在底漆涂布之前,往往需要对金属基材进行表面处理,以实现涂层与基材间的良好结合。据统计,近一半的涂层失效都是由于基材表面处理不当引起的,表面处理的好坏直接关系到涂层与基材间的附着力,也在一定程度上决定了涂层性能的优劣[20~24]。涂料涂覆前,常用的金属表面处理方法有手动处理 (St) 和喷砂处理 (Sa),手动处理分为St2和St3两个等级,喷砂处理分为Sa1、Sa2、Sa2.5和Sa3 4个等级,数字越大代表表面处理等级越高[25]。有学者[26]对不同表面处理下环氧防腐涂料的性能进行了研究,发现随着表面处理等级的降低,涂层的耐腐蚀性能不断降低,其中经过Sa2.5或St3等级表面处理得到的涂层电阻值达到108 Ω·cm2以上,耐蚀性能优异。通常在施工时,需要将金属基材表面处理至Sa2.5等级以上,使涂层与基材产生良好的粘附效果[27],但是表面处理等级越高,意味着涂装前的操作工序越复杂繁琐,涂装成本也随之升高。目前国内低表面处理涂料发展较为缓慢,相比于国外的成熟产品,市场认可度较低,特别是一些功能较单一的低表面处理涂料,无法满足多种复杂环境下的防腐应用,产品局限性较大。目前国内市场上同时满足低表面处理和优异防腐性能的成熟涂料产品较少,但随着我国海洋强国战略等政策的布局和实施,对低表面处理防腐涂料提出了更高的要求,低表面处理防腐涂料的研制和应用研究也逐渐成为防腐涂料发展的重点和热点之一[28~30]。
针对目前国内低表面处理涂料效果较为单一,无法同时兼顾多种复杂环境下的防腐要求的问题,本文研制出一种低表面处理环氧防腐底漆,为厚浆型高固体份涂料,固含高达80%,可实现钢材的带锈涂装,同时具备优异的底材附着力,相比于其他溶剂型低表面处理底漆对环境污染小;同时厚浆型涂料一次施工便可获得较高的膜厚,施工方便、成本低。此外,本工作研制的低表面处理底漆附着力较高,且耐腐蚀性能十分优异,可集环保、低成本、耐腐蚀等效果于一体,综合性能较优异。
1 实验方法
实验所用原材料分为A组分和B组分,其中A组分包括双酚A型环氧树脂 (江苏三木化工股份有限公司),二甲苯 (济南骏腾化工有限公司),正丁醇 (上海凯茵化工有限公司),云母氧化铁灰(河南颍川新材料股份有限公司),磷酸锌 (济南裕才化工有限公司),钛白粉 (杜邦中国集团有限公司),分散剂 (德国毕克化学有限公司),消泡剂 (德国毕克化学有限公司);B组分包括聚酰胺固化剂 (纳尔美新材料集团有限公司)。
在23 ℃、50%湿度条件下,分别将A组分和B组分所用材料按照配方进行配置,使用SFJ-400高速搅拌分散器搅拌使其分散均匀,然后将分散好的A组分和B组分进行混合,在1000 r/min速率下高速搅拌30 min以上使其充分反应,将分散好的涂料刷涂在尺寸为150 mm×75 mm×3 mm的碳钢板上 (钢板喷砂处理至Sa2等级),测试其干燥时间,待涂层完全干燥后,对其膜厚、附着力、耐室外暴晒、耐酸碱及中性盐雾性能、电化学性能进行了测试。
按照GB/T 1764-1979,在干燥后的样板上选取多个点,采用磁性测厚仪法对涂层厚度进行测试。按照GB/T 1728-2020,对漆膜的表面干燥时间和实际干燥时间进行测定。
按GB/T5210拉拔法,使用Positest AT-M 20 mm拉拔仪和铝质拉拔柱,哥俩好AB胶 (双组分丙烯酸胶) 胶黏,粘胶18 h后测附着力。
