本研究是在青岛中港进行了普碳钢表面热浸锌、冷镀锌和富锌涂料3种保护层的部分浸入腐蚀试验,进行全过程各阶段海水界面腐蚀产物膜、腐蚀表征及污损生物等分析检测。通过对腐蚀产物的表征分析,明确了腐蚀界面腐蚀产物层的变化,揭示了防腐锌涂层的防腐防污效果及其机理。
1 实验方法
将普碳钢 (M60) 加工成600 mm×60 mm×5 mm (—端打孔,孔径18 mm),分别进行了涂覆富锌涂层 (JR-FX) 以及冷镀锌和热浸锌处理。热浸锌处理时,首先通过抛丸处理去除钢铁试板表面的锈污,处理后试板表层呈银灰色。试板经18% (体积分数) 六次甲基四胺的稀盐酸酸洗后,浸入锌液中,使试板表面均匀附上锌层。所使用锌原料为葫芦岛60号出口锌 (纯度99.99%)。浸锌后的试板用2% (质量分数) NH4Cl溶液进行漂洗。
冷镀锌处理中的镀层锌液为JP1618型,即将锌粉加入JP-SZ-20型树脂液中搅拌均匀,待混胶体可以在刮板上平整形成涂层时,过滤保存。冷镀锌时,先对碳钢试板进行机械除锈,使其光洁度达到Sa2.5 级 (ISO 8501-1:2007)。将配套用稀释剂以0.15∶1的比例加入JP1618型冷镀锌的镀液中,搅匀、过滤并稀释。使用有气喷涂的方法正面均匀喷涂,膜厚约为120 μm。喷涂后的试板需静置7 d,使涂膜实干,再对试板另一面进行喷涂。
富锌涂层的涂覆时,试板表面处理与冷镀锌前处理相同。富锌涂料的双组份按A∶B=9∶1的比例混合,将配套用稀释剂加入富锌涂料中,搅匀、过滤。涂装方法与冷镀锌处理工艺相同。
锌防护层试板均用螺栓紧固到固定装置上,制成实验用的试架。标记冷镀锌挂板为C,富锌挂板为F,热浸锌挂板为H,后文中各试样标号与此一致。每块试板又被均分为6个区域,以便于后续的表征与分析。
2014年4月,将试架投放到青岛中港海中,使各试板的3/4浸入海水中,1/4暴露在大气中。分别在浸海10、17、24、58和89 d后取出,目测和手触摸并照相记录表观状态。2014年7月~2018年7月间共进行了36次月检和4次年检。
从挂件上切取10 mm×10 mm的小试样,利用JSM-6700F扫描电镜 (SEM) 及JSM-6700F能谱分析仪 (EDS) 观察形貌,分析结构及成分。刮取试板表面的腐蚀产物,利用X射线衍射仪 (XRD,D/max-rA) 测试,扫描2θ角为5°~90°,扫描速率为10°/min。采用Fourier变换红外光谱仪 (FTIR,BRUKER TENSOR 27) 进行分子结构分析。其具体参数设置如下:光源光谱范围为500~4000 cm-1,光源波数精度为0.01/2000 cm-1,分辨率参数为0.4~1 cm-1,信噪比参数为4000∶1 (p/p值),吸收精度参数为0.01%T。
