相关研究表明[3~8]:混凝土质量、界面粗糙程度、钢筋锈蚀程度、界面剂性能等因素均对混凝土的界面粘结劈裂强度产生重要影响。胡良明等[9]利用劈拉试验探究了水泥净浆界面剂的粘结性能随着水灰比的增大而降低的影响。Al-Sulaimani等[10]和Auyeung等[11]通过拉拔试验证明钢筋锈蚀率为1%时是粘结强度的临界点。张小平等[12]论证复合型阻锈剂对混凝土的工作性能、现场施工无负面影响,并提高混凝土的抗压强度。目前对于混凝土常采用的界面处理主要有物理法、化学试剂法,物理法有高压水射法、人工凿毛法、喷蒸汽法等方式,化学试剂包括粉类界面剂、乳液界面剂等[13,14]。调研表明,鼓浪屿上1920年左右的历史建筑混凝土现场实测强度在C10~C15之间[1]。因此,找到一种针对历史建筑混凝土界面不同碳化程度以及锈蚀钢筋不同工况,且施工方便、性能可靠的修复工艺与修补材料具有重要意义。本工作设置6种施工工艺,按界面处涂刷钢筋锈蚀转化剂、基体DPS补强剂和混凝土表面阻锈剂进行简化施工的实验研究。
1 实验方法
试验浇筑混凝土平均抗压强度为13.9 MPa。将已锈蚀钢筋钢筋 (ϕ12 mm,L=130 mm) 进行分组编号1#、2#、3#、4#、5#。钢筋锈蚀率 (%) 分别为5.19%、5.33%、5.48%、5.41%、5.34%。采用自主研制的低收缩高粘性多元复合修复砂浆 (LSHVRM)[15],28 d抗压强度为51.3 MPa,抗弯强度为14.6 MPa,单轴拉伸强度为4.9 MPa,28 d粘结拉伸强度1.97 MPa,7 d收缩率0.53%,28 d收缩率0.82%,稠度为65~75 mm。
DPS补强剂主要成分为聚碳酸酯活化二氧化硅,渗透深度可达20 mm;ZX-03锈蚀转化剂使钢筋表面钝化;PCI-2015阻锈剂为混合型水溶液,其性能指标如表1所示。
表1 修复材料性能指标
Table 1
| Material | DPS reinforcing agent | ZX-03 corrosion conversion agent | PCI-2015 rust inhibitor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Transparence | Brownish black | Amber |
| Density | 1.10 g/cm3 | - | 0.88-1.00 kg/L |
| pH value | 11 | - | 10-12 |
| Viscosity | 11.1/s | - | 11 mPa·s |
| Surface tension | 20.7 mN/m | - | 32.5 |
| Gelation time | 280 min | - | - |
| State | - | Liquid | - |
| Active ingredient content | - | 72% | - |
| Volatile organic compounds content | - | <60 g/L | - |
| Amount of coating | - | 0.3-0.7 kg/m2 | - |
| Drying time (25 ℃) | - | 12 h | - |
| Surface tension | - | ≈32.5 mN/m | |
| Flash point | - | ≥90 ℃ |
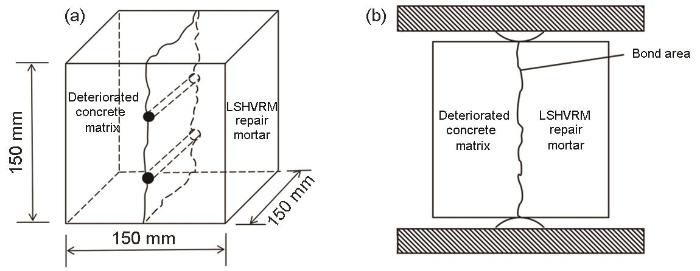
图1
图1
修复混凝土基体及混凝土试件劈裂加载示意图
Fig.1
Schematic diagram of repairing concrete matrix (a) and splitting loading (b) of concrete specimens
表2 模拟混凝土界面处理工艺
Table 2
| Process name No. | Classification | Treatment of corroded steel bar | Matrix reinforcement | Concrete surface protection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measure 1 | No embedded steel at interface | - | - | - |
| Measure 2 | - | - | PCI-2015 rust inhibitor | |
| Measure 3 | - | DPS reinforcing agent | PCI-2015 rust inhibitor | |