将干燥好的样板放置于露天阳台,5 a后取回观察其腐蚀、开裂等情况。耐酸碱性测试则是将干燥好的样板分别放置于10%H2SO4溶液和10%NaOH溶液 (质量分数) 中,浸泡30 d后取出观察其腐蚀情况。按照GB10125-2012,利用F-90型盐雾耐腐蚀试验机对涂层试样进行中性盐雾试验测试,溶液浓度为50 g/L NaCl溶液,pH值为6.5~7.2,实验温度为(35±2) ℃,24 h连续喷雾,实验周期为2000 h。
采用三电极体系在CS310X型电化学工作站上进行电化学实验,环氧密封好的涂层试样作为工作电极 (工作面积为1 cm×1 cm),饱和甘汞电极作为参比电极,铂铌棒 (ϕ3 mm×80 mm) 作为辅助电极,电解质溶液为3.5% (质量分数) NaCl溶液。电化学阻抗谱 (EIS) 的测试频率范围为105~10-2 Hz,交流电 (AC) 幅度为10 mV,测试了其海水浸泡2400 h的耐腐蚀性能,对其电化学阻抗谱图进行分析,采用等效电路解析阻抗谱参数随浸泡时间的变化。
采用KH-8700数字式三维视频显微镜对涂层经海水浸泡前后不同倍率的表面形貌进行了表征,同时采用Nicolet IS10型Fourier变换红外光谱 (FTIR) 仪对涂层固化前后的化学成分进行了分析。
2 结果与讨论
在喷砂处理Sa2等级的碳钢板上制备出了双组份环氧防腐涂层 (C-1),成膜物质为双酚A型环氧树脂,涂层厚度处于150~180 μm之间,其在室温下的表干时间和实干时间分别为0.5和4 h,相比与常用的环氧底漆,C-1环氧底漆可有效提升施工效率,大大缩短第二道漆的刷涂时间。
图1
图1
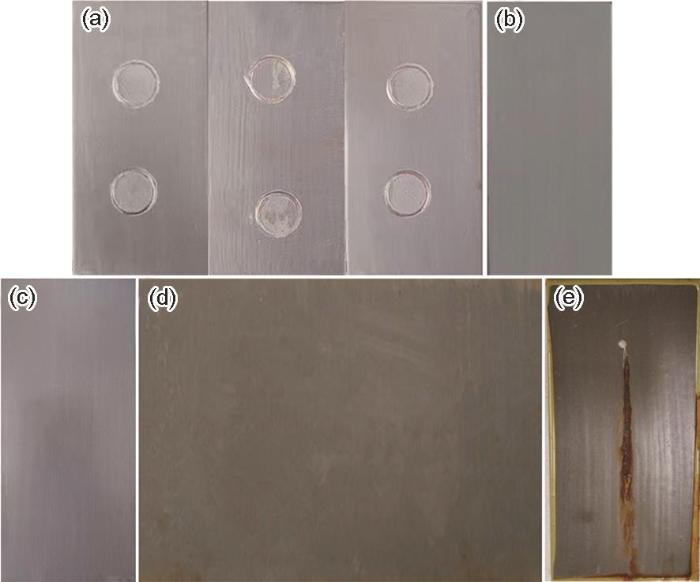
不同环境条件下试样涂层宏观形貌图
Fig.1
Macro topography of the coating: (a) adhesion failure diagram, (b) immersed in 10%H2SO4 for 30 d, (c) immersed in 10%NaOH for 30 d, (d) after 5 a of outdoor exposure,(e) after 500 h salt spray test
用于不同环境下的钢材所需涂层性能的侧重点不同,有些钢材常暴露于酸或碱介质下,有些则长期暴露于户外风吹日晒,因此对涂层的耐酸、碱、户外暴晒、盐雾性能提出了较高要求。图1b和c分别为在10%H2SO4溶液和10%NaOH溶液中浸泡30 d后的样板的宏观形貌图,从图中可以看出,涂层经过30 d的强酸介质和强碱介质的浸泡,表面并无气泡、开裂、锈蚀等现象,表明涂层的耐酸、碱介质腐蚀性能优异,图1d为室外暴晒5 a的涂层样板宏观形貌图,可以看出,涂层表面基本没有明显的开裂、脱落、锈蚀等现象,可满足露天环境下5 a以上长期使用的要求。图1e为500 h中性盐雾试验后样板的形貌图,可以看出经过500 h中性盐雾试验后,涂层划痕处发生腐蚀,生成的腐蚀产物覆盖于划痕之上,阻止了腐蚀的继续发生,但并未出现向周边大面积蔓延的迹象,说明涂层耐中性盐雾性能良好。
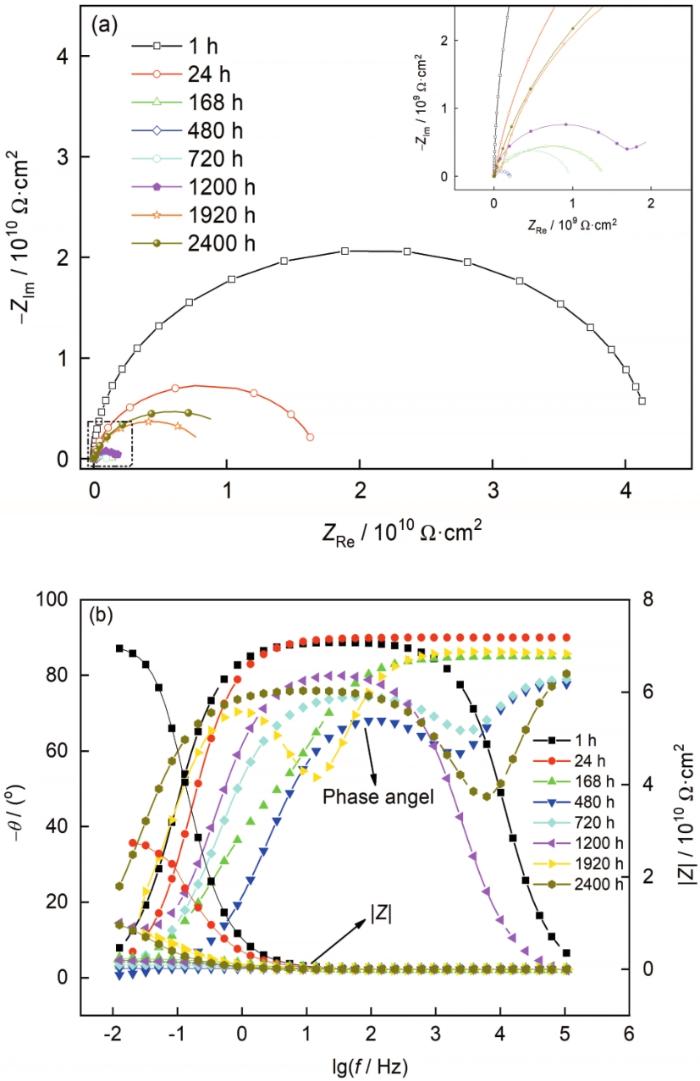
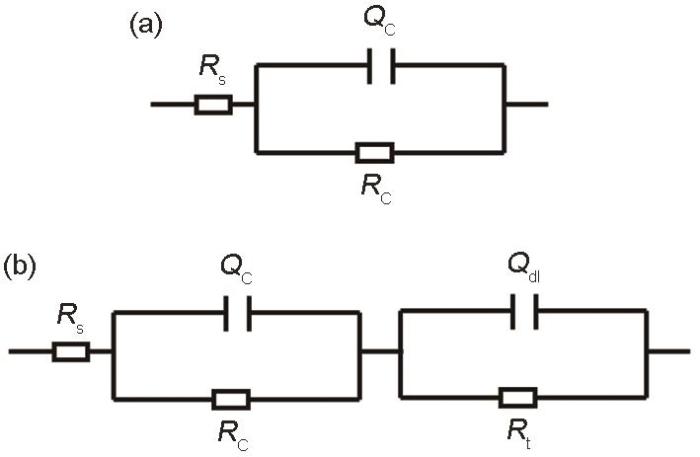
