为了降低CO2腐蚀带来的经济损失和安全风险,已经开展和研发了一系列防腐措施和技术,其中添加有机类缓蚀剂是油气田系统中最常用且有效的腐蚀防护手段。然而,在油水气多相流动的复杂工况下,缓蚀剂的应用仍非常具有挑战性,流动特性[13]、原油成分[14]、界面聚集[12]等都可能会降低缓蚀剂的效果或无法把握其正确的用量。目前人们对有机类缓蚀剂的缓蚀机理作了一些研究,但主要围绕水相溶液[15~17]或油水乳化[18]等实验模拟条件下的研究,对关于含CO2环境中油水交替润湿的缓蚀评价和作用机理的研究甚少。鉴于多相流环境中流体与流型之间的复杂性和原油对缓蚀剂的“毒化”作用[14],明确缓蚀剂与油水界面的相互作用变得尤为重要。
本文选择油溶性和水溶性两种咪唑啉类缓蚀剂在“交替润湿池”进行实验测试,评价其对油膜耐久性的影响,探究在含CO2油水交替润湿环境中的油膜自修复性和可靠性。通过在分子层面解释它们对油/水/碳钢界面的影响,揭示不同缓蚀剂缓蚀效果差别的深层次原因,希望可以为含CO2多相流的腐蚀控制中提供新的见解。
1 实验方法
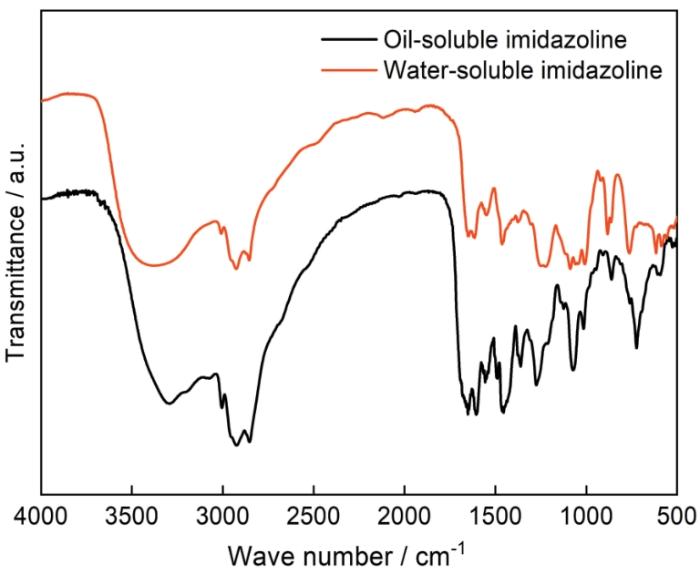
利用Nicolet IS5022 Fouier红外光谱仪对油溶性咪唑啉(上海麦克林生化科技有限公司)和复配的水溶性咪唑啉(中石化石油工程设计有限公司自行研制)两种缓蚀剂进行测试。光谱参数设置为:扫描范围500~4000 cm-1,扫描速率0.158 cm/s。所用咪唑啉分子均为含氮五元杂环,通过C=N双键上C原子的憎水支链和C—N键上N原子的亲水支链调控其亲水亲油特性。
制备了不含缓蚀剂、添加油溶性咪唑啉(加入油相,80 mg/L)和添加水溶性咪唑啉(加入水相,80 mg/L)3种CO2持续鼓泡的碳酸化系统。该浓度属于油田常用缓蚀剂添加范围。其中,油相为100#矿物油,水相为0.1 mol/L NaCl溶液。
利用“交替润湿池”装置[19]在电化学工作站(PARSTAT4000, AMETEK)上进行电化学测试,其中由20#碳钢制成的旋转圆柱电极(RCE)为工作电极WE。RCE浸油5min后浸入水相,同时进行恒电位极化测试(-300 mV vs. SCE),记录油膜破裂时间(阳极电流升至50 μA的时间记为tb),即是附着在RCE表面的油膜的耐久性。另外,进行油水交替润湿实验来了解油膜的可靠性和两种缓蚀剂的缓蚀效果,条件为:油润湿10 s,水润湿50 s,循环30圈;用于模拟油水交替润湿时间为1:5的情形。实验涉及流体的静态、层流(< 400 r/min,对应Reynolds数为2080)和湍流(600~1000 r/min,对应Reynolds数为3120~5200)。
油膜破裂实验后立即使用Lecia DVM6三维体视显微镜记录光学图像,获取RCE的腐蚀表面特征信息。通过Phenom XL型扫描电镜(SEM)和自带的能谱分析(EDS)对RCE表面形貌和成分进行分析。
