大气腐蚀是材料在工业大气环境中因化学或电化学反应而发生的降解现象,对全球经济造成了巨大的经济损失。在中国,仅钢铁材料的大气腐蚀每年就造成超过1万亿元的损失,占总腐蚀损失的一半以上[1~3]。随着电子时代的到来,金属材料(如Cu、Ag等)的大气腐蚀问题也逐渐凸显,尤其是在大数据运算中心,室内大气管理成为保障设备正常运行的关键因素之一[4~7]。传统的大气腐蚀监测方法包括质量损失挂片法、电化学阻抗谱(EIS)法和线性极化电阻(LPR)法等[8,9]。其中,质量损失挂片法是最广泛使用的方法,但其实验周期长、结果受环境影响大且难以控制,无法提供实时信息,难以满足现代快速评估的需求[10,11]。EIS法通过施加小幅度正弦波电压并测量电流响应来解析腐蚀体系的阻抗特性,提供了详细的腐蚀动力学参数和机制信息,但由于其复杂的分析过程和高精度设备要求,限制了现场长期监测的应用[12~14]。LPR法通过测量金属表面由于微小电位偏移引起的电流变化来估算腐蚀速率,适用于短期腐蚀速率的动态监测,但在多相合金或非均匀腐蚀情况下效果有限[15]。因此,为了更精确地捕捉和描述钢铁材料在实际使用环境中的腐蚀行为,迫切需要开发更加高效、连续的监测技术来弥补现有方法的不足[16]。电阻法不仅能提供更为丰富的数据支持,还能显著缩短研究周期,提高对腐蚀过程的理解和预测能力。
电阻法早在1928年就被首次应用于大气腐蚀研究中。美国材料试验协会(ASTM)自1906年开始建立材料大气腐蚀测试网络,并对多种材料进行了大气腐蚀测试[17]。中国的自然环境腐蚀试验始于20世纪50年代中期,1980年系统地开展了大气、海水和土壤中常用材料的腐蚀试验,积累了大量实验数据[1]。2003年,日本腐蚀与防护学会成立了大气腐蚀评价小组,经过6 a时间研究了不同大气环境下腐蚀传感器的腐蚀性评估方法[18]。此外,MetriCorr公司通过集成多种传感器的远程监控系统,展示了其在复杂海洋环境下对腐蚀情况的有效跟踪能力[19~21]。韩国原子能研究所开发的波导超声系统与非线性超声波测量技术进一步提升了腐蚀监测精度,美国Teledyne Cormon公司的CEION系列海底及海面腐蚀感应器以其卓越的性能著称[22,23]。中国同样在推进该领域的发展,尽管自主研发产品相对较少且市场占有率较低,但近年来国内企业和研究机构开始重视此问题,并取得了若干突破性进展。这表明,在全球范围内,电阻探针(ER)技术正朝着更加广泛应用和更高技术水平的方向快速发展[24]。
