构件服役安全是评价增材制造技术可行性的关键指标,而腐蚀失效是常见的安全隐患[8~10]。因此,研究增材制造钛合金的腐蚀行为具有重要意义,近年来逐渐受到学界的关注。一般认为,钝化膜是钛合金具有良好耐蚀性的主要原因,也是钛合金腐蚀研究的重要课题[11,12]。有文献报道SLM成形TA15钛合金比传统锻件具有更少缺陷,在硫酸溶液中的钝化膜有更优的耐蚀性[13];有学者研究表明SLM成形TC4钛合金的钝化膜呈n型半导体特性[14],而关于WAAM-TC4钛合金腐蚀行为的报道较为匮乏。值得注意的是,SLM与WAAM因热源特性不同,导致其显微组织、残余应力及缺陷分布存在显著差异,进而可能影响钝化膜的生成与稳定性。
因此,本文分别采用SLM和WAAM两种增材工艺和传统的锻造+退火工艺方法制备3种状态的同一种TC4钛合金,利用电化学和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)等方法比较不同工艺制备的TC4钛合金的钝化行为,揭示其钝化膜的组成与性质。
1 实验方法
实验采用3种TC4钛合金:SLM-TC4钛合金、WAAM-TC4钛合金及传统商用的轧制退火态TC4钛合金。所有试样经线切割加工后依次用400#至2000#砂纸打磨,酒精超声清洗10 min并干燥;利用Bruker D8 Advance型X射线衍射仪(XRD),扫描范围30°~80°,步长0.02°分析物相组成,并通过扫描电镜(SEM,Regulus 8230)搭配电子背散射衍射仪(EBSD)表征晶粒取向、晶界分布及织构特征。用电火花线切割将3种钛合金加工成尺寸为10 mm × 10 mm × 3 mm的样品,由150#逐级打磨至3000#,随后进行机械抛光至1.5 μm,后采用电解抛光制样,直流30 V,时长为40 s。腐蚀测试溶液为3.5% (质量分数) NaCl水溶液(pH = 6.8 ± 0.2),实验在常温(25 ± 1) ℃常压下进行。
在CHI350电化学工作站上进行电化学测试,采用三电极体系,工作电极为暴露面积1 cm2的TC4钛合金试样,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE),对电极为Pt电极。测试流程包括:开路电位(OCP)稳定1800 s,动电位极化曲线扫描(-1.2 V至+1.2 V (vs. SCE,下同)),速率1 mV/s),通过Tafel外推法计算腐蚀动力学参数;为研究3种钛合金钝化膜,对其进行了恒电位极化,电位为0.2和0.6 V,持续1800 s;恒电位极化处理后进行M-S曲线测试,测试范围为-0.5~0.5 V。