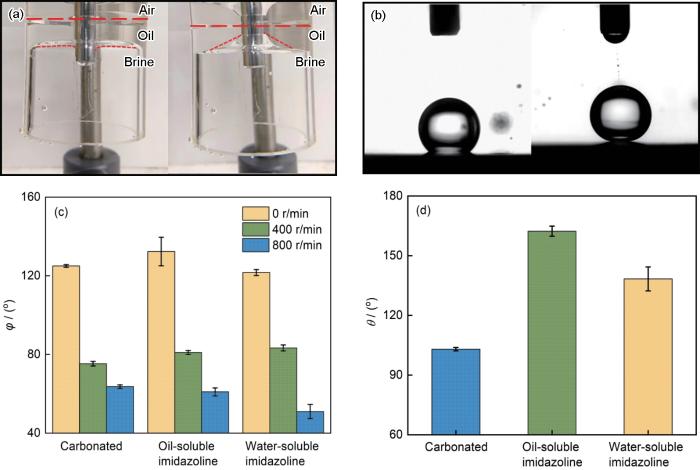
在“交替润湿池”中观察在动态条件下观察油水界面的几何形状,通过摄像机拍摄油水界面照片来计算动态接触角(φ)。参照标准ISO/TS 14778:2021,使用接触角测量仪记录浸油的碳钢表面上盐水滴(3 μL盐水)的光学图像并计算静态接触角(θ)。
利用本课题组提出的弱化信号主导检测法来识别油水界面的Raman光谱信号[20]激光检测点首先放置在距宏观油水界面左侧30 μm处,每步扫描5 μm左右的运动路径。实验中遵照GBT33252-2016,共聚焦显微Raman光谱仪(Horiba SAS-HR Evolution)的参数设置为:激光波长532 nm,激光强度5%,放大倍数50倍。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 两类咪唑啉缓蚀剂的结构表征
图1
图1
油溶性和水溶性咪唑啉的红外光谱图
Fig.1
Infrared spectra of oil-soluble and water-soluble imidazoline inhibitors
2.2 缓蚀剂对油膜破裂过程的影响
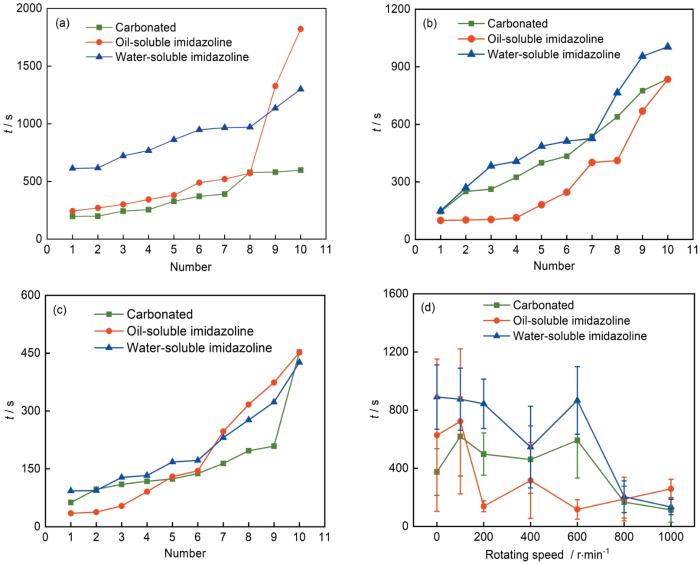
图2为添加或不添加两类缓蚀剂对油膜破裂时间(tb)的影响规律。在静态或缓慢流动下,与初始CO2饱和溶液体系相比,添加油溶性咪唑啉提高了油膜的耐久性。而提高转速时tb值急剧减小,说明高流速下该缓蚀剂无法抑制油膜破损。对于水溶性咪唑啉,可以看出所有转速下均可有效延长油膜破裂时间。随转速增加(800和1000 r/min),水溶性咪唑啉对油膜的延时效果降低,说明此时流速起决定性作用,而溶液化学和油水界面差异已影响不大。
图2
图2
不同缓蚀剂添加体系中覆油RCE表面油膜破裂时间统计分析
Fig.2
Rupture time of oil layer on oil coated RCE in different solution systems under the conditions of 0 (a), 400 r/min (b) and 600 r/min (c), average rupture time at different rotating speeds (d) of oil layer
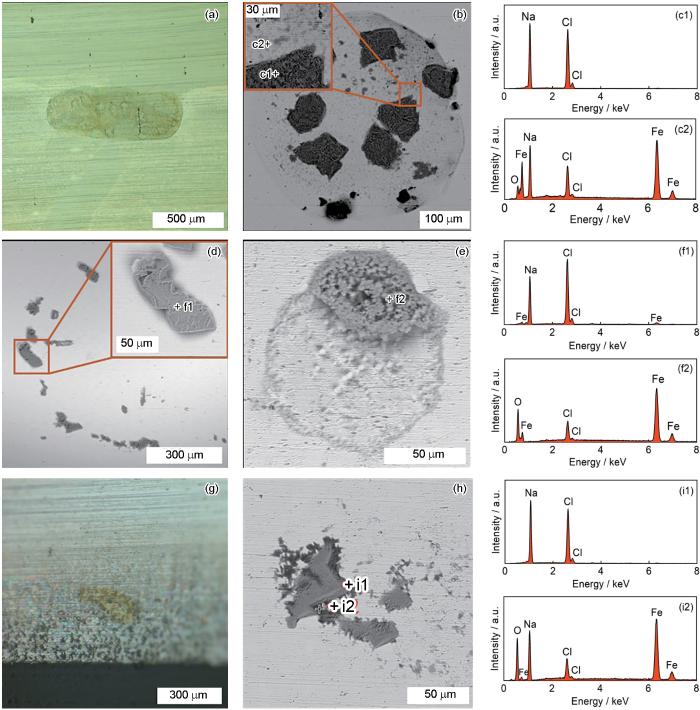