本文介绍一种新型大气腐蚀监测技术,采用冷加工制备探针,简化制作流程,降低成本和监测难度。新型ER系统支持多达6支探针的数据采集,提升监测效率和覆盖范围[25]。该系统集成温度、湿度等环境参数监测功能,为全面理解腐蚀机制提供重要信息。这些改进弥补了传统方法的不足,尤其在电力、离岸风力发电及博物馆藏品保护等领域展示了高效监测和预警的巨大潜力。
1 实验方法
1.1 腐蚀监测工作站介绍
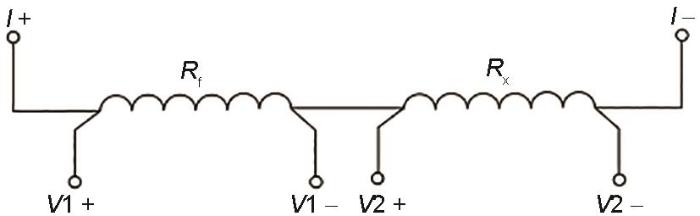
本文使用的大气腐蚀监测工作站为自主设计,型号为ECCM2105,具有多通道阵列式探针结构,支持6通道并行监测,允许同步进行多种材料体系或同种材料多个样本组的对比研究。工作站集成了温湿度、SO2浓度、紫外线强度等多参数同步检测单元,核心控制系统采用32位ARM Cortex-M4微处理器,配合自适应Kalman滤波算法,将数据采集精度提升至0.1%FS,并通过LoRa无线传输模块实现10 km范围内的实时数据回传。该工作站采用高精度微电阻测量方法(图1),以提高电阻测量的准确性。在图1中,Rx表示与腐蚀环境接触的测量元件,其电阻值随着腐蚀进程逐渐增加;而Rf则是封装在探针内部的参考测量元件,由相同材料制成但不发生腐蚀,并且与Rx处于相同的温度区域。通过同时测量两个电阻(Rf和Rx)两端的分压并计算其比值,可以基于该比值随时间的变化情况,推算出任意时刻的剩余厚度、减薄量以及腐蚀速率变化等信息。
图1
其中,测试元件的电阻Rx 可由
式中,ρ0是温度为T时测试元件的电阻率,k为电阻的温度系数,d为测试元件的实时厚度,a为电阻的宽度。l为测试元件长度。相同地,用ρf表示温度为T时参考元件的电阻率,则Rx和Rf之间比值的计算如
当腐蚀过程开始时,Rx的电阻会逐渐增大,而Rf 作为参照保持不变。系统实时采集这两个电阻的电压降,并通过精确的算法计算它们的比值。随着时间的推移,这一比值的变化反映了材料的腐蚀程度。根据
1.2 探针制备与安装