| Measure 4 | Embedded steel bar at interface | Steel brush to remove rust | - | - |
| Measure 5 | Steel brush to remove rust | DPS reinforcing agent | PCI-2015 rust inhibitor | |
| Measure 6 | ZX-03 corrosion conversion agent | DPS reinforcing agent | PCI-2015 rust inhibitor |
2 结果与讨论
2.1 试件破坏现象
低收缩高粘性多元复合修复砂浆 (LSHVRM) 与加速碳化混凝土的粘结劈拉强度按照(1)式计算[16]:
式中:fts为复合构件的粘结劈裂强度,MPa;F为破坏荷载,N;A为劈裂面面积,mm2。
试验所得数据代入 (1) 式计算得出试验结果,平均劈裂强度结果如表3所示。
表3 劈裂试验平均劈裂强度结果
Table 3
| Sample No. | Steel specifications | Carbonization duration / d | Process name No. | Splitting strength / MPa | Maximum error / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | 7 | Measure 1 | 1.49 | 2.01 |
| 2 | - | 7 | Measure 2 | 1.52 | 3.28 |
| 3 | - | 7 | Measure 3 | 1.58 | 5.06 |
| 4 | ϕ=12 mm | 7 | Measure 4 | 1.45 | 2.06 |
| 5 | ϕ=12 mm | 7 | Measure 5 | 1.55 | 9.03 |
| 6 | ϕ=12 mm | 7 | Measure 6 | 1.69 | 9.46 |
| 7 | - | 14 | Measure 1 | 1.46 | 1.36 |
| 8 | - | 14 | Measure 2 | 1.44 | 1.39 |
| 9 | - | 14 | Measure 3 | 1.50 | 3.33 |
| 10 | ϕ=12 mm | 14 | Measure 4 | 1.48 | 2.70 |
| 11 | ϕ=12 mm | 14 | Measure 5 | 1.53 | 2.61 |
| 12 | ϕ=12 mm | 14 | Measure 6 | 1.55 | 3.22 |
| 13 | - | 28 | Measure 1 | 1.48 | 2.02 |
| 14 | - | 28 | Measure 2 | 1.58 | 8.22 |
| 15 | - | 28 | Measure 3 | 1.59 | 6.91 |
| 16 | ϕ=12 mm | 28 | Measure 4 | 1.56 | 8.33 |
| 17 | ϕ=12 mm | 28 | Measure 5 | 1.57 | 4.45 |
| 18 | ϕ=12 mm | 28 | Measure 6 | 1.63 | 9.20 |
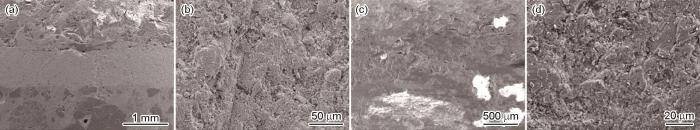
图2
图2
混凝土基体内聚破坏形貌
Fig.2
Images of cohesive failure of concrete matrix of measure 1 treatment interface (a) and measure 4 treatment interface (b)
图3
图3
粘结修复界面破坏形貌
Fig.3
Images of bond repair interface damage of measure 2 treatment interface (a) and measure 5 treatment interface (b)
图4
图4
混凝土基体与界面混合破坏形貌
Fig.4
Images of mixed failure of concrete matrix and interface of measure 3 treatment interface (a) and measure 6 treatment interface (b)
2.2 破坏试件分析