此外,还对试板表面产物及试板基体进行了元素能谱分析、金相分析 (金相显微镜,XJP-200) 等表征检测,确定腐蚀产物的形貌、结构、成分及试板的金相组织变化。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 锌防护层钢板宏观腐蚀形貌
图1
图1
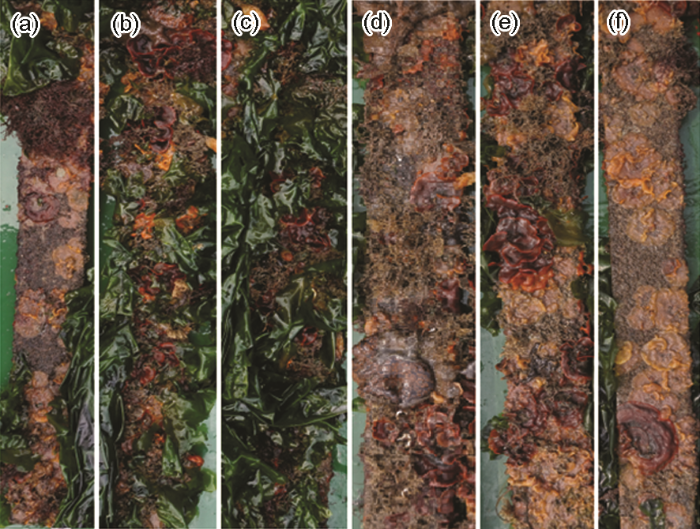
3种挂板实海浸入5 a后的正反面照片
Fig.1
Photos of the front (a~c) and back (d~f) sides of cold galvanized (a, d), zinc rich (b, e) and hot dip (c, f) galvanized hanging plates after immersion for 5 a
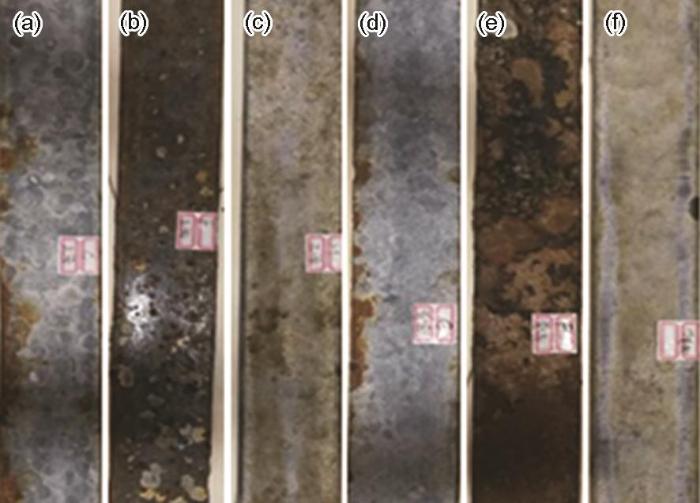
挂板经自来水进行冲洗,轻微刷除顽固残留生物后,再用去离子水冲洗3遍,放置到鼓风干燥箱之中,60 ℃干燥8 h。待干燥后对挂片进行拍照分析,如图2和3所示。看出,热浸锌挂板和冷镀锌挂板表面锈蚀较轻微,有一层牢固的沉积层;而富锌挂板涂层脱落,碳钢全面腐蚀,干湿交替区腐蚀最严重。
图2
图2
3种挂板海水全浸区正反面照片
Fig.2
Photos of the front (a~c) and back (d~f) sides of the full immersion zones of cold galvanized (a, d), zinc rich (b, e) and hot dip (c, f) galvanized hanging plates after exposure test for 5 a
图3
图3
3种挂板干湿交替区的宏观形貌
Fig.3
Macromorpholgies of the dry-wet alternation zones of zinc rich (a), hot dip galvanized (b) and cold galvanized (c) hanging plates after exposure test for 5 a
2.2 锌防护层钢板腐蚀显微形貌表征与分析
2.2.1 SEM测试分析
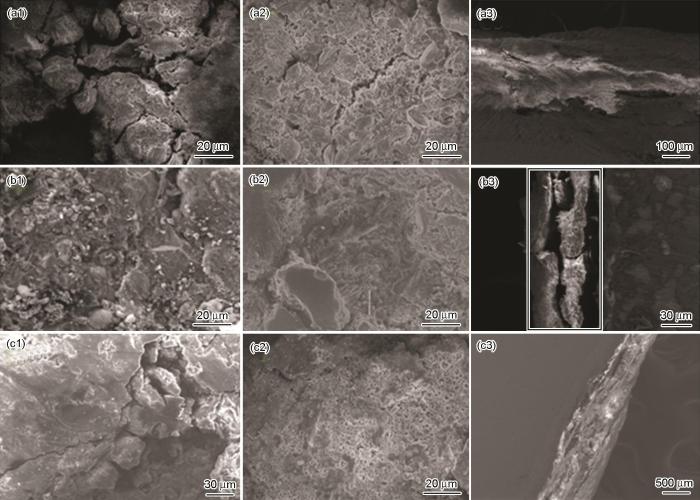
图4是对3种不同镀锌层钢板浸入实验后不同位置的SEM分析结果。如图所示,3种不同镀锌钢的表面均发生了严重的点蚀、缝隙腐蚀等局部腐蚀。在1000倍下的SEM图片中可以看到一些生物,而这些生物一般存在于腐蚀坑,表明其对腐蚀进程有影响。从截面的SEM图片可以看出,冷镀锌和热浸锌的镀层内没有明显裂纹,且与基体结合良好;而富锌镀层内有明显裂纹,说明钢基体发生了腐蚀,而且基体与镀层之间存在缝隙,镀层与基体的结合不致密。综上所述,冷镀锌和热浸锌镀层对碳钢基体材料发挥了良好的保护作用,而富锌镀层对钢铁基体的保护性差。
图4
图4
3种挂板正面、背面及横截面的SEM形貌