本研究采用冷加工方法制备电阻探针,确保探针的初始电阻大于1 mΩ。通过真空封装的方法进行样品处理,减少缝隙腐蚀的影响并提升实验结果的可靠性,其原理图如图2所示。该装置的工作原理基于金属材料的电阻与其厚度成反比的关系,即当金属材料因腐蚀逐渐变薄时,其电阻值会相应增加。采用自主设计的大气探针装置能够通过精确测量电阻的变化实时监测金属材料的腐蚀情况,提供可靠的数据支持,从而有效评估大气环境对材料的影响。这种设计不仅提高了监测的灵敏度和准确性,还简化了数据采集过程,使得长期连续监测成为可能。在实际应用中,参考片与测试片不一定需要保持相同的几何形状或尺寸,但必须确保两者之间存在明确的关系,以准确反映腐蚀进展。为了保证试样的代表性和一致性,本研究中所采用的挂片和探针的试片均从实际板材上取样后通过线切割这种冷加工方式制备,确保其与原板材的使用状态一致,具体操作遵循美国机械工程师协会( ASME)标准关于试片制作的相关规范[26]。
图2
由于数模转换器(ADC)对电压识别有特定精度区间,电阻变化引起的电压波动需超过一定阈值才能被精确捕捉。为确保最低响应精度,探针初始电阻应至少为1 mΩ。传统探针制备方法因材质不均和表面粗糙度问题难以满足高精度需求。本研究采用真空封装处理样品,在加入抗紫外线剂的环氧树脂浇灌后抽真空,并通过表面处理去除多余树脂,精确控制薄膜厚度和成分,有效提高探针初始电阻,增强测量精度和实验结果可靠性。选取0.5和2 mm两种厚度的探针,薄探针(0.5 mm)提升灵敏度,厚探针(2 mm)减少物理损害风险,延长使用寿命。这种方法不仅解决了传统方法的问题,还提升了探针的长期稳定性和系统准确性[27]。
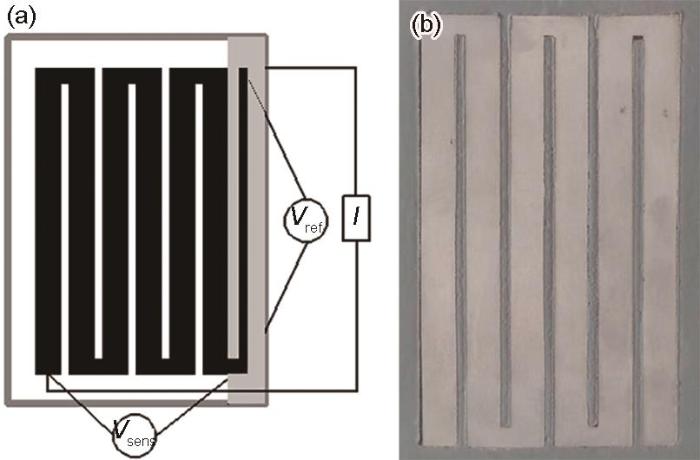
图3为大气探针的测量示意图及其实物图。该装置采用专门设计的探针,材料直接取自待研究的基础材料,确保测试结果的高度相关性和准确性。测试片的尺寸可根据精度和电阻特性灵活调整,初始电阻应大于1 mΩ。测试片与参考片形状可不同,探针也可设计成多种形状,适应各种复杂研究需求,确保高精度监测。这种设计不仅提供准确的腐蚀速率数据,还增强了后续分析和防护策略的科学依据,提升了设备的适应性和实用性,使研究人员能定制最适合的监测方案。无论实验室或实际应用现场,本装置都能高效、精确地完成大气腐蚀监测任务,为科研和工程实践提供强有力的支持。
图3
图3
测量原理示意图及探针实物图
Fig.3
Measurement principle diagram (a) and physical image of the probe (b)