3种钛合金在3.5%NaCl溶液中,经0.2 V极化处理后,采用THS-103型XPS研究它们表面钝化膜的组成,测量结果与284.0 eV的C峰进行校对,并利用XPSPeak软件进行拟合处理。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 微观结构
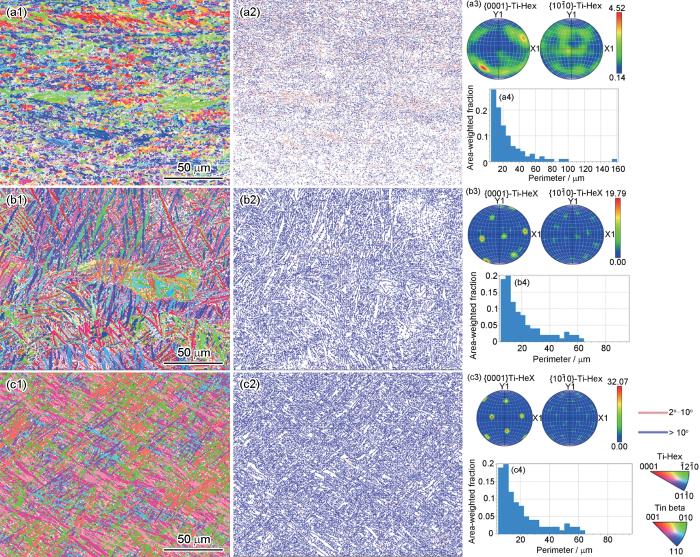
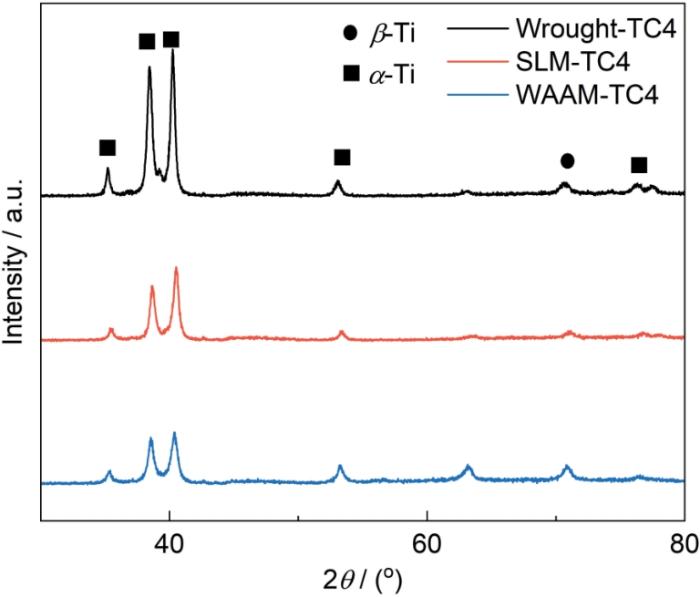
图1为SLM、WAAM和传统商用TC4钛合金的EBSD测试结果图。由图1a1、b1和c1所示的反极图(IPF)可知,两种增材制造钛合金的各向异性低于传统钛合金;这与大多数文献中的报的吻合。由晶界图可知(图1a2、b2和c2),两种增材TC4钛合金以大角度晶界为主,而传统钛合金上有更多的小角度晶界。由晶粒尺寸图(图1a4、b4和c4)可知,WAAM的晶粒尺寸最大,加权后周长约为25.7 μm,SLM-TC4略小于该值,约为21.0 μm;传统钛合金晶粒最小,约为18.9 μm,这与制备方法的能量有关,WAAM和SLM过程中高输入的热能导致了晶粒长大,尤其是WAAM的过程[15,16]。由极图(图1a3、b3和c3)可知,增材TC4钛合金有强织构存在,择优取向明显,且WAAM的更为显著;而传统TC4钛合金并未表现出强织构特征。图2为SLM、WAAM和传统商用TC4钛合金的XRD结果,3种钛合金均由α-Ti和β-Ti组成,峰强度有一定差别。
图1
图1
传统SLM和WAAM TC4钛合金的EBSD结果
Fig.1
EBSD results of traditional TC4 (a), SLM-TC4 (b) and WAAM-TC4 Ti-alloys (c): (a1, b1, c1) IPF map; (a2, b2, c2) grain boundary map; (a3, b3, c3) pole map; (a4, b4, c4) grain size map
图2
图2
SLM、WAAM和传统TC4钛合金的XRD谱
Fig.2
XRD spectra of SLM, WAAM and traditional TC4 Ti-alloys
2.2 电化学测试
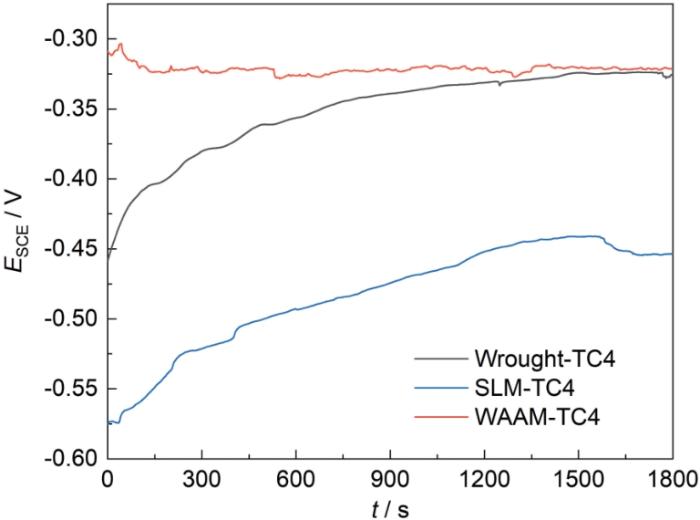
图3为SLM、WAAM和传统TC4钛合金浸泡1800 s的开路电位(OCP)图。由图可知,SLM和传统钛合金的开路电位接近,在-0.3 V左右,这与文献中报道的钛合金OCP接近;而WAAM-TC4相对偏低,在-0.45 V左右。
图3
图3
SLM、WAAM和传统TC4钛合金浸泡1800 s的OCP
Fig.3