图3为不添加与添加不同类型咪唑啉缓蚀剂时油膜破裂后RCE的腐蚀相貌。当电流达到50 μA时马上取出RCE,只有强“钉扎”的水滴会留在表面上,弱附着或漂浮的水滴则会滑脱。可以发现附着在RCE表面的水滴的几何形状多种多样,高转速时水滴会朝着与流动相反方向被拉长(图3a)。EDS结果表明腐蚀点主要有NaCl和一些分散的Fe2O3、碳酸铁等(图3b~c)。不添加缓蚀剂与添加油溶性咪唑啉的腐蚀形貌区别不大,因为油溶性咪唑啉对“钉扎”稳定后的水滴影响不大(图d~f)。图3g~h为添加水溶性咪唑啉时RCE表面腐蚀形貌。该条件下油膜破裂的区域多是集中在RCE电极与树脂相接的底部区域(图3g)。这是因为再浮力作用下RCE表面油膜下半部分优先减薄所致。另外,有些情况下发现表面某一区域有许多NaCl晶粒和范围<5 μm的腐蚀点。这可能是水溶性咪唑啉分子的极性基团吸附在RCE表面,同时其疏水基团阻碍了水滴向金属表面扩散,致使水滴铺展过程中被水溶性咪唑啉形成的吸附膜隔离而形成。
图3
图3
油膜破裂后RCE的局部腐蚀形态
Fig.3
Localized corrosion morphologies of RCE after rupture of the oil layers in the solutions without (a-c) and with oil-soluble (d-f) and water-soluble (g-i) inhibitors
2.3 油水交替环境中的缓蚀效果评价
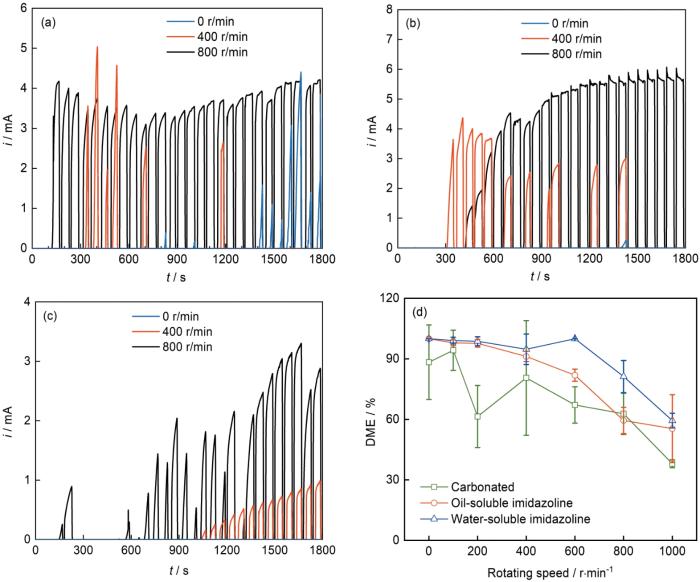
为了分析缓蚀剂添加对油膜动态修复的影响,开展了油水交替润湿实验。在不添加缓蚀剂的饱和CO2溶液系统中,油水交替(油润湿10 s、水润湿50 s)腐蚀的恒电位极化电流响应如图4a所示。当RCE浸没在油相时电流为零,浸入水相后,仍然保持零电流直至油膜破裂;随后电流快速上升,当再次进入油相将恢复至零;在后续油水交替中,局部油膜破损的RCE再次浸入水相时,电流在短时间内上升,循环往复,趋于稳定。另外,有些情况下破裂油膜经过一个或几个循环后会再次恢复完整性,此时浸入水相的RCE没有电流响应,即电化学腐蚀停止,我们将这种现象称为油膜的自修复作用。
图4
图4
不同转速下RCE分别在不含缓蚀剂以及含油溶性和水溶性咪唑啉的碳酸化溶液体系中交替循环润湿30周期的恒电位极化电流-时间曲线,以及3种CO2饱和溶液体系中经过油水交替循环测试得出的缓蚀率(DME)
Fig.4
Potentiostatic polarization curves of RCE after dry-wet alternative exposure for 30 cycles at different rotating speeds in the carbonated solutions without (a) and with oil-soluble (b) and water-soluble (c) inhibitors, and correspondingly measured dissolution mitigation efficiency (DME) (d)
式中,η表示缓蚀率,t0表示油水交替润湿开始的时间,t1表示结束时间,I(t)表示油水交替润湿过程中阳极溶解电流函数,I0(t)表示RCE在水溶液中利用脉冲电压形成的阳极溶解电流函数。越大的DME值意味着RCE的电流响应次数越少,电流峰值越低。