Fig.4
SEM photographs of the front (a1~c1) and back (a2~c2) sides and cross section (a3~c3) of cold galvanized (a) , zinc rich (b) and hot-dip galvanized (c) panels after exposure test
2.2.2 EDS测试分析
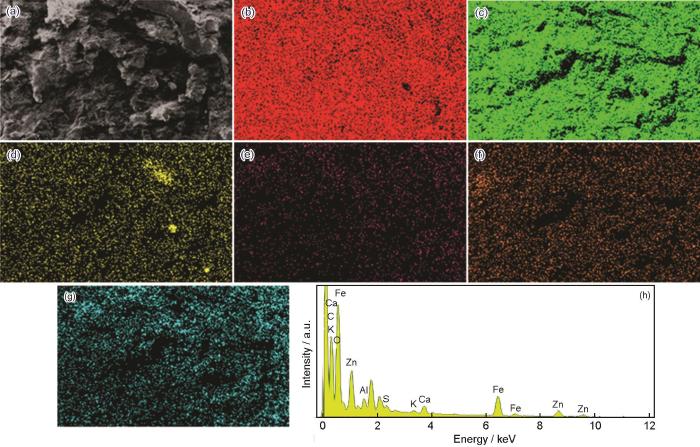
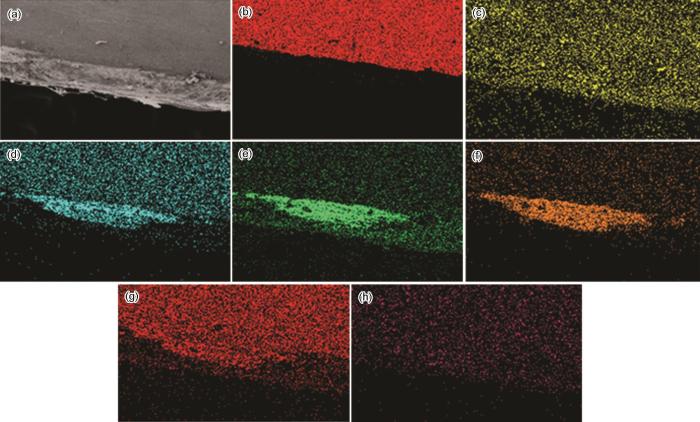
图5
图5
冷镀锌板表面腐蚀形貌及EDS分析
Fig.5
SEM image (a) and EDS elemental mappings of Fe (b), O (c), Ca (d), Zn (e), Cl (f), Na (g) and element contents of the surface (h) of the corrosion product layer formed on cold galvanized plate after exposure test
图6
图6
冷镀锌板断面腐蚀形貌及EDS分析
Fig.6
SEM image (a) and EDS elemental mappings of Fe (b), O (c), Ca (d), Zn (e), Cl (f), Na (g) and element contents (h) of the cross section of the corrosion product layer formed on cold galvanized plate after exposure test
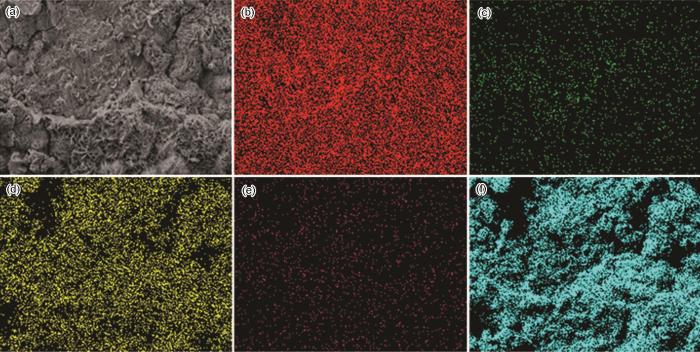
图7
图7
富锌板表面腐蚀形貌及EDS分析
Fig.7
SEM image (a) and EDS elemental mappings of Fe (b), Zn (c), Zr (d), Pt (e) and O (f) of the corrosion product layer formed on zinc rich plate after exposure test
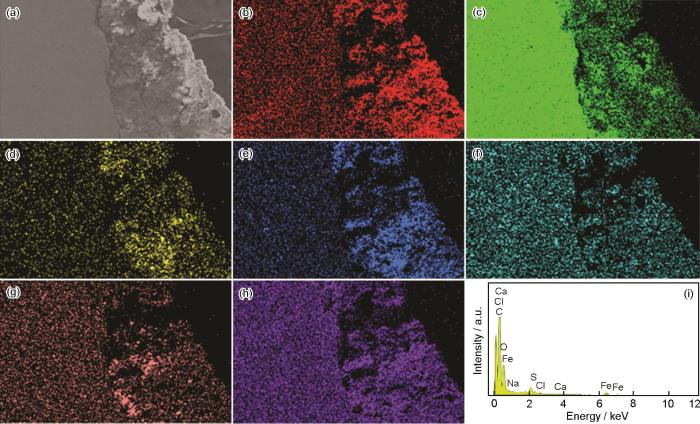
图8
图8
富锌板断面腐蚀形貌,EDS分析及表面腐蚀产物EDS分析
Fig.8
SEM cross-sectional image (a) and EDS elemental mappings of C (b), Fe (c), Zn (d), Na (e), Cl (f), Al (g), O (h) of the corrosion product layer formed on zinc rich plate after exposure test and EDS analysis result of the corrosion products (i)