从图5a可以看出,随着混凝土基体加速碳化时长增加,碳化14 d的劈拉强度略低于7、28 d的劈拉强度。这是由于在加速碳化14 d时混凝土内部孔隙率达到最大[22],劈裂试件后的界面存在大量孔隙以及分层剥离状态,孔隙的存在会影响界面处的力学性能。这说明加速碳化时长对混凝土的粘结性能影响较小。
图5
图5
工艺1~6的混凝土劈裂强度
Fig.5
Concrete splitting strength of measure 1 (a), 2 (b), 3 (c), 4 (d), 5 (e) and 6 (f)
图5b中PCI-2015迁移型阻锈剂作用在钢筋表面,对混凝土的微观孔结构、抗中性化和抗氯离子的渗透性影响较大。碳化7、14和28 d下的平均劈拉强度为1.52、1.44和1.58 MPa,变化幅度-1.4%~6.8%之间,同样说明了混凝土表面不同碳化程度下PCI-2015涂刷迁移型阻锈剂对粘结性能的影响较小。图5c是混凝土界面喷涂DPS补强剂和PCI-2015迁移型阻锈剂,DPS补强剂会渗透入混凝土内部,并与混凝土中的游离碱离子产生反应,生成性质稳定的枝蔓状晶体物质,增强混凝土界面的强度。碳化时长7、14、28 d下的平均劈拉强度提高幅度2.7%~7.4%之间,说明混凝土表面不同碳化程度下喷涂DPS补强剂对粘结性能均有所提高。
图5d-f中混凝土界面内均埋置锈蚀钢筋。从图5d中可以看出,碳化时长7、14和28 d下的平均劈拉强度为1.45、1.48和1.56 MPa,而且对粘结性能的影响幅度在-2.7%~5.4%之间波动,说明钢刷处理对于锈蚀钢筋来说,差异性不大,混凝土表面不同碳化程度下锈蚀钢筋经过钢刷处理后对粘结性能的影响很小。图5e中与图5c的差异在于混凝土界面内埋置锈蚀钢筋,经过7、14、28 d的碳化时长下的平均劈拉强度为1.55、1.53、1.57 MPa,提高幅度0.6%~6.9%之间。这是由于DPS补强剂增强混凝土表面强度外,PCI-2015迁移型阻锈剂中阻锈成分以液态和气态的形式渗透,形成峰状粒子吸附于钢筋表面,表面粗糙度提高LSHVRM砂浆与锈蚀钢筋的机械咬合力。图5f中,锈蚀钢筋采用ZX-03锈蚀转化剂处理,其碳化时长7、14和28 d下的平均劈拉强度为1.69、1.55、1.63 MPa。说明混凝土表面不同碳化程度下,钢筋锈蚀转化剂后喷涂DPS补强剂和PCI-2015涂刷迁移型阻锈剂均可以提高粘结性能,提高幅度4.5%~16.6%之间。
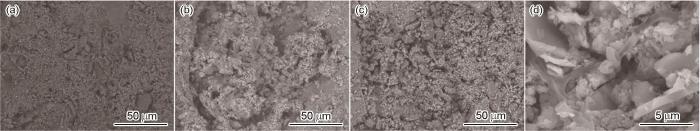
同期浇筑的混凝土基体试件碳化时长7、14和28 d的平均碳化深度为7.9、15.6、20.1 mm,混凝土基体碳化深度与碳化时间成正比。从图6b观察不同时长碳化下深度孔隙的变化SEM形貌可以看出,混凝土内部孔隙数量明显增多、孔径增大,混凝土基体强度变低导致粘结性能下降;当加速碳化28 d后,内部孔隙孔径减少,高倍镜下颗粒状碳酸钙的存在,说明混凝土基体内发生碳化,此时混凝土基体强度增加,从而促进粘结性能。
图6
图6
碳化混凝土基体微观形貌
Fig.6
Carbonation depth of concrete matrix under 7 d (a), 14 d (b), 28 d (c, d) carbonation time
图7
图7
混凝土界面(Y-1#)和3%D-ZX阻锈剂(Y-2 #)的表面形貌
Fig.7
SEM of images of concrete interface (Y-1#) (a, b) and 3% D-ZX rust inhibitor (Y-2#) (c, d)
3 结论
(1) 混凝土内无埋置锈蚀钢筋时,界面不同碳化程度、涂刷PCI-2015迁移型阻锈剂对粘结性能的影响较小;由于DPS补强剂增强混凝土界面的强度,当界面同时喷涂DPS补强剂和PCI-2015迁移型阻锈剂时,粘结性能有所提高,提高幅度2.7%~7.4%之间,碳化时长28 d,效果最佳。
(2) 混凝土界面埋置锈蚀钢筋时,钢刷处理后不同碳化程度对粘结性能的影响幅度在-2.7%~5.4%之间,影响较小;界面喷涂DPS补强剂和PCI-2015迁移型阻锈剂时,粘结性能有所提高,随着碳化时长增加,提升幅度下降;经ZX-03锈蚀转化剂增强钢筋氧化膜后,界面喷涂DPS补强剂和涂刷PCI-2015迁移型阻锈剂可大幅提高粘结性能,提高幅度4.5%~16.6%之间。
(3) ZX-03阻锈剂能够改善孔隙和孔径收缩,当掺量为3%时,混凝土的密实度、分子间作用力效果最为明显;混凝土基体碳化时长7、14和28 d下平均碳化深度为7.9、15.6、20.1 mm,14 d的孔隙数量明显增多、孔径增大,混凝土基体强度变低导致粘结性能下降。
参考文献
