X70钢具有高强度、高冲击韧性、抗氢致开裂等优良性能,被广泛应用于石油、天然气等管道运输领域[1-3]。然而,它的腐蚀会造成巨大的经济和能源损失,甚至还会引发燃烧、爆炸等严重危害人民生命及财产安全的重大事故。基于金属及其合金器件很容易被氧化,其在使用之前通常都要经过酸洗工艺处理来除去表面氧化产物等污渍,进而来延长其使用期限,提高经济效益,并且有效地消除安全隐患。值得注意的是,在酸洗除锈、工艺设备酸洗及酸化采油等酸性环境中,酸溶液会对金属造成过度腐蚀,不仅给生产生活带来很多不便,而且会造成经济能源损失。因此,在酸洗过程中,常常通过添加缓蚀剂这种方法来减少或者消除对金属的过度腐蚀,进而来保护金属[4-7]。传统的高效缓蚀剂是含有N、O、S、P或共轭体系的有机物,其溶解性差、易挥发且毒性较大,对环境不友好,使其在工业应用中受到很大限制[8-13]。为满足绿色化工和生态文明建设的要求,加快酸洗环境中高效绿色缓蚀剂的开发势在必行,这对工业中酸洗工艺的提高和发展具有重大意义。
离子液体作为低温熔融盐,是完全由阴阳离子组成的化合物,可以通过改变阴离子和阳离子的组合,设计出不同的离子液体。其毒性低、溶解性好、不易挥发、稳定性好、生物相容性好,可作为潜在的绿色高效缓蚀剂[14,15]。目前,有研究证实了离子液体缓蚀剂阳离子的不同会对缓蚀效率产生显著影响[16,17]。Qiang等[1]表明咪唑溴盐离子液体对Cu在酸溶液中的腐蚀有显著的抑制作用,且取代基的链长对缓蚀效果有显著影响,这可能是由于不同的取代基其供电子效应和空间位阻效应不同造成的。Zaky等[18]合成了3种新型阳离子不同的咪唑离子液体,并表明阳离子不同的离子液体对钢的缓蚀作用是有差异的。以上这些研究都证实了阳离子不同会对缓蚀效率产生影响。然而,离子液体阴离子对缓蚀效果的影响研究较少,且其阴阳离子之间的相互作用机理尚不明确。
基于此,本文探究了含不同卤素阴离子 (I-,Cl-和Br-) 的咪唑基离子液体缓蚀剂在0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中对X70钢的腐蚀抑制效果以及缓蚀机制。该研究进一步加深了对咪唑基离子液体对X70钢缓蚀过程的理解,也为未来设计和开发绿色高效缓蚀剂提供了理论指导。
1 实验方法
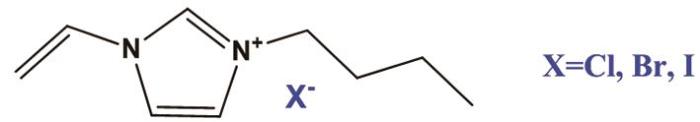
实验使用的离子液体1-乙烯基-3-丁基咪唑氯盐 (1-vinyl-3butylimidazolium Chloride,[VBIM]Cl)、1-乙烯基-3-丁基咪唑溴盐 (1-vinyl-3butylimidazolium Bromide,[VBIM]Br) 和1-乙烯基-3-丁基咪唑碘盐 (1-vinyl-3butylimidazolium iodide,[VBIM]I),均购买自上海成捷化学公司,纯度为99 %,其结构如图1所示。实验所用的钢材其组成 (质量分数,%) 为:Mn 1.7,Si 0.45,S 0.01,P 0.02,V 0.06,Mo 0.35,Ti 0.06,Nb 0.05,余量为Fe。测试溶液为含有不同浓度离子液体缓蚀剂的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液,不含缓蚀剂的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液作为空白对照组。
图1
图1
咪唑基离子液体缓蚀剂的化学结构
Fig.1
Chemical structures of imidazole-based ionic liquid inhibitors
电化学实验在CHI 604D电化学工作站上进行。采用三电极体系,工作电极是工作面积为1 cm2嵌入环氧树脂的X70钢,辅助电极为铂电极,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极。实验前,均用400#、600#、1500#、2000#和3000#砂纸依次打磨至镜面,再分别用蒸馏水和无水乙醇超声清洗30 s,室温干燥备用。测试前,依次进行开路电位测试、电化学阻抗谱测试和电动位极化曲线测试。其中开路测试时间为500 s,达到一个稳定的状态后,进行阻抗谱测试,测试的频率范围为105~10-2 Hz,激励信号为5 mV的正弦电压。最后进行动电位极化曲线测试,极化曲线的极化范围是基于开路电位的±250 mV,扫描速率为1 mV/s。其缓蚀效率计算为[19,20]:
式中,Icorr,0和Rct,0及Icorr和Rct分别为空白硫酸溶液和添加了不同浓度离子液体缓蚀剂时的腐蚀电流密度和电荷转移电阻。
用扫描电子显微镜 (SEM,JEOL-JSM-7800F) 和原子力显微镜 (AFM,MFP-3D-BIO) 观察分析样品的表面形貌,样品尺寸分别为0.3 cm×0.5 cm×0.5 cm和1 cm×1 cm×0.1 cm。测试前,将打磨好的样品分别浸泡到不含和含离子液体缓蚀剂的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中,4 h后取出样品并用蒸馏水清洗,冷风干燥后。以上所有实验均在室温 (25 ℃) 下进行,通过恒温水浴锅将温度控制在 (298±0.5) K。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 电化学阻抗谱分析