1.3 数据采集与分析
工作站采用高速低功耗微控制器单元(MCU)和高精度低功耗模数(AD)转换器,实现了微电阻测量分辨率达到10-6 mΩ。其中,MCU负责整个系统的控制与数据处理,确保数据采集的高效性和准确性;AD转换器则用于将传感器获取的模拟信号转化为数字信号,以便于后续的数据分析。内置温度补偿电路通过实时调整测量值来抵消温度变化带来的影响,有效减少了温度对测量数据的影响。特别地,大气探针是该系统的核心组件之一,它直接与待测材料接触,通过监测电阻的变化来评估材料的腐蚀程度。探针内部设有参考元件,即使在恶劣环境下也能提供稳定对比基准。
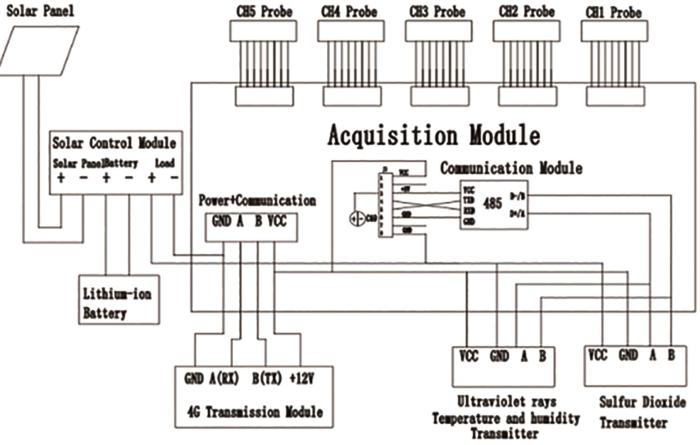
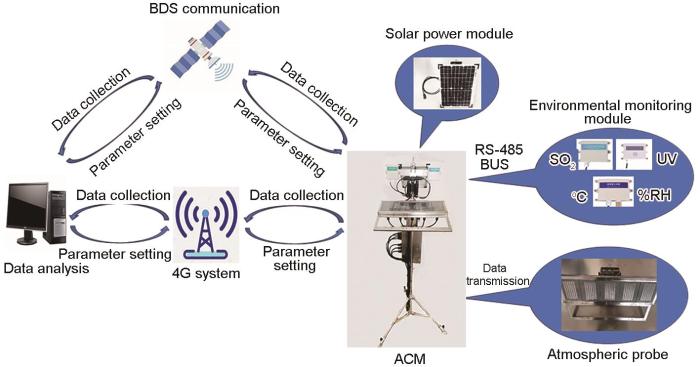
该装置的数据采集与传输流程如图4所示。其中,发射箱采用太阳能供电,确保了设备在野外环境中的能源自给自足;常规区域可通过4G或无线网络进行数据传输,而在无信号区域,则可使用卫星通信以保证数据的连续性。所有接口均采用防水设计,并经过严格测试,确保设备在各种恶劣天气条件下仍能稳定工作。此外,该工作站还配备了环境监测传感器,能够实时监测温度、湿度、紫外线强度及SO2浓度的变化,便于用户分析环境介质对腐蚀的影响。
图4
2 结果与讨论
2.1 长期腐蚀速率监测
本实验在河南省濮阳市高新技术创业孵化园(经度:114.987,纬度:35.787)进行,通过安装在监测站的传感器连续在线监测温度、湿度、紫外线强度和SO2浓度等参数,并与探针及挂片的腐蚀情况关联分析。实验采用大气探针监测与传统挂片两种方法,使用常见低碳钢作为实验材料,工作站的5个通道中,4个通道安装了厚度为0.5和2 mm的芯片探针(编号1#和5#,初始电阻分别为4.6465和7.9626 mΩ),另外1个通道用于传统挂片对比分析。
图5
2.2 探针厚度对测量结果的影响
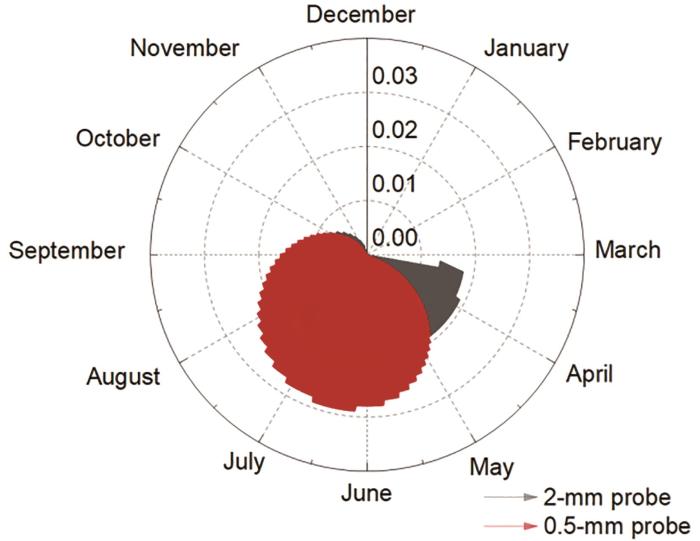
为了展示1 a周期内的腐蚀速率,将其绘制成如图6所示的罗盘图,以4月份的腐蚀速率值为起点,展示2和0.5 mm两种厚度的探针监测到的数据,在径向轴上对比了不同时间的腐蚀速率变化。
图6