Deterioration status and reason analysis of concrete components in Gulangyu historic buildings
[J].
鼓浪屿历史建筑混凝土构件劣化现状及原因分析
[J].
Research progress on corrosion and anti-corrosion technology of ribbed steel
[J].
带肋钢腐蚀及其防腐蚀技术研究进展
[J].
Study on adhesive shear strength of young on old concrete
[J].
新老混凝土粘结的剪切强度研究
[J].
Experimental study on splitting strength of new-to-old concrete in short age
[J].
短龄期旧混凝土与新混凝土劈裂强度的研究
[J].
Influencing factors and mechanism of bonding between new and old concrete under the action of new interfacial agents
[D].
新型界面剂作用下新老混凝土粘结影响因素及机理研究
[D].
Influence of inhibitors on reinforced bar corrosion of coral aggregate seawater concrete
[J].
阻锈剂的掺入方式对全珊瑚海水混凝土中钢筋锈蚀的影响
[J].
Composite organic compound as corrosion inhibitor for reinforced steel in simulated concrete pore solution or mortar specimen
[J].
有机氨基醇阻锈剂在混凝土模拟孔隙液和砂浆试块中对钢筋的阻锈作用
[J].
Impacts from different bonding agents on bonding strength between new and old concretes of second age
[J].
不同界面剂对第二龄期新老混凝土粘结强度的影响
[J].
Influence of corrosion and cracking on bond behavior and strength of reinforced concrete members
[J].
Bond behavior of corroded reinforcement bars
[J].
Effect of composite rust inhibitor on corrosion resistance of reinforcement in concrete and its application research
[J].
复合型阻锈剂对混凝土中钢筋耐蚀性的影响及应用研究
[J].
Study on low shrinkage and high viscosity multi-component composite repair mortar for historical building restoration
[D].
历史建筑修复用低收缩高粘性多元复合修复砂浆研究
[D].
Experimental research on treating interface of young on old concrete with high pressure water jet method
[J].
采用高压水射法处理新老混凝土粘结面的试验研究
[J].
Experimental study on bond-slip properties and influence factors between rebars and recycled concrete
[J].
钢筋与再生混凝土粘结性能及影响因素研究
[J].
Study on bond-slip behavior of steel bar and concrete subjected to freezing-thawing and stirrup corrosion
[D].
考虑冻融和箍筋锈蚀影响的钢筋混凝土粘结性能试验研究
[D].
Bonding model and microstructure analysis of new and old concrete
[J].
新老混凝土的粘结模型及微观结构分析
[J].
Effect of carbonization on concrete pore structure
[J].
碳化对混凝土孔结构的影响
[J].