EIS可以实现较宽频率下涂层体系的测量,得到不同频率段涂层的电容、电阻,能够很好地反映涂层腐蚀的动力学过程[33,34]。通常当涂层的电阻值达到108 Ω·cm2以上时,表明涂层的耐蚀性能十分优异,低于106 Ω·cm2时,表明涂层的屏蔽作用已经失效[35,36]。采用EIS方法对涂层在3.5%NaCl溶液中的电化学腐蚀性能进行了表征,得到了涂层在海水浸泡2400 h下电化学阻抗的Nyquist图和Bode图,如图2所示。由图2a可见,浸泡1 h,涂层的电阻为4×1010 Ω·cm2,展现出优异的海水屏蔽性能,随着浸泡时间的延长,涂层的电阻有所降低,浸泡480 h时,涂层阻抗值最低,降至2×108 Ω·cm2,这是因为随着浸泡时间的延长,腐蚀介质不断向涂层内部渗入,到达基材表面,此时电解质溶液向涂层的渗透已经达到饱和,形成了腐蚀微电池,导致了涂层电阻的降低,但此时涂层依然具备较为优异的耐蚀性能。结合图2b可见,在浸泡前期 (480 h前),相位角在较宽频率范围内处于90°附近,同时对应于低频阶段的涂层电阻值较大,阻值在中低频范围内随频率的变化表现为一条斜线,此时涂层电容值很小,电阻值很大,起到了一个隔绝层的作用[37,38]。1~480 h海水浸泡阶段,涂层所表现出来的腐蚀特征符合图3a所示的等效电路模型,其中Rs表示溶液电阻,Qc和Rc分别表示涂层电容和电阻。
图2
图2
涂层经2400 h海水浸泡的EIS图
Fig.2
Nyquist (a) and Bode (b) diagrams of the coating soaked in seawater for 2400 h
图3
图3
涂层浸泡初期及中后期等效电路模型图
Fig.3
Equivalent circuit model at the initial stage (a), and the middle and late stage (b) of coating immersion
浸泡480 h之后,随着浸泡时间的延长,涂层电阻开始逐渐增大,从图2a的Bode图可以看出,浸泡480 h之后表现出两个时间常数,此时涂层与基材界面处的腐蚀微电池已经达到平衡状态。到2400 h时涂层电阻基本稳定在1010 Ω·cm2,表现出优异的耐海水腐蚀性能。此阶段涂层所表现出来的腐蚀特征符合图3b所示的等效电路模型。这段时间涂层阻值的增大与涂层中的磷酸锌颜料的反应密切相关,浸泡之初,涂层中渗入的溶液较少,磷酸锌溶解度较低,浸泡480 h之后,涂层中已经渗入了足够的溶液,使得磷酸锌大量溶解,磷酸根离子与基材发生化学反应,在基材表面形成了一层保护膜,阻止了腐蚀的继续发生,使得涂层电化学阻值的进一步增大。此外,涂层浸泡中后期电阻值的增大可能与腐蚀产物的堆积也有一定的关系[39]。
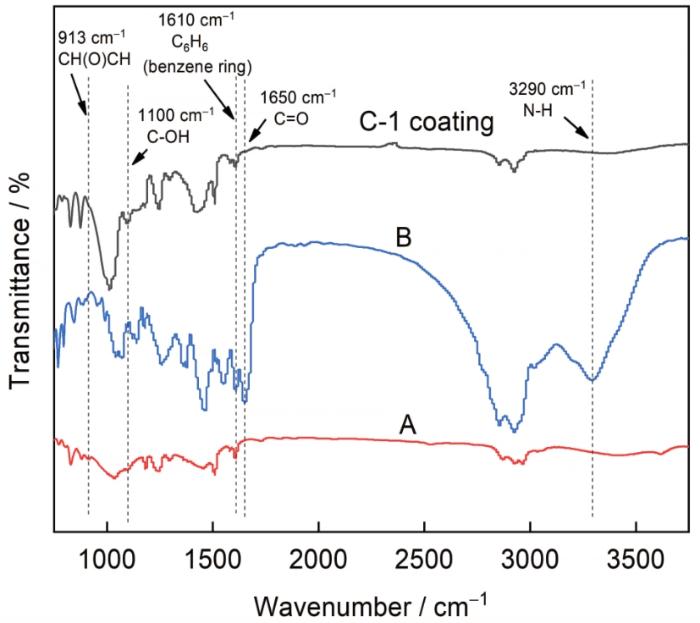
C-1防腐底漆之所以能够实现低表面处理,同时具备优异的耐海水腐蚀性能,这与其特殊的成分配比和特殊的防腐机理密不可分。A、B组分通过固化反应形成致密的涂层是实现防腐的基础,A组分中的双酚A型环氧树脂和B组分的聚酰胺反应是固化成膜的关键,固化反应机理可通过图4的FTIR图谱反映,对比A、B组分和涂层的红外图谱可以看出,A、B组分固化反应后,A组分913 cm-1处CH(O)CH (环氧基) 的特征吸收峰消失不见,但1610 cm-1处C6H6 (苯环) 的特征吸收峰并未出现明显变化,B组分聚酰胺1650 cm-1处C=O (酰基) 的特征吸收峰和3290 cm-1处N-H (氨基) 的特征吸收峰固化后消失不见,取而代之的是涂层在1100 cm-1处新生成的C-OH(羟基) 的特征吸收峰。FTIR图谱中官能团的变化说明A、B组分之间的固化反应是A组分中的CH(O)CH(环氧基) 和B组分中的C=O(酰基)、N-H(氨基) 反应,生成C-OH(羟基) 的过程,环氧树脂中的C6H6(苯环) 并未参与反应。