由图6可见,2 mm探针在腐蚀初期采集的腐蚀速率数据(0.018 mm/a)高于0.5 mm探针,随着腐蚀速率增加,两探针数据逐渐接近。春季(3月23日至4月15日),2 mm探针腐蚀速率为0.018 mm/a,环境条件温和,腐蚀作用较小。夏季(8月24日至9月19日),腐蚀速率略下降至0.017 mm/a,雷雨天气可能影响局部微环境。秋季(9月16日至10月13日),腐蚀速率降至0.015 mm/a,气候干燥减少水分滞留,减缓腐蚀。冬季(3月23日至3月31日),腐蚀速率为0 mm/a,低温抑制化学反应。0.5 mm探针数据显示,春季腐蚀速率较低且稳定(0.018~0.02 mm/a),夏季和秋季较高(0.027~0.029 mm/a),冬季最低甚至为0。这主要是因为春季较高湿度(平均相对湿度(RH)75%)促进初期腐蚀(速率0.018 mm/a),而冬季低温(< 5 ℃)抑制阴极氧还原反应,导致腐蚀速率趋近于0。
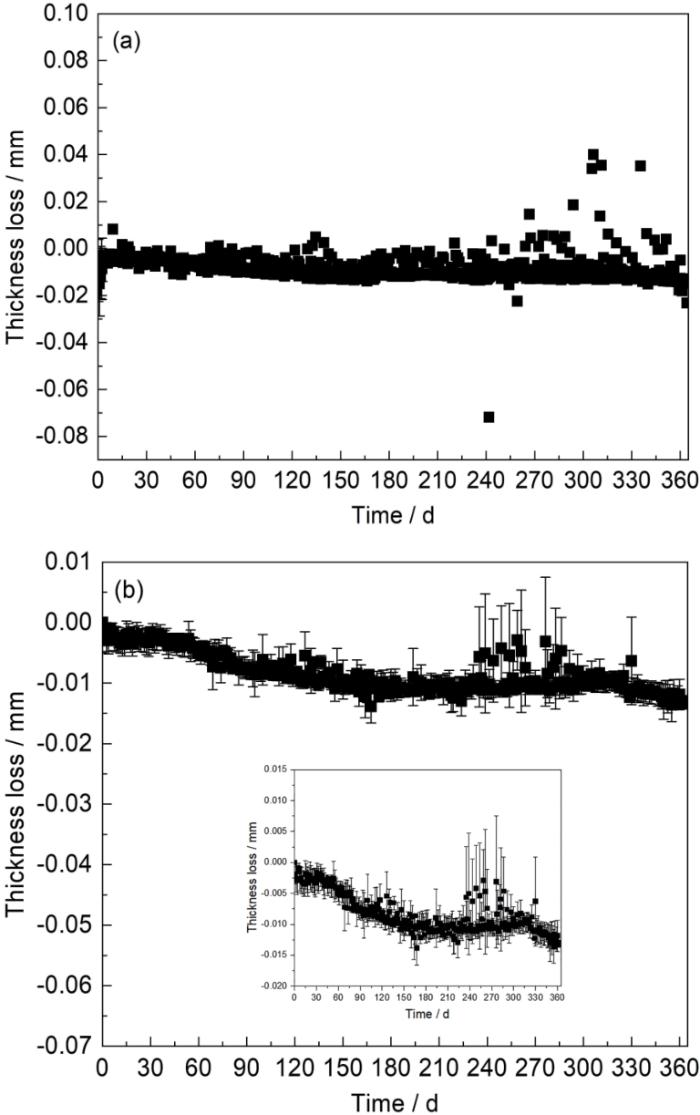
图7
图7
2和0.5 mm探针所采集的剩余厚度的方差
Fig.7
Variances of the remaining thicknesses collected by 2 (a) and 0.5 mm (b) probes
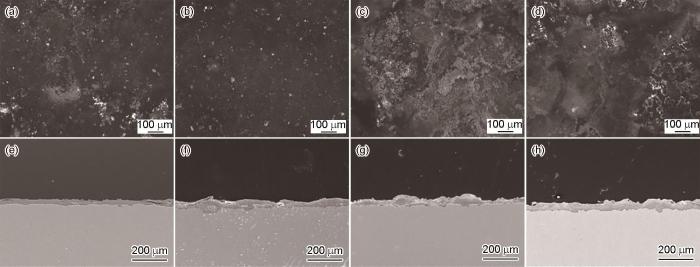
2.3 微观形貌及成分分析
图8
图8
探针和挂片正反面的微观形貌
Fig.8
Microscopic morphologies of 2 (a, e) and 0.5 mm (b, f) probes, and the front (c, g) and back (d, h) surfaces of experimental coupons
3 结论
本研究研发的大气腐蚀监测工作站通过集成高灵敏度环境传感器阵列和智能补偿算法,实现了大气环境中材料腐蚀状态的实时动态监测。实验数据表明,该装置对温湿度等环境参数的响应灵敏度达到μs级,其中0.5 mm超薄探针可实现0.05 mm级厚度变化分辨率,而2 mm标准探针则展现出超过8000 h的持续监测能力。该工作站不仅适用于炼油、电力、化工等工业腐蚀监测,其模块化设计还兼容博物馆、净化室等精密环境需求。
参考文献
Introduction to atmospheric corrosion research in China
[J].