在未添加缓蚀剂体系中,RCE静止时油水交替作用的缓蚀效率约为87%,明显高于盐水溶液中的缓蚀率(~74%,50ppm)[14],在100 r/min时DME达到最高值94.2%,表明低流动条件下油膜具有更好的修复能力;1000 r/min时DME仅有38.0%,RCE表面油膜短时间大面积破坏。
添加油溶性咪唑啉的体系中,在0~400 r/min转速下表现出较高的DME,此时RCE表面油膜的自修复作用明显增强。虽然油膜在较短时间会出现破裂情况,但是通过自我修复作用会再次保持完整性,隔断电解液通道,电流响应时间较短。在800和1000 r/min湍流状态时,DME分别为59.5%和55.4%,油膜已经无法完成自我修复。
添加水溶性咪唑啉的体系中,0~600 r/min时RCE的DME表现优异,处于94.7%~100%之间。与添加油溶性咪唑啉不同,添加水溶性咪唑啉对油膜自修复作用的影响不大。缓蚀率更高的原因有两个:首先是油膜的耐久性好,所以静态和200 r/min (图4c)情形下30圈循环实验后油膜一般不会破裂;其次,该条件下电流增长减缓,电流峰值降低,可能是由于对油膜破裂后水滴的铺展过程的抑制。
2.4 动态与静态润湿行为
图5
图5
动态接触角测量示意图与统计结果及静态油包水接触角测试图与统计结果
Fig.5
Measurement schemes (a, b) and statistical results (c, d) of dynamic contact angle (a, c) and water-in-oil static contact angle (b, d)
2.5 缓蚀效果差异的微观解释
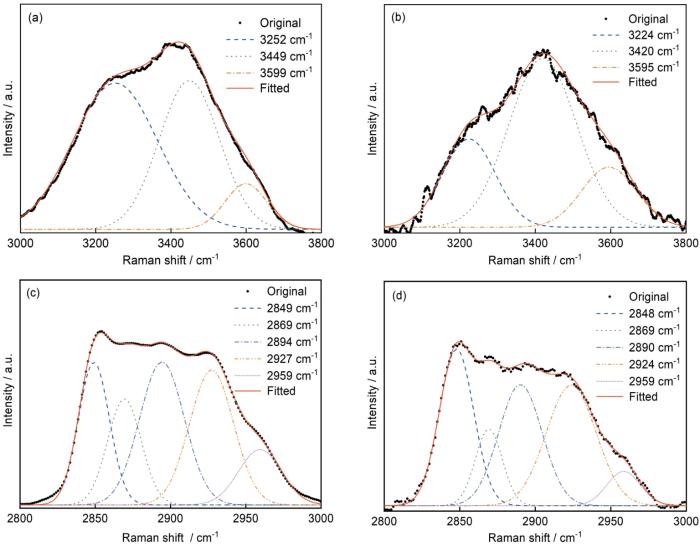
借助显微Raman技术探究缓蚀剂添加对油水界面行为的影响。油相(2800~3000 cm-1)和盐水相(3000~3800 cm-1)子峰对应的官能团和振动模式如表1所示。以不添加缓蚀剂的溶液体系为参照,分析两种缓蚀剂的添加对CO2饱和溶液体系的油水界面影响进行分析。
表1 100#矿物油和0.1 mol/L NaCl 溶液的Raman光谱信息
Table 1
| Sample | Raman shift / cm-1 | Molecular formula | Functional group | Vibration type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100# mineral oil | 2850 | —CH2 | C—H | vsym.a | [25,26] |
| 2869 | —CH3 | C—H | vsym.a | [25] | |
| 2890 | —CH | C—H | vsym.a | [27] | |