Open circuit potential (OCP) of SLM, WAAM and traditional TC4 Ti-alloys after soaking for 1800 s
图4
图4
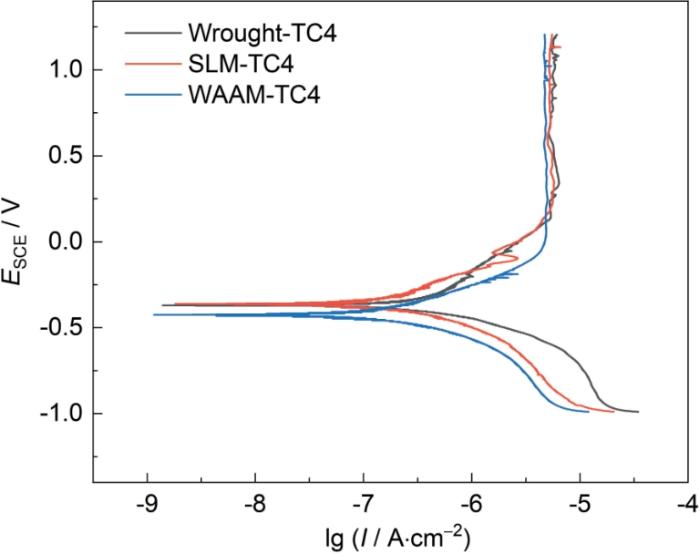
SLM、WAAM和传统TC4钛合金的动电位极化曲线
Fig.4
Dynamic potential polarization curves of SLM, WAAM and traditional TC4 Ti-alloys
表1为极化曲线分析结果,传统、SLM和WAAM-TC4钛合金的自腐蚀电位(Ecorr,vs. SCE)分别为-0.372、-0.369和-0.423 V,表明WAAM-TC4钛合金的腐蚀倾向更为突出,这可能与WAAM-TC4钛合金热过程形成的特殊微观组织有关。3种不同制备工艺的钛合金自腐蚀电流密度(Icorr)差别不大。就维钝电流密度(Ipass)而言,WAAM-TC4钛合金更小,SLM-TC4钛合金其次,传统TC4钛合金略微偏大,表明WAAM-TC4钛合金更易形成稳定钝化膜。
表1 SLM、WAAM和传统TC4钛合金的动电位极化曲线的拟合结果
Table 1
| Alloys | Ecorr, SCE / V | Icorr / A·cm-2 | Ipass / A·cm-2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wrought-TC4 | -0.372 | 4.09 × 10-7 | 5.57 × 10-6 |
| SLM-TC4 | -0.369 | 2.21 × 10-7 | 5.25 × 10-6 |
| WAAM-TC4 | -0.423 | 1.104 × 10-7 | 4.79 × 10-6 |
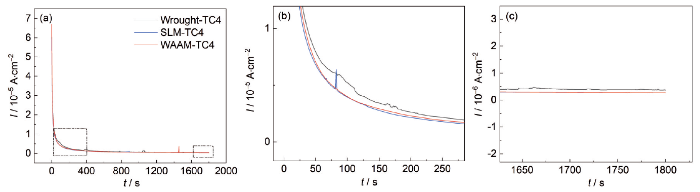
图5为3种钛合金的恒电位极化曲线。在0.2 V的外加电位作用下,3种钛合金都经历了电位先快速下降后趋于稳定的过程,电流密度相对稳定的区域代表了钝化的形成和溶解达到了相对动态平衡的状态。极化初期传统钛合金较晚达到电流稳定状态,两增材钛合金接近;传统TC4钛合金的电流密度波动大,且电流密度高于增材钛合金,后者的电流密度波动轻微;这表明此时增材TC4钛合金的钝化膜稳定性好于传统TC4钛合金,WAAM和SLM-TC4接近。
图5
图5
SLM、WAAM和传统TC4钛合金的恒电位图
Fig.5
Potentiostatic diagram of SLM, WAAM and traditional TC4 Ti-alloys: (a) overall view, (b) enlarged view of the red-framed area, (c) enlarged view of the yellow-framed area