图2
图2
拟合含和不含感抗阻抗数据所用的等效电路
Fig.2
Equivalent circuits used to fit impedance data with (a) and without (b) inductive impedance
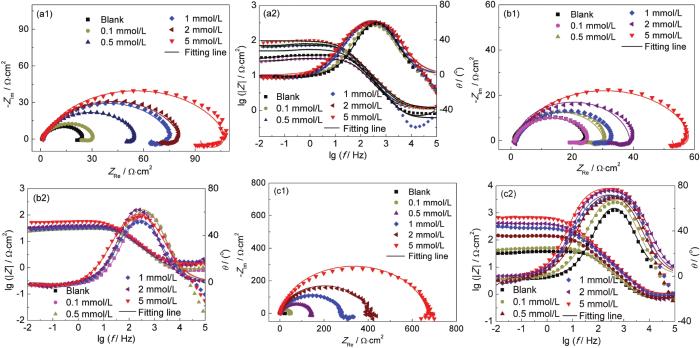
图3
图3
X70钢电极在不同浓度[VBIM]Cl、[VBIM]Br和[VBIM]I的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的Nyquist和Bode图
Fig.3
Nyquist and Bode plots of X70 steel electrode in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solutions with different concentrations of [VBIM]Cl (a), [VBIM]Br (b) and [VBIM]I (c) at 298 K
式中,fZim-Max对应的是阻抗虚部最大时的频率。
表1 X70钢电极在不同浓度[VBIM]Cl、[VBIM]Br和[VBI M]I的 0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的电化学阻抗数据
Table 1
| Inhibitor | C / mmol·L-1 | Rs / Ω·cm2 | Y0 / 10-5 Ω·cm2 | n | Cdl / μF·cm-2 | Rct / Ω·cm2 | L / Ω·cm2 | RL / Ω·cm2 | η / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0 | 0.93 | 17.75 | 0.90 | 98.5 | 23.70 | 71.0 | 181.0 | --- |
| [VBIM]Cl | 0.1 | 1.18 | 17.65 | 0.89 | 94.5 | 29.30 | 222.4 | 152.0 | 19.1 |
| 0.5 | 1.21 | 17.25 | 0.86 | 94.3 | 54.53 | 346.3 | 460.4 | 56.5 | |
| 1 | 1.42 | 16.13 | 0.85 | 87.0 | 75.16 | 297.2 | 395.4 | 68.5 | |
| 2 | 1.09 | 16.52 | 0.83 | 83.1 | 81.24 | 551.6 | 495.1 | 70.8 | |
| 5 | 1.35 | 17.18 | 0.80 | 80.9 | 108.40 | 961.5 | 593.6 | 78.1 | |
| [VBIM]Br | 0.1 | 1.22 | 17.61 | 0.89 | 98.1 | 24.80 | 144.1 | 112.7 | 4.4 |
| 0.5 | 0.93 | 16.94 | 0.90 | 96.0 | 29.45 | 284.8 | 148.5 | 19.5 | |
| 1 | 1.67 | 14.71 | 0.85 | 95.7 | 32.07 | 105.9 | 183.6 | 26.1 | |
| 2 | 1.68 | 13.81 | 0.94 | 94.9 | 37.24 | 588.0 | 225.6 | 36.4 | |
| 5 | 1.37 | 12.44 | 0.82 | 84.7 | 58.81 | 176.2 | 406.4 | 59.7 | |
| [VBIM]I | 0.1 | 0.77 | 15.93 | 0.90 | 90.8 | 49.40 | 100.1 | 347.0 | 52.0 |
| 0.5 | 0.74 | 13.72 | 0.88 | 79.8 | 140.90 | 155.5 | 567.0 | 83.2 | |
| 1 | 0.90 | 10.06 | 0.87 | 58.2 | 285.60 | --- | --- | 90.8 | |
| 2 | 0.67 | 7.33 | 0.89 | 47.7 | 402.20 | --- | --- | 94.1 | |
| 5 | 1.02 | 5.51 | 0.91 | 39.9 | 669.10 | --- | --- | 96.5 |
从Nyquist图中可以看出,Nyquist图是由高频区的容抗弧和低频区的感抗弧组成,高频区的容抗弧主要与电荷转移电阻和双电层电容有关,而低频区的感抗弧是由于吸附离子如 (H+)ads和 (SO42-)ads的弛豫过程引起的[24]。随着[VBIM]Cl浓度的增加,容抗弧的半径逐渐增大,这表明随缓蚀剂浓度的增大,其在电极表面的吸附增加,电荷转移电阻增大,X70钢在0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的腐蚀得到了有效控制,且缓蚀效率随缓蚀剂浓度的增大而增强,并且[VBIM]I对X70钢的腐蚀抑制效果依次优于[VBIM]Cl和[VBIM]Br。在Bode图中,随着缓蚀剂浓度的增大,阻抗模值和相位角逐渐增大,也进一步说明离子液体缓蚀剂的加入有效地抑制了X70钢在0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的腐蚀。