图4
图4
C-1涂层及A、B组分的FTIR图谱
Fig.4
FTIR spectra of C-1 coating and components A and B
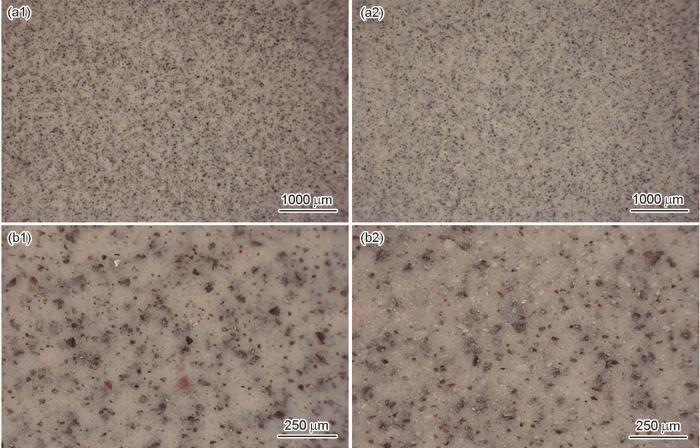
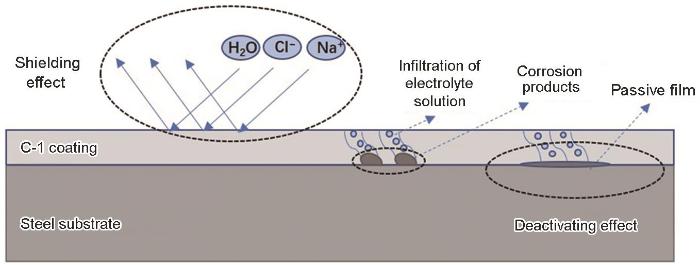
环氧树脂与聚酰胺固化交联生成的致密涂层是实现防腐的关键一步,结合图5中涂层的三维显微镜图片可以进一步看出涂层表面腐蚀前后的状态,对比海水浸泡区和未浸泡区可以发现,两者在表面形貌上并无明显差别,均表现为较为致密的屏蔽层,海水浸泡区涂层表面并无明显孔洞、起泡等现象。根据电化学阻抗分析结果,低表面处理环氧防腐涂层在海水中的具体腐蚀机理如图6所示。聚酰胺与环氧树脂固化交联形成的致密涂层,在海水浸泡前期将溶液中的H2O分子、Cl-和Na+隔离在外,起到了很好的屏蔽作用。浸泡中后期,随着电解质溶液到达基材表面,磷酸锌等颜填料溶解速度加快,与基材表面的金属离子反应,形成一层致密的钝化膜,对基材起到了很好的保护作用。涂层在后期能够具备优异的耐海水腐蚀性能主要得益于涂层中的磷酸锌成分,相关文献表明[39],磷酸锌与金属基材生成的腐蚀产物中包括Fe(PO3)2、Zn2Fe(PO4)2·4H2O等多种不溶物,覆盖了腐蚀活性点,显著抑制了金属基材的腐蚀。另外,随着腐蚀的不断进行,磷酸锌与基材金属反应生成的腐蚀产物不断堆积,变厚的腐蚀产物堵塞了涂层中的微观孔隙,阻碍了腐蚀介质的进一步扩散,涂层的耐蚀性能得到了提高。本文中低表面处理指的是允许涂料在钢材表面进行带锈涂装,本工作通过在涂料中加入磷酸锌活性颜料,使磷酸锌水解后产生的磷酸根离子与钢材表面铁锈中的活性成分发生反应,生成稳定的络合物,并将其转化为涂料中的稳定成分,同时钢材表面生成的络合物嵌入涂层内部,还可促进钢材与涂层的界面结合,提高涂层附着力,从而实现较低基材表面处理。
图5
图5
2400 h海水浸泡前后C-1涂层表面形貌
Fig.5
Surface morphology of C-1 coating before (a1, b1) and after (a2, b2) 2400 h seawater immersion
图6
3 结论
(1) 本文制备出一种厚浆型低表面处理环氧防腐底漆 (C-1),固含高达80%,只需将金属基材表面处理至Sa2等级即可涂布使用,可实现钢材的带锈涂装,其漆膜附着力可达10 MPa,实际干燥时间仅需4 h。
(2) C-1涂层耐室外暴晒性能及耐酸、碱、中性盐雾腐蚀性能优异,置于户外露天环境5 a涂层表面几乎无任何脱落、开裂、腐蚀等现象,经过10% NaOH溶液和10% H2SO4溶液中浸泡30 d,涂层样板表面无任何起泡、锈蚀等现象,经过500 h盐雾试验涂层划痕处锈蚀无蔓延。