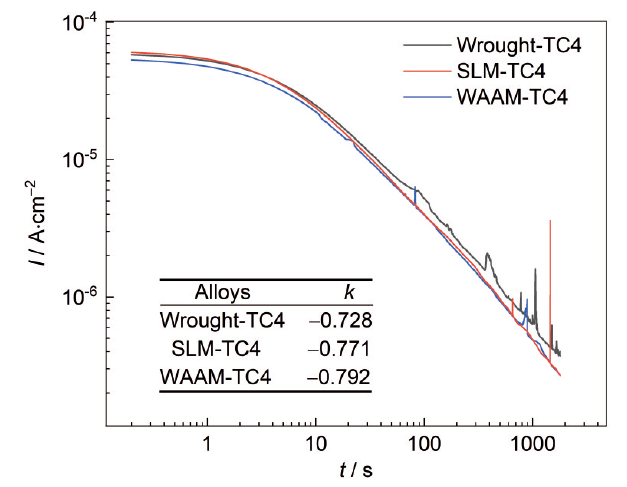
图6
图6
SLM、WAAM和传统TC4钛合金浸泡1800 s的恒电位极化对数处理图
Fig.6
Logarithmic treatment diagram of constant potential polarization for SLM, WAAM and traditional TC4 Ti-alloys after soaking for 1800 s
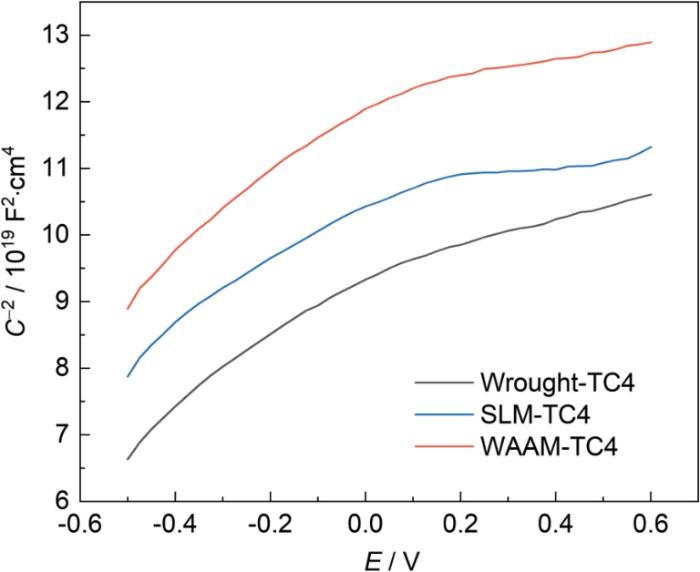
通过M-S曲线获得了钝化膜与金属之间的电容值,这种方法通常用于研究金属表面形成的钝化膜的半导体特性。图7为3种钛合金在0.2 V电位下极化30 min后的M-S曲线,3种合金的M-S曲线上均存在正斜率的线性区域,该正向斜率表明钝化膜呈n型半导体特征,制备工艺不会改变钝化膜的半导体类型。3种钛合金的平带电位(Efb)接近,通常认为Efb主要受溶液pH值的影响。
图7
图7
SLM、WAAM和传统TC4钛合金的M-S曲线
Fig.7
M-S curves on SLM, WAAM and traditional TC4 Ti-alloys
式中,C是空间电荷电容,E是外加电位,ND是膜载流子密度,Efb是平带电位,e是电子电荷1.602 × 10-19 C,ε是膜介电常数15.6,ε0是真空介电常数8.854 × 10-14 F/cm,K是Bottzman常数1.38 × 10-23 J/K,T是绝对温度。
图8
图8
SLM、WAAM和传统TC4钛合金钝化膜的ND值
Fig.8
ND values of passivation films on SLM, WAAM and traditional TC4 Ti-alloys
2.3 XPS分析
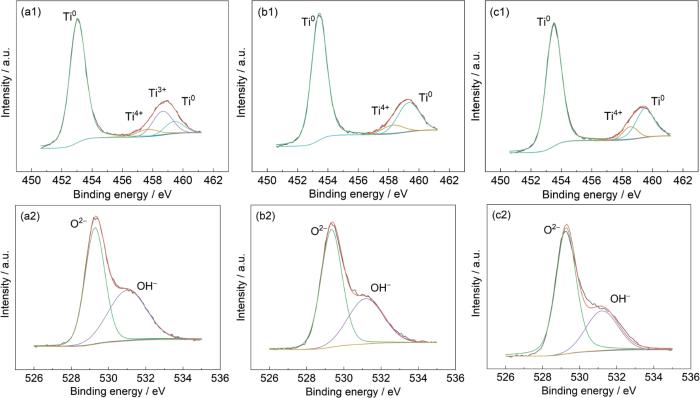
图9为经恒电位极化处理后3种方法制备的TC4钛合金表面的XPS分析结果。由图9a1、b1和c1可知,钛合金表面主要由Ti (453.1和459.4 eV)、Ti3+ (457 eV)和Ti4+ (458.6 eV)[13]组成,普遍认为Ti3+容易被氧化为Ti4+,WAAM和SLM的TC4钛合金表面的Ti3+较少,而传统TC4钛合金有一定量的Ti3+,传统和增材TC4钛合金中O元素均主要可分为O2- (529.2 eV)和OH- (531.1 eV)[13],如图9a2、b2和c2所示。有文献认为,O2-/OH-的比值越大代表了钝化膜的致密性越好[24,25],经XPSpeak软件分析发现3种TC4钛合金O2-/OH-的比值为58.1% (传统TC4钛合金),62.6% (SLM-TC4钛合金),68.3% (WAAM-TC4钛合金),但比值相差不大,这也与电化学结果一致。