其中,ε0为空气介电常数,ε为双电层的局部介电常数,S为工作电极面积,d为双电层的厚度。随着缓蚀剂浓度的增大,缓蚀剂逐渐取代了金属表面的水分子吸附到金属表面,且吸附厚度随浓度增大而增大。一般地,有机缓蚀剂的介电常数小于水分子的介电常数,也进一步说明,随着缓蚀剂浓度的增大,越来越多的缓蚀剂吸附到金属表面来抑制腐蚀性物质对X70钢的腐蚀。此外还可以得出,3种阴离子不同的离子液体缓蚀剂 ([VBIM]I、[VBIM]Br、[VBIM]Cl) 对X70在0.5 mol/L H2SO4中的缓蚀效率顺序为:[VBIM]I依次优于[VBIM]Cl和[VBIM]Br,这主要归因于I-优异的吸附特性。这一结果进一步揭示了所研究的3种离子液体缓蚀剂的阴阳离子之间存在协同缓蚀作用[25-27]。当阳离子相同时,阴离子为I-缓蚀剂的缓蚀效应要优于阴离子Cl-和Br-。
2.2 动电位极化曲线图
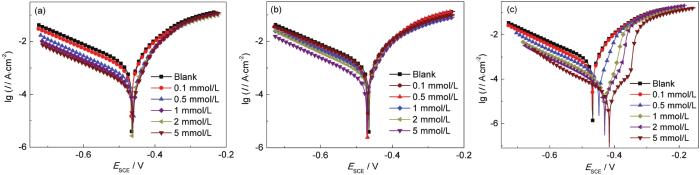
图4为X70钢分别在不同浓度[VBIM]Cl、[VBIM]Br和[VBIM]I的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的动电位极化曲线图。相应的极化数据根据Tafel直线外推法得到并列于表2中。在图4中,随着缓蚀剂浓度的增加,腐蚀电位向正方向移动,腐蚀电流密度逐渐降低,说明X70钢在0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的腐蚀得到了有效的控制。电流密度的降低既体现在阳极支又体现在阴极支,说明所研究的缓蚀剂是混合型缓蚀剂[28,29]。同时可以看出,随着浓度的增加,极化曲线平行下降,线的形状并没有发生改变,表明浓度的增加并没有改变离子液体的缓蚀机理。在图4c阳极极化中,电流密度有一个骤升的拐点,这个点对应的电位为[VBIM]I缓蚀剂的脱附电位,即从脱附电位向正方向极化的过程中,缓蚀剂开始脱附,且极化过程中电流密度降低的越快,即缓蚀剂的脱附越快,腐蚀越严重。脱附电位越正,缓蚀剂越不容易脱附。而在图4a和b中,并没有观察到电流密度的骤升,说明在该极化范围下,缓蚀剂的脱附不是很严重。在离子化合物中,阴阳离子之间的作用力为库仑力,其大小与阴阳离子的电荷数量及半径有关,电荷数量相同时,离子半径越大,它们之间的作用力越小。I的半径依次大于Br和Cl,即I-与咪唑阳离子之间的作用力较Cl-和Br-更小,因此,在进行阳极极化时,[VBIM]I更容易发生脱附。此外,从表2中可以得出,添加不同浓度离子液体缓蚀剂后,其腐蚀电位相对空白的变化值均小于85 mV,进一步说明所研究的离子液体缓蚀剂均为混合型缓蚀剂[30,31]。相同体系中,[VBIM]I对X70钢的腐蚀抑制效果最好,而[VBIM]Br的最差。在酸溶液中,离子液体阴阳离子的协同作用阻碍了溶液中腐蚀性物质对金属的进攻,有效地保护X70钢免受腐蚀。极化曲线和电化学阻抗谱得出的结论是一致的。
图4
图4
X70钢电极在含不同浓度[VBIM]Cl、[VBIM]Br和[VBIM]I的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的极化曲线图
Fig.4
Polarization curves of X70 steel electrode in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solutions with different concentrations of [VBIM]Cl (a), [VBIM]Br (b) and [VBIM]I (c) at 298 K
表2 X70钢电极在含不同浓度[VBIM]Cl、[VBIM]Br和[VBIM]I的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的极化曲线参数
Table 2
| Inhibitor | C / mmol·L-1 | Ecorr SCE / V | Icorr / mA·cm-2 | -βc / mV·dec-1 | βa / mV·dec-1 | η / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0 | -0.477 | 1.840 | 168.4 | 101.6 | --- |
| [VBIM]Cl | 0.1 | -0.468 | 1.463 | 167.0 | 108.0 | 20.5 |
| 0.5 | -0.461 | 0.588 | 156.4 | 87.6 | 68.0 | |
| 1 | -0.466 | 0.374 | 146.1 | 83.4 | 79.7 | |