(3) 通过电化学阻抗技术 (EIS) 测试,表明C-1涂层具备优异的耐海水腐蚀性能,经过2400 h海水浸泡后的涂层电阻值达到1010 Ω·cm2,同时涂层电阻随浸泡时间的延长表现为先减小后增大的趋势,后期电阻的增大与涂层与基材界面处钝化膜的形成和腐蚀产物堆积有关。环氧树脂和聚酰胺固化交联形成的致密涂层对腐蚀介质起到了很好的屏蔽作用,中后期磷酸锌颜料与钢材表面铁锈反应生成的稳定络合物阻止了腐蚀介质的渗入,是其耐腐蚀和实现低表面处理的关键。
参考文献
Novel anticorrosive coatings based on nanocomposites of epoxy, chitosan, and silver
[J].
An overview of the application of graphene-based materials in anticorrosive coatings
[J].
Research progress on application of halloysite nanotubes for modification of smart anti-corrosion coating
[J].
埃洛石纳米管负载改性及其在智能防腐涂层中的应用研究进展
[J].
Research progress on corrosion behavior and key influencing factors for structural materials of waste power plant boiler
[J].
垃圾电站锅炉腐蚀速度及关键影响因素研究进展
[J].针对垃圾电站锅炉受热面日益严重的腐蚀问题,以经典的腐蚀曲线为对象,对垃圾炉四管受热面的腐蚀速率规律做了分析和归纳,并对在全温域内随管道壁温变化的腐蚀机理进行了综述。提炼出腐蚀速度曲线具有双峰、突变、虚实等三个显著特征。根据从低到高的壁温变化,对腐蚀速率按照电化学腐蚀和高温腐蚀两部分分别进行了评述并分段解构,根据不同壁温度区间腐蚀规律和机理进行了系统论述。探讨了烟温对腐蚀速率的影响,最后对腐蚀速率曲线的时效性进行了进一步的探讨。
Worldwide corrosion day and thinking of corrosion prevention & control
[J].
世界腐蚀日及腐蚀防控的思考
[J].
Current situation and prospect of on-line monitoring technology for atmospheric corrosion testing of metallic materials
[J].
大气腐蚀在线监测技术研究现状与展望
[J].综述了大气环境下金属腐蚀和涂层腐蚀在线监测技术。对于金属大气腐蚀,介绍了电阻探针法、电偶腐蚀电池、电化学阻抗谱、电化学噪声法、表面超声波技术、石英晶体微天平技术和射频识别技术等多种在线监测方法的原理及其研究现状;对于大气环境涂层腐蚀,从电化学方法、非电化学方法、不同监测方法相结合等三方面进行了阐述。总结了当前大气腐蚀在线监测亟待解决的问题,并从“互联网+”智慧防腐方向出发,结合腐蚀大数据的发展,对大气腐蚀在线监测技术未来方向进行了展望。
Effect of alternating pressure on electrochemical behavior of solvent-free epoxy coating in simulated ultra-deep sea environment
[J].