图9
图9
SLM、WAAM和传统TC4钛合金钝化膜的XPS结果
Fig.9
XPS results of passivation films on traditional TC4 (a), SLM-TC4 (b) and WAAM-TC4 Ti-alloys (c): (a1-c1) Ti spectra, (a2-c2) O spectra
3 结论
(1) 锻造并退火态的合金表现为各向异性。两种增材制造的TC4钛合金择优取向更为明显,而电弧增材制造的尤甚。
(2) 3种TC4合金的钝化膜均表现为n型半导体,但它们的钝化膜缺陷浓度存在差异,而电弧增材和激光选区熔化增材制造的TC4合金的钝化膜则相对致密。
(3) 3种方法制造的TC4合金的钝化膜均由Ti和Al的氢氧化物和氧化物组成,制备方法则导致钝化膜成分的差异。
参考文献
The effect of dissolved oxygen and Shewanella algae on the corrosion mechanism of titanium in a simulated marine environment
[J].
Stress corrosion cracking of the titanium alloys under hydrostatic pressure resulting from the degradation of passive films
[J].
Influence of sulfides on the passivation behavior of titanium alloy TA2 in simulated seawater environments
[J].
Effect of annealing treatment on the phase transformation and mechanical properties of TA15 alloy fabricated by WAAM
[J].
Microstructure evolution and fracture behavior of Ti-6Al-4V fabricated by WAAM-LDM additive manufacturing
[J].
Corrosion characterization and ion release in SLM-manufactured and wrought Ti6Al4V alloy in an oral environment
[J].