| 2 | -0.461 | 0.363 | 152.5 | 77.1 | 80.3 | |
| 5 | -0.463 | 0.286 | 151.9 | 76.8 | 84.5 | |
| [VBIM]Br | 0.1 | 0.468 | 1.738 | 166.9 | 114.1 | 5.5 |
| 0.5 | -0.469 | 1.415 | 164.9 | 98.4 | 23.1 | |
| 1 | -0.470 | 1.332 | 167.2 | 104.7 | 27.6 | |
| 2 | -0.470 | 1.227 | 173.2 | 114.6 | 33.3 | |
| 5 | -0.471 | 0.579 | 153.9 | 92.1 | 68.5 | |
| [VBIM]I | 0.1 | -0.478 | 0.747 | 145.0 | 91.9 | 59.4 |
| 0.5 | -0.453 | 0.249 | 134.9 | 102.8 | 86.5 | |
| 1 | -0.433 | 0.086 | 130.2 | 105.4 | 95.4 | |
| 2 | -0.426 | 0.027 | 131.2 | 48.9 | 97.9 | |
| 5 | -0.399 | 0.010 | 140.5 | 37.4 | 99.4 |
2.3 SEM分析
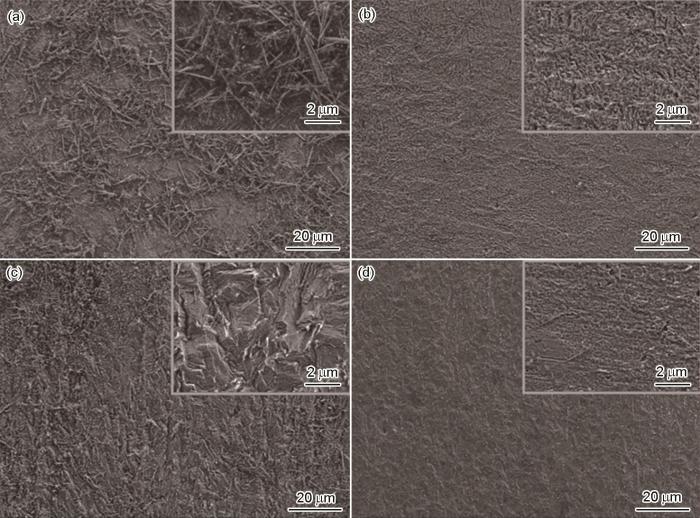
图5为X70钢分别含和不含5 mmol/L [VBIM]Cl、[VBIM]Br和[VBIM]I的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中浸泡4 h后的SEM形貌。可以看出,经过腐蚀溶液浸泡后,样品的表面均遭到不同程度的破环,空白样品的腐蚀最为严重,腐蚀痕迹更加明显。相较于空白,添加了缓蚀剂的样品,其表面状态有了明显的改善。对比高倍率下的3种缓蚀剂对应的SEM图发现,[VBIM]I比[VBIM]Cl和[VBIM]Br样品表面更加光滑平整,说明[VBIM]I的缓蚀效率比[VBIM]Cl和[VBIM]Br更好,这与电化学实验结果相吻合。
图5
图5
X70钢电极在不含和含有 5 mmol/L [VBIM]Cl、[VBIM]Br和[VBIM]I的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中浸泡4 h后的SEM形貌
Fig.5
SEM images of X70 steel electrode immersed for 4 h at 298 K in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solutions without (a) and with 5 mmol/L [VBIM]Cl (b), [VBIM]Br (c) and [VBIM]I (d)
2.4 AFM分析
图6为X70钢分别浸泡在含有和不含有离子液体的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中4 h后的AFM 3D形貌,可以看出,空白样品表面很粗糙,有很多腐蚀坑,表面高度变化范围很大,说明其在0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中遭受了严重的腐蚀,致使表面变得粗糙。加了缓蚀剂以后,样品表面的腐蚀痕迹明显减弱了很多,3D图变得光滑平整,表面粗糙度明显下降,由空白的89.970 nm降低到61.034 nm ([VBIM]Br)、37.244 nm ([VBIM]Cl) 和35.250 nm ([VBIM]I),说明缓蚀剂的加入有效地抑制了X70钢的腐蚀。且粗糙度更小的[VBIM]I比[VBIM]Cl和[VBIM]Br具有更优异的腐蚀抑制效果,这与电化学得到的结果是一致的。
图6
图6
X70钢电极在不含和含有5 mmol/L [VBIM]Cl、[VBIM]Br和[VBIM]I的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中浸泡4 h后的AFM形貌
Fig.6
AFM and corresponding height images of X70 steel electrode immersed for 4 h at 298 K in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solutions without (a) and with 5 mmol/L [VBIM]Cl (b), [VBIM]Br (c) and [VBIM]I (d)
2.5 缓蚀机理分析
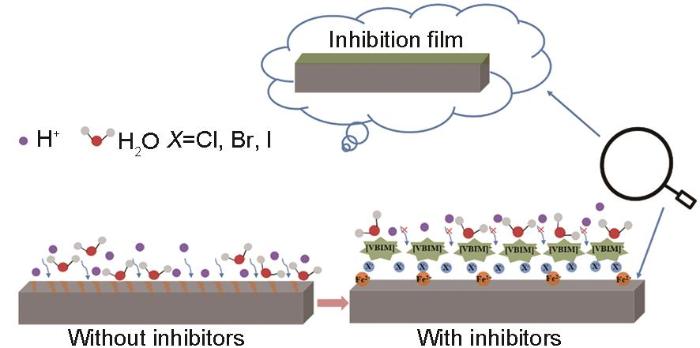
