。结果表明,Nb涂层厚度约为18 μm,无孔洞、裂纹等缺陷,在 (200) 晶面呈现择优取向。涂层表面钝化膜成分主要为Nb<sub>2</sub>O<sub>5</sub>。相比TC4基体,涂层具有更高的开路电位E<sub>OCP</sub>、腐蚀电位E<sub>corr</sub>和更低的腐蚀电流密度I<sub>corr</sub>;涂层与基体合金试样均表现出单一容抗弧,但涂层具有更高的阻抗和较低的有效电容值;两种试样的钝化膜均表现出n型半导体特性,在不同的成膜电位E<sub>f</sub>下,Nb涂层的钝化膜具有更低的平带电位E<sub>fb</sub>,施主密度N<sub>d</sub>和扩散系数D<sub>0</sub>。
On the role of Nb-related sites of an oxidized β-TiNb alloy surface in its interaction with osteoblast-like MG-63 cells
[J].