交变压力对无溶剂环氧涂层在模拟超深海环境下的电化学行为
[J].通过EIS和LEIS对环氧粉末涂层和无溶剂环氧液体涂层分别在模拟超深海环境中0.1~20和0.1~30 MPa交变压力腐蚀环境下浸泡480 h的失效行为进行了研究,分析了超深海交变压力对涂层耐腐蚀性能的影响,并利用SEM观察了浸泡后涂层/Q345钢界面的表面形貌。研究表明,两种涂层在0.1~30 MPa交变压力作用下涂层的失效过程较为明显,环氧粉末涂层在0.1~30和0.1~20 MPa交变压力浸泡480 h后涂层阻抗值分别下降了2个和1个数量级,无溶剂环氧液体涂层在同样环境下浸泡后阻抗值分别下降了3个和2个数量级,说明了环氧粉末涂层在交变压力条件下对Q345的保护性能更优,阻绝离子渗透能力更强。从LEIS结果分析出在较高交变压力下,涂层微观局部腐蚀扩散速率更快。
The synergetic effect of tannic acid as adhesion promoter in electrodeposition of polypyrrole on copper for corrosion protection
[J].
A comparative study of chloride adsorption ability and corrosion protection effect in epoxy coatings of various layered double hydroxides
[J].The positive influence of chloride adsorption on the enhanced protection effect was always emphasized in the published literature. The concrete contribution of chloride adsorption and physical barrier effect of LDH in coatings still remains unclear at present. This work was aimed at exploring the significance of the chloride adsorption role of LDH in the corrosion protection of epoxy coatings. The synthesized LDH samples were characterized by scanning electronic microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) to show the influence of different parameters on its morphology, structure and composition, respectively. The corrosion-electrochemical behavior was investigated using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and salt spray test. It was found that although CaAl-LDH presented a lower chloride adsorption ability in comparison with other samples; it showed effective corrosion protection due to the higher physical barrier effect of CaAl-LDH with typically hexagonal and plate-like morphology due to good compatibility with the epoxy coatings. The results indicated that the corrosion protection effect of the incorporated LDH was more closely related to its physical barrier role rather than the role of the chloride adsorption, which was misunderstood in the previous publications. This work clarified the contribution comparison of the chloride adsorption and physical barrier of LDH in epoxy coating corrosion protection for the first time.
In-situ growth and excellent corrosion protection properties of molybdenum dioxide/boron nitride heterojunction composites
[J].
Advanced Protective Films Based on Binary ZnO-NiO@polyaniline Nanocomposite for Acidic Chloride Steel Corrosion: An Integrated Study of Theoretical and Practical Investigations
[J].Due to their thermal stability characteristics, polymer/composite materials have typically been employed as corrosion inhibitors in a variety of industries, including the maritime, oil, and engineering sectors. Herein, protective films based on binary ZnO-NiO@polyaniline (ZnNiO@PANE) nanocomposite were intended with a respectable yield. The produced nanocomposite was described using a variety of spectroscopic characterization methods, including dynamic light scattering (DLS), ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) approaches, in addition to other physicochemical methods, including X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), and selected area electron diffraction (SAED). By using open-circuit potentials (OCP) vs. time, electrochemical impedance spectroscopic (EIS), and potentiodynamic polarization (PDP) methods, the inhibitory effects of individual PANE and ZnNiO@PANE on the mild steel alloy corrosion in HCl/NaCl solution were assessed. The ZnNiO@PANE composite performed as mixed-type inhibitors, according to PDP findings. PANE polymer and ZnNiO@PANE composite at an optimal dose of 200 mg/L each produced protective abilities of 84.64% and 97.89%, respectively. The Langmuir isotherm model is used to explain the adsorption of ZnNiO@PANE onto MS alloy. DFT calculations showed that the prepared materials’ efficiency accurately reflects their ability to contribute electrons, whereas Monte Carlo (MC) simulations showed that the suitability and extent of adsorption of the ZnNiO@PANE molecule at the metal interface determine the materials’ corrosion protection process.
Research progress of inorganic silicate zinc-rich anticorrosive coating
[J].
无机硅酸盐富锌防腐涂料的研究进展
[J].
Design and application of hot water immersion testing for anticorrosion coating of deep-water pipeline
[J].
深水管道防腐涂层耐热水浸泡试验设计及应用研究
[J].
Influence of chemical bonding interface of modified basalt/epoxy coating on its corrosion resistance
[J].
改性玄武岩/环氧涂层化学键合界面对涂层防腐性能的影响
[J].利用硅烷偶联剂KH550对玄武岩鳞片表面进行化学改性,制备了改性玄武岩。通过红外光谱、扫描电子显微镜等技术对改性玄武岩鳞片进行表征;采用沉降实验、涂层横截面微观形貌观察分析了改性玄武岩鳞片在环氧树脂中的分散性和相容性;利用附着力测试和电化学阻抗谱技术,研究了改性玄武岩鳞片/环氧树脂复合涂层的附着性能和防腐性能。结果表明:KH550通过化学键合附着在玄武岩鳞片表面上,使玄武岩鳞片与环氧涂层形成化学键合界面,从而提高了玄武岩鳞片与环氧树脂的相容性,增强了涂层的屏蔽性能和附着力,进而提升了涂层的防腐性能。
Waterborne epoxy primer and its preparation method
[J].
水性环氧底漆及其制备方法
[J].