离子液体的缓蚀机理如图7所示。在0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中,X70钢表面带正电荷,当溶液中含有咪唑基离子液体时,卤素阴离子会通过静电作用优先吸附到X70钢表面,然后咪唑基阳离子会进一步吸附,卤素离子的“架桥”作用使得咪唑基阳离子更容易吸附。阴阳离子在金属表面有序吸附形成稳定致密的吸附保护膜,阻碍了溶液中腐蚀性物质 (如水分子和氢离子等) 对X70钢的腐蚀进攻,达到了有效的腐蚀抑制作用。阳离子相同时,I-的特异性吸附使得[VBIM]I具有较[VBIM]Cl和[VBIM]Br更优的缓蚀效果[25]。3种阴离子相比,Cl原子的半径依次小于Br和I,理论上Cl原子电性要依次大于Br和I,即Cl-更容易在带正电荷的X70表面发生吸附。然而,实验结果表明阴离子为I-时的缓蚀效率要依次大于Cl-和Br-。这主要是由于I-的半径和体积较大,原子核对外层电子的束缚能力弱,使得的I-的可极化性和变形性更强,表现出特异的吸附能力。进而使得阴离子为I-的离子液体表现出比Cl-和Br-更优的缓蚀效率。这一结论对未来离子液体缓蚀剂设计和开发具有一定的理论指导意义。
图7
图7
离子液体缓蚀机理示意图
Fig.7
Schematic diagram of corrosion inhibition mechanism of ionic liquid inhibitors
3 结论
(1) 在0.5 mol/L的H2SO4溶液中,[VBIM]X (X=Cl、Br、I) 可以有效的抑制X70钢的腐蚀,且均属于混合型缓蚀剂,且都存在阴离子和阳离子的协同作用。
(2) 3种缓蚀剂的缓蚀效率随浓度的增大而增大,在浓度为5 mmol/L时,缓蚀效率皆达到最大。
(3) 当阳离子相同时,阴离子为I-的离子液体的缓蚀效率最高,其次为阴离子为Cl-的,而阴离子为Br-的缓蚀效率最低,这主要与I-的特异性吸附有关。
参考文献
Evaluation of Ginkgo leaf extract as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor of X70 steel in HCl solution
[J].
Experimental and theoretical studies of benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acid media
[J].The inhibition behavior of three benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone derivatives namely p-methoxybenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (MOBT), p-carboxybenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (COBT) and p-ethylbenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (EBT) for mild steel in 1.0 M HCl solution was studied systematically using gravimetric measurements, potentiodynamic polarization, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectrum. Gravimetric measurements revealed that the corrosion rate decreased with the increase of inhibitor concentration and COBT inhibitor exhibited the highest inhibition efficiency of 96.4% at 300 mu M. Potentiodynamic polarization results suggested that these three compounds acted as mixed-type inhibitors. Adsorption of these three inhibitors on mild steel surface in 1.0 M HCl solution conforms to Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Theoretical calculations were also performed and the results agreed well with the experimental measurements. (C) 2018 Elsevier B.V.
Evaluation of Ficus tikoua leaves extract as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in HCl media
[J].