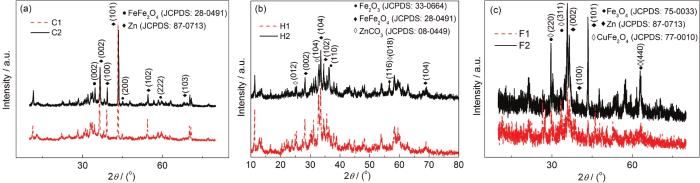
图9
图9
3种锌板正反面腐蚀产物的XRD谱
Fig.9
XRD patterns of the corrosion products formed on the front and back sides of cold galvanized plate (a) hot dip galvanized plate (b) and zinc rich plate (c)
冷镀锌挂板断面处的EDS分析表明,镀层处Zn仍为主体元素,并伴有Cl、Na、O等,而Fe含量很少,这表明了镀锌层的完整性,且基体未发生明显的氧化腐蚀,导致镀层中Fe的氧化物较少。
热浸锌挂板的EDS测试分析结果与冷镀锌测试结果相近,同样含有O、Zn、K、C、Al、S、Ca、Fe等,且断面EDS的元素分析也观察到了Zn为主的镀层元素分布情况,表明了热浸锌层对于碳钢基体的有效保护。
由图7和8可知,富锌挂板表面的主要元素仍为O、Fe、Zn、C、S、Ca、Na等元素。由其断面的EDS分析结果可以明显看出,镀层内的主体元素为Fe,而Zn的含量低于Fe。可见,富锌镀层在挂件试验期间发生了严重的破损,导致碳钢基体发生了腐蚀。
2.2.3 XRD检测
实验后的冷镀锌板的XRD分析结果如图9a所示。冷镀锌的腐蚀产物比较单一,正反面腐蚀产物相同,均为FeFe2O4。相比富锌板,冷镀锌基体表面仍然存在大量的Zn。结合EDS分析结果,证明涂层的防护作用较好。
实验后的热浸锌板表面的XRD分析结果如图9b所示。可知,正反两面的腐蚀产物基本相同,均为FeFe2O4、Fe2O3和ZnCO3。结合FT-IR和EDS的结果判断,基体表面的热浸锌涂层比较致密、含Zn量大,腐蚀防护效果在3种锌涂层中最佳。
实验后的富锌板表面XRD分析结果如图9c所示。正反两面的腐蚀产物中均有Zn,是刮取腐蚀产物时从镀层中刮下来的。由测试结果可知,正反面的腐蚀产物基本相同,主要为Fe3O4和CuFe2O4。结合FT-IR和EDS的结果判断,基体表面的富锌涂层基本被破坏,涂层已基本失效。
2.2.4 Fourier红外检测
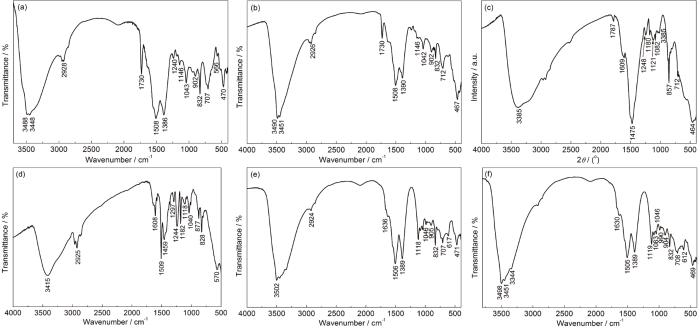
表1 相关红外吸收峰对应的基团
Table 1
| Absorption peak / cm-1 | Chemical bondig group |
|---|---|
| 3442 | Hydroxyl |
| 2922、2847、2923、2359 | HCO3- |
| 1788 | Carbonyl |
| 1636、1637 | HCO3- |