The effect of atmospheric corrosion on steel structures: A state-of-the-art and case-study
[J].Atmospheric corrosion can seriously affect the performance of steel structures over long periods of time; thus, it is essential to evaluate the rate of corrosion and subsequent modification of dynamic properties of a structure over different time periods. Standards and codes represent the general guidelines and suggest general protection techniques to prevent structures from corrosion damage. The available models in the literature propose the thickness reduction method that accounts for the exposure time of structures in corrosive environments. The purpose of this study is to review the existing corrosion models in the literature and report as well as compare their effectiveness in low (C2 level), medium (C3 level) and high (C4 level) corrosivity class in accordance with the ISO standard. Furthermore, the influence of corrosion loss during the lifetime of a structure is studied through a realistic case study model using FEM (finite element method) in both linear and nonlinear regions. The results showed that the corrosion can considerably affect the dynamic characteristics of the structure. For instance, the vibration period rose up to 15% for the C4 class and 100-year lifespan. Additionally, the corroded structure presented higher acceleration and drift demand, and the base reaction forces were reduced up to 60% for the same class and time period.
Evaluation of atmospheric corrosion damage to steel space structures in coastal areas
[J].
Atmospheric corrosion of silver, copper and nickel exposed to hydrogen sulphide: A multi-analytical investigation approach
[J].
Corrosion monitoring in atmospheric conditions: A review
[J].A variety of techniques are available for monitoring metal corrosion in electrolytes. However, only some of them can be applied in the atmosphere, in which case a thin discontinuous electrolyte film forms on a surface. In this review, we describe, evaluate and compare both traditional and state-of-the-art real-time corrosion monitoring techniques to identify those suitable for atmospheric conditions. For atmospheric corrosion monitoring (ACM), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), electrochemical noise (EN), electrical resistance (ER) probes, quartz crystal microbalance (QCM), radio-frequency identification sensors (RFID), fibre optic corrosion sensors (FOCS) and respirometry, the underlying principles, characteristics and application examples are described, and their advantages and drawbacks outlined. Finally, the techniques are compared in terms of their sensitivity, ease of setup, data processing, ability to identify underlying corrosion mechanisms and applicability in different fields of atmospheric corrosion protection and research.
Corrosion management for data centers
[A].
Preservation methods of historical iron objects: An overview
[J].
Application of an electrical resistance sensor-based automated corrosion monitor in the study of atmospheric corrosion
[J].An automated corrosion monitor, named the Internet of Things atmospheric corrosion monitor (IoT ACM) has been developed. IoT ACM is based on electrical resistance sensor and enables accurate and continuous measurement of corrosion data of metallic materials. The objective of this research is to study the characteristics of atmospheric corrosion by analyzing the acquired corrosion data from IoT ACM. Employing data processing and data analysis methods to research the acquired corrosion data of steel, the atmospheric corrosion characteristics implied in the corrosion data can be discovered. Comparing the experiment results with the phenomenon of previous laboratory experiment and conclusions of previously published reports, the research results are tested and verified. The experiment results show that the change regulation of atmospheric corrosion data in the actual environment is reasonable and normal. The variation of corrosion depth is obviously influenced by relative humidity, temperature and part of air pollutants. It can be concluded that IoT ACM can be well applied to the conditions of atmospheric corrosion monitoring of metallic materials and the study of atmospheric corrosion by applying IoT ACM is effective and instructive under an actual atmospheric environment.