| 2928 | —CH2 | C—H | vsym.a | [27] | |
| 2959 | —CH3 | C—H | vasym.b | [27] | |
| 0.1 mol/L NaCl solution | 3255 (peak1) | H2O | O—H | vasym.b | [28] |
| 3452 (peak2) | H2O | O—H | vc | [28] | |
| 3603 (peak3) | H2O | O—H | vc | [28] |
图6
图6
含有水溶性咪唑啉的碳酸化系统中主相和油水界面的Raman光谱分峰
Fig.6
Bulk (a, c) and interfacial (b, d) Raman peaks of water (a, b) and oil (c, d)
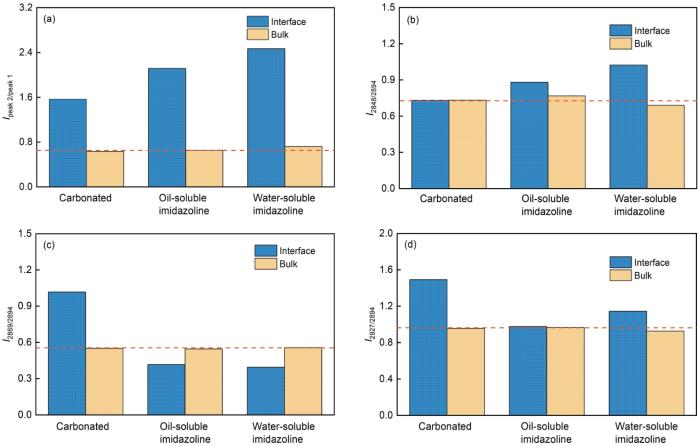
图7
图7
不同条件下水和油Raman子峰的相对面积比(I)
Fig.7
Relative areal ratios of Raman sub-peaks of water and oil under different conditions: (a) water peak, (b) oil peak 2848 cm-1, (c) oil peak 2869 cm-1, (d) oil peak 2927 cm-1
根据拟合的水相子峰计算出的相对面积强度比(I)如图7a所示,3种条件下盐水主相水分子的O-H拉伸峰的强度比I(peak2/peak1)值相近。两种缓蚀剂在油水界面的影响类似,不加缓蚀剂时I(peak2/peak1)是1.57,添加油溶性和水溶性咪唑啉时I(peak2/peak1)分别为2.12和2.47。这两种缓蚀剂都能在界面抵消CO2对油水界面稳定性的影响,即水溶性咪唑啉可以有效减弱CO2溶于水中产生的极性物质在油水界面的聚集吸附,抑制水滴进入油相,在静态或低速时油膜破裂时间延长。图7b~d为3种条件下油子峰与2894 cm-1的面积强度比I。缓蚀剂添加对油主相的I值基本没有影响,但是均能不同程度改变界面处油子峰的强度比。综合两种缓蚀剂在油水界面的影响,油溶性咪唑啉的作用低于水溶性咪唑啉,这也是二者油膜耐久性和可靠性有所差别的原因。
结合前文所述,我们认为油溶性咪唑啉分子主要通过增强RCE浸入油相时油膜的自修复作用来降低腐蚀程度,受水滴铺展过程的影响较弱。水溶性咪唑啉主要通过改变RCE表面油膜在水中的稳定性,即可以明显抑制水滴的形成和长大,并阻止其在金属表面铺展,最终减缓RCE表面的腐蚀程度。
3 结论