| 856 | NO3- |
| 1439 | CO32- |
| 1083 | C—O stretching vibration |
| 1034、1096 | SO42- |
| 914 | PO43- |
| 800~1200 | [SiO4] tetrahedron Si—O stretching vibration |
| 650~1000 | C—H out of plane bending vibration region |
图10
图10
3种不同镀锌板腐蚀产物的FT-IR图谱
Fig.10
FT-IR spectra of the corrosion products of three different galvanized sheets: (a) front of cold galvanized, (b) back of cold galvanized, (c) front of zinc rich, (d) back of zinc rich, (e) front of hot dip galvanized, (f) back of hot dip galvanized
2.3 锌防护层钢板表面污损生物表征与分析
2.3.1 微型污损生物
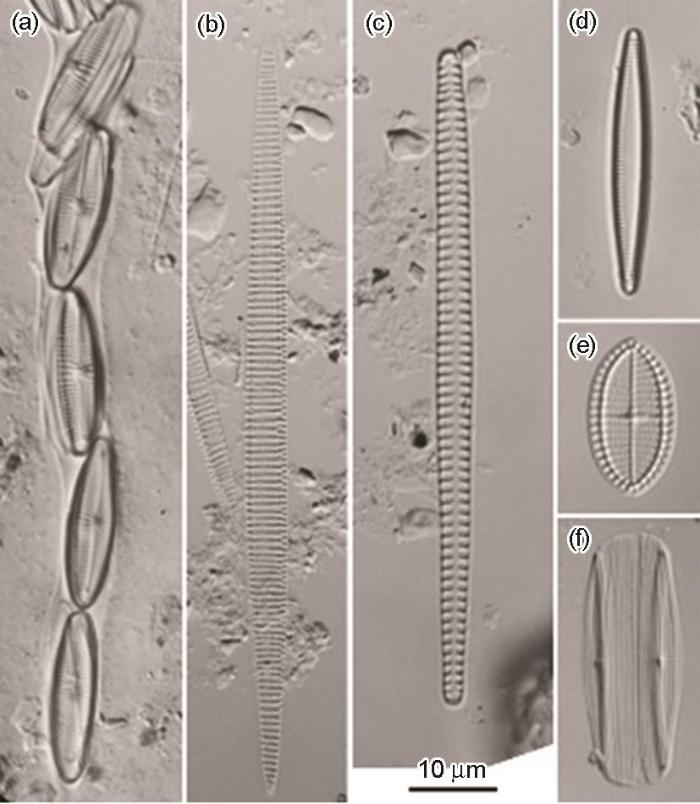
图11
图11
试片附着硅藻优势种
Fig.11
Dominant species of diatoms attaching on the test sheets e (1 bar=10 μm): (a) Parlibellus berkeleyi, (b) Pseudo-nitzschia cf.cuspidata,(c) Tabulariain-vestiens,(d) Tabularia parva, (e) Cocconeisstauron-eiformis, (f) Proschkinia cf. hyalosirella
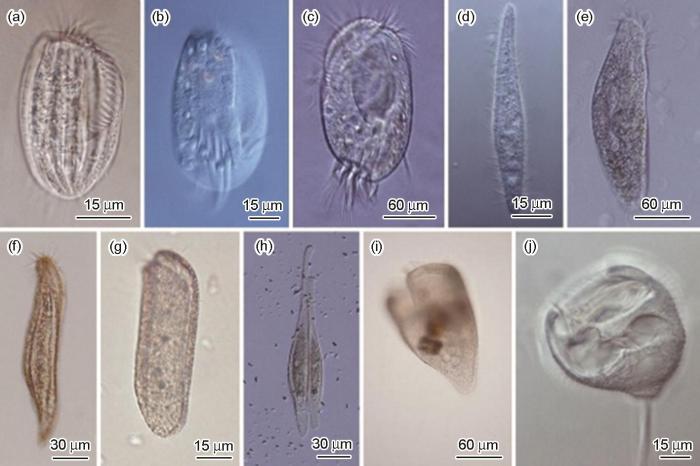
图12
图12
显微镜下玻片附着的纤毛虫活体照片
Fig.12
Microscope views of the living ciliates attaching on the slide: (a) Euplotes raikovi; (b). Euplotes harpa, (c) Diophrys scutum, (d) Cohnilembusverminus, (e) Apokeronopsiscarssa, (f) Anteholostichagracilis, (g) Dysteriaprocera, (h) Loxophyllumperihoplophorum, (i) Condylostentorauriculatus, (j) Pseudovorticella sp.