Corrosion behavior of laser-interference structured AA2024 coated with a chromate-containing epoxy primer
[J].In this study, the corrosion behavior of laser-interference treated AA2024-T3 specimens, which are coated with a primer, is presented. The surface of as-received AA2024-T3 specimens were laser-interference structured by splitting the primary beam of a Q-switched Nd:YAG pulsed nanosecond laser into two beams and focusing them to the same spot on the specimen surface. After being stored in plastic cases for up to 70 d, without any additional cleaning, the specimens were spray painted with a chromate-containing epoxy primer, CA7233, compliant to MIL-PRF-23377 Type I Class C2 specification. The corrosion behavior of laser-interference specimens was assessed against that of specimens prepared by chromated conversion coating and sulfuric acid anodizing treatments. After the ASTM B117 corrosion exposure, it was found that the laser processed specimens exhibited only few blisters. On one hand, most specimens prepared at a laser fluence of 1.78 J/cm2, without any additional chemical cleaning, were found to develop one very small blister after only 96 h of exposure. However, the growth of these blisters was not significant even after 1,000 h of salt spray exposure. On the other hand, only a fraction of the specimens prepared at a laser fluence of 1.24 J/cm2 and acetone wiped right after the laser structuring were found to develop several tiny blisters after 790 h and longer exposure. Overall, it was found that the corrosion damage was minimized at a laser rastering speed of 4 mm/s, a condition for which only 33% of specimens developed very minor corrosion damage. The ASTM D1654 creepage ratings, which was used to evaluate the corrosion damage along the scribe lines, were found to be at least nine for all coated panels. These results indicate that the laser-interference technique with the additional acetone wiping has the potential to be further developed as a nonchemical surface preparation technique for chromate-containing epoxy primers coating systems.
Corrosion behavior of PANI nanofiber/modified GO/waterborne epoxy composite coating on stainless steel
[J].
不锈钢表面聚苯胺纳米纤维/改性氧化石墨烯/水性环氧复合涂层的制备与防护性能研究
[J].在氧化石墨烯纳米片 (GO) 改性的基础上,于非盐酸介质中采用原位共聚法合成了聚苯胺纳米纤维/改性氧化石墨烯复合材料 (PANI-F/CTGO),将其作为防腐增效组分引入到水性环氧聚合物乳液 (WEP) 中构建复合涂料。采用电化学方法和盐雾实验研究了涂料在加速腐蚀条件下对不锈钢的腐蚀防护作用,对腐蚀产物结构进行了分析。复合材料中PANI-F与CTGO的化学键接提高了PANI-F/CTGO在环氧乳液中的分散性和相容性。非盐酸介质条件下制备的PANI纳米纤维没有腐蚀介质盐酸的引入,在涂层中能发挥出更好的耐蚀性;PANI-F/CTGO /WEP涂层具有较高的开路电位 (OCP) 值和阻抗模,耐盐雾时间达到720 h,显示了优异的防腐性能,这主要是PANI-F/CTGO的主动钝化与物理阻隔协同作用的结果。
Influence of simulated deep sea pressured-flowing seawater on failure behavior of epoxy glass flake coating
[J].
深海压力-流速耦合环境对环氧玻璃鳞片涂层失效行为的影响
[J].采用吸水率测试EIS、附着力测试SEM、FT-IR等方法,对比研究常压-静态环境 (0.1 MPa-0 m/s)、流体流动环境 (0.1 MPa-4 m/s)、高静水压力环境 (10 MPa-0 m/s) 和压力-流速耦合环境 (10 MPa-4 m/s) 下环氧玻璃鳞片涂层的失效行为和机制。实验结果表明,耦合环境下,填料与涂层基体间的界面结合被显著削弱,涂层的物理结构发生严重破环,腐蚀介质在涂层中加速扩散,并在涂层缺陷和涂层/金属界面处大量聚集,导致涂层吸水率大幅上升,力学性能显著下降,附着力迅速丧失,发生大面积鼓泡,快速失效。
Study on preparation surface-tolerant coating on high-chromium steel
[J].
高铬钢低表面处理涂料制备研究
[J].
Failure behavior of fresh water tank coating in different water
[J].
淡水舱涂层在不同水环境中的失效行为研究
[J].利用附着力测试、吸水率测试和电化学阻抗谱测试等手段,研究了淡水舱涂层在反渗透水、调质水、自来水等淡水以及盐水中的腐蚀失效行为。结果表明,自来水比盐水具有更快的渗透速度,导致涂层在淡水中会优先失效。淡水舱涂层在反渗透水、调质水和饮用水3种淡水中的腐蚀失效历程相同,根据电化学阻抗谱的变化特征可分为3个阶段:水的快速渗透、涂层/金属界面金属基体的腐蚀和涂层中颜填料对金属的缓蚀。
New applications of low surface treatment coatings
[J].
低表面处理涂料新应用
[J].
Molecular dynamics simulation of water molecule diffusion in graphene-reinforced epoxy resin anticorrosive coatings
[J].