为了探明缓蚀剂在含CO2多相流环境中对20#碳钢管道的缓蚀效果及其作用机理,选择油溶性和水溶性咪唑啉对附着在碳钢表面的油膜的耐久性、可靠性和自修复作用进行分析。实验表明,不同流速下水溶性咪唑啉的缓蚀效果均比油溶性咪唑啉更好,静态和层流状态时二者差距较小。利用显微Raman分析方法可见两种缓蚀剂在静态和低速时都能有效减弱CO2在油水界面的作用,且水溶性咪唑啉的影响更大。油水交替润湿时二者缓蚀机制不同:油溶性咪唑啉分子主要通过增强油相一侧的自修复作用来提高碳钢表面的缓蚀效果;水溶性咪唑啉分子则是影响水相一侧水滴进入油膜的传播过程来降低表面水湿润的程度,即抑制水滴的形成和长大,减慢水滴的铺展速度,从而有效减缓两相流中碳钢管道的腐蚀。
参考文献
Corrosion control in CO2 enhanced oil recovery from a perspective of multiphase fluids
[J].
Research progress on application of carbon dioxide in energy development
[J].
二氧化碳在能源开发应用中的研究进展
[J].
CCUS and its application in Shengli Oilfield
[J].
胜利油田CCUS技术及应用
[J].
Suggesting to conduct large-scale CCUS demonstration and industrial cluster construction
[J].
中国二氧化碳捕集利用与封存(CCUS)年度报告(2021)发布 建议开展大规模CCUS示范与产业化集群建设
[J].
Current situation of carbon dioxide recovery and utilization in China
[J].
我国二氧化碳回收和利用现状
[J].
Corrosion behavior of X65 pipeline steel at oil-water interface region in hyperbaric CO2 environment
[J].
X65管线钢在油水两相界面处的CO2腐蚀行为研究
[J].利用失重法、电化学极化法、电化学阻抗谱及腐蚀形貌观察和腐蚀产物物相分析,研究了油水分层介质中X65管线钢在油水两相界面处的腐蚀行为及不同缓蚀剂在油水界面处的作用效果。结果表明,在CO<sub>2</sub>分压为0.9 MPa,温度为60 ℃,静止状态下的油水分层介质中,X65钢在油相区几乎不发生腐蚀,在油水两相界面处发生局部腐蚀,在水相区发生严重腐蚀。添加水溶性缓蚀剂十七烯基胺乙基咪唑啉季铵盐使得X65钢在该工况下的腐蚀速率降低,添加油溶性缓蚀剂癸硫醇反而使得X65钢在油水两相界面处的局部腐蚀加重,甚至出现了腐蚀沟槽。
Effect of pH on electrochemical corrosion and stress corrosion behavior of X100 pipeline steel in CO2-3/HCO-3 solutions
[J].