Effect of stereochemical conformation into the corrosion inhibitive behaviour of double azomethine based Schiff bases on mild steel surface in 1 mol L-1 HCl medium: an experimental, density functional theory and molecular dynamics simulation study
[J].
Sebacic acid as corrosion inhibitor for hot-dip galvanized (HDG) steel in 0.1 M NaCl
[J].
4-aminoazobenzene modified natural glucomannan as a green eco-friendly inhibitor for the mild steel in 0.5 M HCl solution
[J].
The performance and mechanism of bifunctional biocide sodium pyrithione against sulfate reducing bacteria in X80 carbon steel corrosion
[J].
2-Mercaptobenzothiazole corrosion inhibitor deposited at ultra-low pressure on model copper surfaces
[J].
Correlations between the inhibition performances and the inhibitor structures of some azoles on the galvanic corrosion of copper coupled with silver in artificial seawater
[J].
Chitosan oligosaccharide derivatives as green corrosion inhibitors for P110 steel in a carbon-dioxide-saturated chloride solution
[J].
Characterization of adsorption of 5-carboxy-3-amino-1,2,4-triazole towards copper corrosion prevention in neutral media
[J].Adsorption behavior of 5-carboxy-3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (COOH-ATA) on copper in neutral (pH 7.4) borate buffer solutions with and without 0.01 M NaCl was studied. Electrochemical polarization methods show significant suppression of the anodic and cathodic currents on the polarization curves in the presence of COOH-ATA. Chronopotential diagrams show increase of open circuit potential during adsorption. Ellipsometric studies has allowed to estimate the free energy of adsorption. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy was applied to examine the surface composition after COOH-ATA adsorption from the inhibitor solution. Spectra analysis shows oxidation of copper to Cu+ and Cu2+ with surface complex formation. Protective properties in humid air and salt fog chamber of such layer are discussed. (C) 2019 Elsevier Ltd.
Effect of electron donating functional groups on corrosion inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid: experimental and quantum chemical study
[J].
Latest research progress of environmentally friendly corrosion inhibitors
[J].
环境友好型缓蚀剂的最新研究进展
[J].