水分子在石墨烯增强环氧树脂防腐涂层扩散的分子动力学模拟
[J].通过Materials Studio软件建立了石墨烯增强DGEBA/3,3'-DDS交联型环氧树脂模型,采用分子动力学模拟方法研究水分子在不同含量石墨烯 (0%,1.1%,2.3%,3.0%,4.2%和5.8%,质量分数) 增强的环氧树脂防腐涂层内部的扩散过程,为实际环氧树脂防腐涂层的改性提供理论指导。结果表明,水分子在环氧树脂中以氢键结合的“束缚水”和内部微孔中存在的“自由水”两种形式存在,水分子在其内部的扩散主要表现为由自由水的扩散过程,扩散系数随着温度的升高而增大;石墨烯的引入使得水分子的均方位移变化在整个模拟过程中趋于稳定,提高了环氧树脂的阻隔性能,当石墨烯含量为4.2%时,阻隔性能最佳。
Development of environmently-friendly general primer with low surface treatment and its application
[J].
环保型低表面处理环氧通用底漆的研制及应用
[J].
Effect of cutback surface preparation on coating performance of steel pipeline
[J].
钢质管道节点处表面处理对涂层性能的影响
[J].
EIS study of organic coatings failure behavior under the different surface pretreatment levels
[J].
不同表面处理等级下有机涂层失效行为的EIS研究
[J].
Influence of different surface treatments on coating properties of transmission tower
[J].
不同表面处理对输电线路铁塔涂层性能的影响
[J].
Development and application of Polymastiff epoxy ethane high tolerance anticorrosive primer
[J].
聚獒合环氧乙烷低表面处理防腐底漆的研发和应用
[J].
Analysis of current situation and development direction of low surface-treatment coatings
[J].
浅谈低表面处理涂料的现状及发展方向
[J].
Preparation of epoxy coating with good tolerance to surface pretreatment
[J].
低表面处理环氧涂料的研究
[J].
Pulse-reverse electrodeposition of a conversion coating based on zinc cation and 3-nitrobenzoic acid on carbon steel to enhance adhesion and protective function of epoxy coating
[J].
The effect of adhesion promoter on the performance of epoxy coatings on the surface of aluminum cathode plate
[J].
附着力促进剂对铝阴极板表面环氧涂层性能的影响
[J].
Study on the rapid evaluation of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of offshore wind turbine
[J].
海上风电塔筒涂层电化学阻抗谱快速评价技术研究
[J].
Fundamentals of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
[J].Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) has been widely used in the field of electrochemical energy technologies such as fuel cells, batteries, supercapacitors, electrolysis of H 2 O and CO 2. This paper systematically reviews the basic theory of EIS, measurement technology, development trend, and application in electrochemical energy technology, and clarifies the accurate understanding of the following four core issues: (1) What is EIS? (2) Why do you need EIS? (3) How to implement EIS diagnosis?<br>(4) What are capability boundaries for EIS? In order to appropriately and accurately use EIS technique, it must be clear about its<br>capability boundaries: what EIS can do, what EIS can’t do, and what EIS is good at. EIS is obviously not omnipotent, however its<br>value and potential will be fully reflected if used correctly, especially for electrochemical energy technologies.<br>
电化学阻抗谱基础
[J].
The application of AC impedance to study the performance of lacquered aluminium specimens in acetic acid solution
[J].
Phosphate coatings: EIS and SEM applied to evaluate the corrosion behavior of steel in fire extinguishing solution
[J].Phosphate coatings are one of the most important methods in preventing metal corrosion, especially iron alloys. The high interest in this method for industrial applications is mainly due to the low costs associated with the phosphating solution component and technological process. Considering this aspect and the advantages offered to the materials (corrosion resistance, good adhesion, wear resistance), this study evaluates the potential of using the phosphate coating method in health and safety applications. Therefore, the deposition of a layer of zinc phosphate on the steel surface used in the manufacture of components for personal protective equipment was approached. Firefighters, during rescue/evacuation operations, use protective equipment for fall arrest, whose accessories (hooks, carabiners) are made of steel. Due to the low corrosion resistance property of carbon steel, these accessories must be replaced frequently. This paper aims to analyze the possibility of improving the corrosion resistance of carbon steel in a fire extinguishing solution. Accordingly, the electrochemical behavior of two different types of coatings was studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). In the literature, different corrosion evaluating methods or systems have been considered, and up until now, there has been no previous study to have approached the corrosive behavior of C45, phosphate C45, and painted phosphate C45 immersed in fire extinguishing solution.
Study and evaluation on organic coatings by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
[J].
电化学阻抗谱方法研究评价有机涂层
[J].
In-situ impedance investigation of 304 stainless steel between pit growth and repassivation state
[J].
电化学阻抗谱法对304不锈钢孔蚀生长和再钝化阶段的原位研究
[J].利用动电位电化学阻抗谱(DEIS)法研究了304不锈钢在0.1 mol/L NaCl 溶液中的孔蚀行为,比较了孔蚀前后钝化膜的电化学阻抗谱的变化。提出了一种改进的双层膜结构,用以评价不锈钢在孔蚀的初始阶段和再钝化阶段各个参数的不同,指出孔蚀对钝化膜外层破坏较内层严重。使用活化控制的膜破裂模式评价孔蚀的初始阶段和再钝化阶段各个参数变化。