2.3.2 可视污损生物
由月检和年检可知,常见污损生物有绿藻 (石莼和浒苔)、褐藻 (裙带菜、角毛藻和带藻)、褐红藻 (金箔藻和蜈蚣藻) 等植物类,以及藤壶、牡蛎、苔藓动物、蛃海鞘、玻璃海鞘、覆海鞘、海绵动物、贻贝、水螅和石灰虫等动物类。
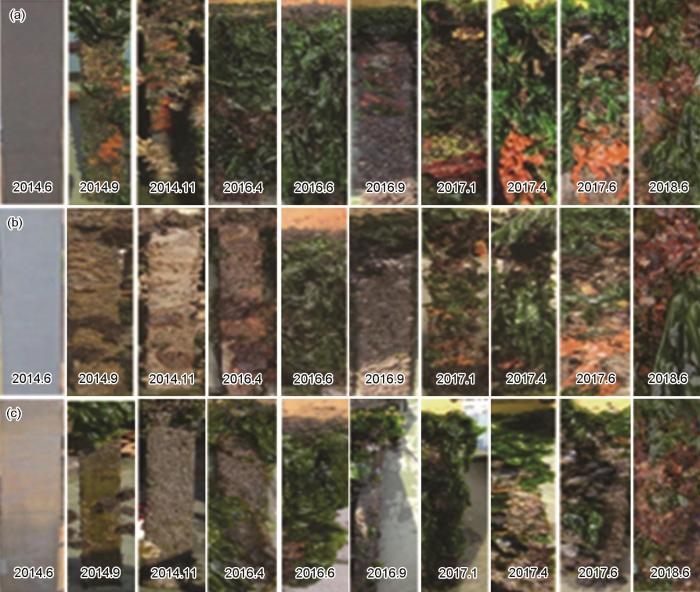
月检表明12月到次年3月为可视生物的休眠期,8,9,10为生长高峰期。不同年份的月变化不同(图13)。同一年的不同月份以及不同年的同一月变化情况均不同。
图13
图13
不同年份富锌涂料、冷镀锌和热镀锌月变化图
Fig.13
Monthly variations of the surface morphologies of zinc rich coating (a), cold galvanizing (b) and hot galvanizing (c) in different years
3 结论
经过长时间实海部分浸入实验后,富锌板涂层由边角裂缝、局部开裂到全部脱落失效,耐蚀性能较差;冷镀锌和热浸锌板在相同条件下保持着较好的阻隔性能,试板表面Zn仍为主体元素,耐蚀性能较好,且热浸锌防护效果更好些。在该海域,主要微型生物为细菌、单胞藻和原生动物,大型生物有20余种。3种材料在浸海的开始阶段,热浸锌和冷镀锌较富锌底漆有较好的防污性能,约三个月后没有明显差异。3种锌涂层按对基体的腐蚀防护作用大小排序为:热浸锌>冷镀锌>富锌涂层。富锌底漆适用于短期防护,及作为底漆同防污防腐漆配套使用;热浸锌或冷镀锌可用于长期防护,防护中还可以用冷镀锌作为热浸锌的修补。
参考文献
A mechanistic study of the enhanced cathodic protection performance of graphene-reinforced zinc rich nanocomposite coating for corrosion protection of carbon steel substrate
[J].