pH值对X100管线钢在CO2-3/HCO-3溶液中的电化学与应力腐蚀行为的影响
[J].通过动电位极化曲线、电化学阻抗图谱、Mott-Schottky曲线和慢应变速率拉伸实验研究了pH值对X100管线钢在CO<sub>3</sub><sup>2-</sup>/HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>溶液中的电化学与应力腐蚀行为的影响。结果表明,随pH值升高,X100管线钢表面膜厚度与致密性提高,点蚀电位提高;高pH-SCC敏感性降低。
Corrosion behavior of hot-dip aluminum coating in “High temperature-salt deposited-CO2/O2” multi-degree coupling environment
[J].
“高温-结盐-CO2/O2”多因素耦合环境下热浸铝镀层腐蚀行为研究
[J].通过微观形貌观察、极化曲线测试、240 ℃-结盐-CO<sub>2</sub>/O<sub>2</sub>多因素耦合环境下的模拟实验,明确了热浸铝镀层在油田重沸器管束中的适用性。热浸铝试样主要由纯Al层和舌状Fe<sub>2</sub>Al<sub>5</sub>合金层组成,厚度在150~200 μm。模拟油田水中的极化曲线对比结果表明,在30 ℃时,热浸铝试样相比20#钢腐蚀电流密度降低约300倍,具有很好的耐蚀性能。采用高温高压反应釜模拟现场管束服役工况,高温高压模拟工况结果表明,240 ℃-结盐-CO<sub>2</sub>/O<sub>2</sub>多因素耦合环境下,20#钢的均匀腐蚀速率为0.68±0.04 mm/a,点蚀深度达到70.5 μm,表面的腐蚀产物主要为Fe<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub>和Fe<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>,产物膜内存在大量裂纹等缺陷;而热浸铝镀层腐蚀速率为0.08±0.02 mm/a,腐蚀主要出现在纯Al层,对应的腐蚀产物为Al(OH)<sub>3</sub>。综合结果表明,热浸铝镀层在240 ℃-结盐-CO<sub>2</sub>/O<sub>2</sub>多因素耦合环境下呈现良好的防腐性能。
The EIS analysis of cathodic reactions during CO2 corrosion of N80 steel
[J].
N80油套管钢CO2腐蚀阴极过程电化学阻抗谱分析
[J].利用电化学阻抗技术研究了N80技术研究了N80钢在不是介质条件下CO2腐蚀过程中可能存在的阴极反应及其反应速度.结果表明,N80钢在CO2腐蚀环境下存在H+和H2O以及H2CO3,HCO3-的还原反应,但在不同条件下各个还原反应的速度并不相同.在酸性的饱和CO2溶液中,H+的还原控制着阴极反应速度,HCO3-和H2CO3的还非法所得反应速度较小;在中性的饱和CO2溶液中,阴极过程以HCO3-和H2CO3的还原为主,H+的还原反应速度比较微弱;在碱性的NaHCO3溶液通入CO2后, HCO3-的还原控制着阴极反应速度.在以上条件下,H2O的还原速度比较微弱,还不会对阴极交换电流产生影响.
Corrosion behaviour of X65 carbon steel under the intermittent oil/water wetting: A synergic effect of flow velocity and alternate immersion period
[J].
Technical Note: Electrochemical corrosion measurements in crude oil
[J].