Effects of laser shock peening on the hot corrosion behaviour of the selective laser melted Ti6Al4V titanium alloy
[J].
Corrosion behavior of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy in Cl--containing solution
[J].
High-temperature oxidation behaviour of Ti65 titanium alloy fabricated by laser direct energy deposition
[J].
Corrosion and passive behavior of SLM and wrought TA15 titanium alloys in hydrochloric acid solutions
[J].
Effect of inserting the Zr layers on the tribo-corrosion behavior of Zr/ZrN multilayer coatings on titanium alloys
[J].
The corrosion behavior of Ti6Al4V fabricated by selective laser melting in the artificial saliva with different fluoride concentrations and pH values
[J].
Comparison of electrochemical characteristics and passive film properties of selective laser melted and wrought TA15 alloys in sulfuric acid solution
[J].
Study of the passivation and repassivation behavior of pure titanium in 3.5wt%NaCl solution and 6M HNO3 solution
[J].
Ti based alloys for aerospace and biomedical applications fabricated through wire + arc additive manufacturing (WAAM)
[J].
A comparative study of surface characterization and corrosion behavior of micro-arc oxidation treated Ti-6Al-4V alloy prepared by SEBM and SLM
[J].
The corrosion behavior of Ti-6Al-3Nb-2Zr-1Mo alloy: Effects of HCl concentration and temperature
[J].Investigation about the corrosion behavior of Ti alloys in different ambient environment is of great significance for their practical application. Herein, we systematically investigate the corrosion behavior of a newfound Ti-6Al-3Nb-2Zr-1Mo (Ti80) alloy in hydrochloric acid (HCl) ranging from 1.37 to 7 M, and temperature ranging from 25 to 55 ℃, by means of electrochemical measurements, static immersion tests and surface analysis. Results manifest that increasing either HCl concentration or temperature can accelerate the corrosion of Ti80 alloy via promoting the breakdown of native protective oxide film and then further facilitating the active dissolution of Ti80 matrix. According to potentiodynamic polarization curves, Ti80 alloy displays a spontaneous passive behavior in 1.37 M HCl at 25 ℃, compared to a typical active-passive behavior under the other conditions. As indicated by cathodic Tafel slope, the rate determining step for cathodic hydrogen evolution reaction is likely the discharge reaction step. The apparent activation energies obtained from corrosion current density and maximum anodic current density for Ti80 alloy in 5 M HCl solution are 62.4 and 55.6 kJ mol-1, respectively, which signifies that the rate determining step in the corrosion process of Ti80 alloy is mainly determined by surface-chemical reaction rather than diffusion. Besides, the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy tests demonstrate that a stable and compact oxide film exists in 1.37 M HCl at 25 ℃, whereas a porous corrosion product film forms under the other conditions. Overall, the critical HCl concentration at which Ti80 alloy can maintain passivation at 25 ℃ can be determined as a value between 1.37 and 3 M. Furthermore, the corroded surface morphology characterization reveals that equiaxed α phase is more susceptible to corrosion compared to intergranular β phase due to a lower content of Nb, Mo, and Zr in the former.
Effect of microstructural evolution and texture change on the in-vitro bio-corrosion behaviour of hard-plate hot forged Mg-4Zn-0.5Ca-0.16Mn (wt%) alloy
[J].
Electrochemical behavior and passive film properties of Ce-added AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloys in sulfuric acid solution
[J].
Passivation behavior and surface chemistry of 2507 super duplex stainless steel in artificial seawater: Influence of dissolved oxygen and pH
[J].
Influence of temperature on the electrochemical and passivation behavior of 2507 super duplex stainless steel in simulated desulfurized flue gas condensates
[J].
Electrochemical and semiconducting properties of thin passive film formed on titanium in chloride medium at various pH conditions
[J].
Electrochemical behaviour of passive film formed on the surface of Ti-6Al-4V alloys fabricated by electron beam melting
[J].
Comparison of electrochemical characteristics and passive behavior of as-cast and heat-treated AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloys in Cl-containing sulfuric acid solution
[J].