Measuring atmospheric corrosion with electrochemical noise: A review of contemporary methods
[J].
Use of weight loss coupons and electrical resistance probes in atmospheric corrosion tests
[J].
The use of corrosion coupons to control atmospheric corrosion salt spray tests
[A].
Trends, challenges, and recent advances in electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
[J].
Review of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy methods for lithium-ion battery diagnostics and their limitations
[J].Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is a measurement method widely used for non-destructive analysis and diagnostics in various electrochemical fields. From the measured dependence of the battery impedance on the frequency, it is possible to determine the parameters of various equivalent electrical circuit models of the battery. The conventional method of battery measurement using single-sine EIS is currently one of the most widely used methods for the analysis of lithium-ion batteries. However, its most significant disadvantage is the relatively long measurement time. For this reason, there is a growing demand for faster methods using fast-Fourier transform or pseudo-random sequences. A description of various EIS methods applications is provided in this paper.
Electrochemical measurements used for assessment of corrosion and protection of metallic materials in the field: A critical review
[J].
Application and prospect of localized electrochemical techniques for microbiologically influenced corrosion: A review
[J].
Latest developments on atmospheric corrosion monitoring technologies for steels
[J].
钢铁大气腐蚀监测技术研究进展
[J].
Effect of distance from sea on atmospheric corrosion rate
[J].The influence of the distance from sea constitutes one of the most important aspects of atmospheric corrosion in coastal areas. Empirically, it is known that the effect of marine atmospheres extends principally some few hundred meters from the shoreline and decays rapidly further inland. As coastal corrosion rate depends on the concentration of chloride in the atmosphere, influence of wind and surf zone on the production of saline droplets and the decrease of the amount of these droplets from settling and impingement were discussed. The complexity of phenomena associated with marine atmospheric corrosion makes it difficult to devise a model that covers all scenarios. However, for the areas closest to the shoreline (~ 400 m to 600 m), using published data, it was shown that the decrease of the corrosion rate with distance from the sea is represented fairly well by a simple exponential relationship.
Evaluation of corrosivity of atmosphere by acm type corrosion sensor
[J].
Corrosion monitoring for offshore wind farm's substructures by using electrochemical noise sensors
[J].
Corrosion evolution and quantitative corrosion monitoring of Q355 steel for offshore wind turbines in multiple marine corrosion zones
[J].
Ultrasonic waves for materials evaluation in fatigue, thermal and corrosion damage: A review
[J].Mechanical properties of materials tend to deteriorate over time and thus become responsible for cracks and malfunctions in mechanical components or civil structures. Non-destructive ultrasonic wave analysis has proven to be a successful investigation method for inspecting mechanical properties of materials. This review has highlighted the main results of research in the field of non-linear ultrasonic wave investigations for the inspection of fatigue damage, thermal damage and chemical damage. In all three cases, non-linear ultrasonic wave survey method was effective in detecting first-stage damage. (C) 2018 Elsevier Ltd.
Corrosion monitoring in steel bars using Laser ultrasonic guided waves and advanced signal processing
[J].
Nonlinear ultrasonic techniques for nondestructive assessment of micro damage in material: A review
[J].
Role of big data and technological advancements in monitoring and development of smart cities
[J].
Establish real-time corrosion map through dual-driven data and knowledge neural network
[J].
Real-time monitoring of indoor air corrosivity in cultural heritage institutions with metallic electrical resistance sensors
[J].
Changes in atmospheric corrosion rate caused by chloride ions depending on rain regime
[J].
Evolution of rust layers and degradation of mechanical properties of Q420B steel in a simulated wet/dry cyclic coastal atmosphere
[J].