Corrosion of multiphase flow pipelines: the impact of crude oil
[J].The control of multiphase flow corrosion during oil production is a challenging task. In this review, the impact of crude oil on pipeline corrosion is broadly discussed, with the notion to reduce corrosion risks of pipelines in aggressive field conditions. First, the properties, emulsion stability, and multiphase flow patterns of crude oil fluids are concisely summarized and correlated to the corrosion behavior. Second, for proper evaluation of the corrosiveness of the oil-brine mixtures, related corrosion test methods and experimental techniques are critically evaluated. Third, the effects of crude oil on corrosion inhibition are conceivably attributed to four aspects, i.e. the entrainment of water, the wetting by crude oil, the partitioning effect, and the modification of the corrosion product layers. Fourth, the presence of crude oil may consume more corrosion inhibitors; however, the inhibitors can produce additional benefits on corrosion mitigation in oil-brine mixed conditions, such as altering the surface wettability to hydrophobic and enhancing the entrainment of water. Finally, some ideas to reduce pipeline corrosion are proposed and future research viewpoints are discussed.
Effect of multiphase flow on corrosion of C-steel in presence of inhibitor: a surface morphological and chemical study
[J].
Fast evaluation of corrosion inhibitors used in oil/water mixed fluids
[A].
The effects of N-pendants and electron-rich amidine motifs in 2-(p-alkoxyphenyl)-2-imidazolines on mild steel corrosion in CO2-saturated 0.5 M NaCl
[J].
Synthesis and corrosion inhibition behavior of imidazoline derivatives based on vegetable oil
[J].
Synthesis of tall oil-based hydroxyethyl imidazoline and study on its corrosion inhibition properties
[J].
妥尔油基羟乙基咪唑啉的合成及缓蚀性能研究
[J].
Alteration of wettability of corroding carbon steel surface by carbon dioxide corrosion inhibitors—effect on carbon dioxide corrosion rate and contact angle
[J].
Electrochemical characterization of an oil/water alternately wetted rotating cylinder electrode
[J].To characterize the corrosion at oil/water interfaces, a vertically adjustable rotating cylinder electrode (VA-RCE) was developed based on the concept of an “alternate wetting cell,” in which the electrochemical current reflecting the wet state of the RCE surface can be continuously monitored. Under a sinusoidal moving mode, the current waveform varied with the rotation rate and the longitudinal displacement speed or amplitude of the VA-RCE, implying that the dynamic wetting behavior of the VA-RCE surface in the oil/water interface region was influenced by the flow conditions; the replacement of oil phase by water phase became easier with increasing flow rate and alternating frequency of change between water wet and oil wet. The results also indicated that the wettability of the VA-RCE surface could be modified by the formation of corrosion products. All of the results suggested that the VA-RCE could be used to quantitatively characterize the dynamic water/oil wetting state and the corrosion at an oil/water interface in a multiphase flow.
Molecular origin of the CO2-enhanced water wetting during corrosion of an oil layer-attached steel surface in water flows
[J].To understand the role of CO2 in multiphase flow corrosion, the durability of an oil layer attached to a steel surface against fluid flows was systematically evaluated. It confirms that CO2 can destabilize the protective oil layer and initiate electrochemical corrosion through the oil layer, showing a solution chemistry governed flow dependency. The CO2-induced oil layer rupture was attributed to the water droplet actions at the oil/water interface and the steel surface, where the generation of microdroplets was facilitated by the interactions between the dissolved CO2 and the oil molecules. It gives new insights into the replacement of oil layer by water in CO2-containing multiphase fluids, which benefits many application fields, such as corrosion and lubrication in oil-water mixed environments.
Synthesis of imidazoline inhibitor from vegetable oil and analysis of its inhibition performance
[D].
植物油制备咪唑啉类缓蚀剂及其缓蚀性能的分析研究
[D].
Synthesis of oleic acid-imidazoline corrosion inhibitor and the effect of self-assembly method on its performance
[D].
油酸基咪唑啉的合成及自组装方式对其缓蚀性能的影响
[D].
Study of the inhibition mechanism and synergistic effect of corrosion inhibitors in sweet system
[D].
二氧化碳腐蚀体系缓蚀剂的缓蚀机理及缓蚀协同效应研究
[D].
Corrosion mitigation behavior of an alternately wetted steel electrode in oil/water media
[J].
Authentication of adulterated edible oil using coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering spectroscopy
[J].
Detection of changes in the environment of hydrocarbon chains by Raman spectroscopy and its application to lipid-protein systems
[J].
Elucidation of protein-lipid interactions in a lysozyme-corn oil system by Fourier transform Raman spectroscopy
[J].