Acidic-functionalized ionic liquid as corrosion inhibitor for 304 stainless steel in aqueous sulfuric acid
[J].
Choline based ionic liquids as sustainable corrosion inhibitors on mild steel surface in acidic medium: gravimetric, electrochemical, surface morphology, DFT and Monte Carlo simulation studies
[J].
Effect of organic anions on ionic liquids as corrosion inhibitors of steel in sulfuric acid solution
[J].Two new ionic liquids (ILs), N-ethyl-N,N,N-trihexylammonium adipate (CPA(6)) and N-ethyl-N,N,N-trioctylammonium ethyl sulfate (ESA(8)), were synthesized and their chemical structures were determined by H-1 and C-13 NMR. The corrosion inhibition effect of the ILs on API-X60 steel in 1 M H2SO4 was studied by weight loss, Tafel polarization curves and polarization resistance. The experimental results show that the ILs were adsorbed on API-X60 steel and blocked surface active sites, reducing the corrosion rate of the metallic substrate. The ILs behaved as mixed-type corrosion inhibitors and their adsorption process obeyed the Langmuir isotherm model. The adsorption phenomenon was studied by means of the XPS, DRIFT and SEM/EDS techniques. Quantum chemical parameters were obtained from the studied ILs, calculated in vacuum and water systems, and correlated with the experimental results. The effect of organic anions on the ILs was analyzed and it was concluded that the ethyl sulfate anion presented better corrosion inhibition properties than the adipate anion; therefore, ESA(8) was a more efficient corrosion inhibitor than CPA(6). (C) 2019 Elsevier B.V.
The synergistic corrosion inhibition study of different chain lengths ionic liquids as green inhibitors for X70 steel in acidic medium
[J].
Synthesis of new ionic liquids based on dicationic imidazolium and their anti-corrosion performances
[J].
Experimental and theoretical studies on the inhibition properties of three diphenyl disulfide derivatives on copper corrosion in acid medium
[J].
Glycyrrhiza glabra extract as an eco-friendly inhibitor for microbiologically influenced corrosion of API 5LX carbon steel in oil well produced water environments
[J].
Understanding the adsorption and anticorrosive mechanism of DNA inhibitor for copper in sulfuric acid
[J].
Self-aggregate nanoscale copolymer of new synthesized compounds efficiently protecting copper corrosion in sulfuric acid solution
[J].
Progress in the development of sour corrosion inhibitors: past, present, and future perspectives
[J].Metallic pipelines and gathering tanks play a vital role during oil and gas exploration, production, transmission, and processing. These facilities are usually attacked by corrosion. The use of corrosion inhibitors is one of the most economical and reliable approaches to control the corrosion of oil and gas metallic facilities. This paper looks at the progress made in the development of sour corrosion inhibitors from early 1900 to date. Scientific literatures were reviewed. The review identified four classes of organic corrosion inhibitors for sour environments, namely, amine-based, imidazoline-based, polymer-based, and Gemini-surfactant-based inhibitors. The strengths and weaknesses of these inhibitors were highlighted. The review revealed that the patronage of amine-based chemistries has declined, and the current technology is based on imidazoline and quaternary salt chemistries. The existing knowledge gap and the future research direction in the area of sour corrosion inhibitors development have been highlighted. (C) 2019 The Korean Society of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. Published by Elsevier B.V.
A combined experimental and theoretical study of the inhibition effect of three disulfide-based flavouring agents for copper corrosion in 0.5 M sulfuric acid
[J].
Synergistic inhibition effects of bamboo leaf extract/major components and iodide ion on the corrosion of steel in H3PO4 solution
[J].
Experimental and theoretical studies of two imidazolium-based ionic liquids as inhibitors for mild steel in sulfuric acid solution
[J].
Research progress of synergistic inhibition effect and mechanism
[J].
缓蚀剂协同效应与协同机理的研究进展
[J].
Comprehensive investigation of steel corrosion inhibition at macro/micro level by ecofriendly green corrosion inhibitor in 15% HCl medium
[J].
Performance evaluation and adsorption behavior of two new mannich base corrosion inhibitors
[J].
两种新型曼尼希碱缓蚀剂的性能及吸附行为研究
[J].
Intra-/inter-molecular synergistic inhibition effect of sulfonate surfactant and 2-benzothiazolethiol on carbon steel corrosion in 3.5%NaCl solution
[J].