Evaluation of corrosion protection performance of electroplated zinc and inc-graphene oxide nanocomposite coatings in air saturated 3.5%NaCl solution
[J].
Improved anti-corrosion performance of epoxy zinc rich coating on rusted steel surface with aluminum triphosphate as rust converter
[J].
Preparation of graphene nanoplate added zinc-rich epoxy coatings for enhanced sacrificial anode-based corrosion protection
[J].
Characteristics and development status of hot-dip galvanizing and zinc alloy coating in continuous strips
[J].
连续板带热镀锌及锌合金镀层的特点与展望
[J].
Research on effect of hot-dip galvanizing on fatigue properties of Q420 steel for transmission tower
[J].
热浸镀锌对输电铁塔用Q420钢疲劳性能影响的研究
[J].
Effects of hot dip time on mechanical properties of pure zinc and RE-containing zinc alloy coatings
[J].
热浸时间对纯锌和含锌RE合金镀层力学性能的影响
[J].
Influence of surface modified nanoilmenite/amorphous silica composite particles on the thermal stability of cold galvanizing coating
[J].
Preliminary study on fouling organisms and their quantification in Qingdao harbor
[J].
青岛港湾污损生物及其量化初探
[J].
Preliminary study on community change of antifouling coatings/seawater interface in Qingdao harbor
[J].
青岛港湾防污涂料/海水界面细菌污损群落变化初探
[J].
Effect of marine fouling creatures on corrosion of carbon steel
[J]. J.
海洋污损生物对碳钢腐蚀的影响
[J].
Inspirations from the scientific discovery of the anammox bacteria: A classic example of how scientific principles can guide discovery and development
[J].
厌氧铵氧化细菌的科学发现及启示—利用科学原理指引科学发现和推动科学发展的经典范例
[J].
Prochlorococcus viruses—from biodiversity to biogeochemical cycles
[J].
原绿球藻病毒研究进展—从多样性到生物地球化学过程
[J].
Aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria and their roles in marine ecosystems
[J].
好氧不产氧光合异养细菌及其在海洋生态系统中的作用
[J].
Contribution of aerobic photoheterotrophic bacteria to the carbon cycle in the ocean
[J].
Antifouling properties and corrosion resistances of three kinds of zinc coating in the Sea
[J]. J.
三种锌防腐层的海水腐蚀与防污性能初探
[J].
Bicarbonate uptake by marine Crenarchaeota
[J].
Pathways of carbon assimilation and ammonia oxidation suggested by environmental genomic analyses of marine Crenarchaeota
[J].
Zinc-reduced graphene oxide for enhanced corrosion protection of zinc-rich epoxy coatings
[J].
Multivariate analysis with primer on marine phytoplankton community structure in mesocosm system
[J].
应用PRIMER软件进行浮游植物群落结构的多元统计分析
[J].
A research on biofouling of cold galvanizing coatings
[J].
冷镀锌涂料的生物污损研究
[J].
A review of marine fouling communities in the South China Sea
[J].
南海污损生物生态研究进展
[J].
The effect of barnacle adhesion on metal corrosion in seawater
[J]. J.
藤壶附着对海水中金属腐蚀的影响
[J].
A preliminary study on bacterial community of micro-biofilm in Qingdao Zhonggang
[J]. J.
青岛中港微型生物膜中污损细菌群落初探
[J].
Corrosion properties of titanium in marine environments
[J].
Corrosion of carbon steel influenced by SRB and IRB anaerobic biofilm
[J].
硫酸盐还原细菌和铁还原细菌混合生物膜对碳钢腐蚀的影响
[J].
Discussion on the influence of marine biofouling of jacket platform security
[J].
浅谈海洋生物污损对导管架平台安全的影响
[J].
Preliminary study on the relationship between marine micro organisms and metal corrosion
[A].
海洋微型生物与金属腐蚀关系的初步探讨
[A].
Study on biofouling of hot-dip galvanizing materials
[J]. J.
热浸锌材料的生物污损研究
[J].
Mathematical simulation action of corrosion depth data of carbon steel in marine environment
[J]. J.
海洋环境下碳钢腐蚀规律的数学模拟
[J].