管道的腐蚀基本发生在管道的下半部分[6],主要表现为:管壁减薄、局部点蚀,因焊接工艺与现场施工各异,焊接接头往往成为腐蚀诱发源头。目前,国内外研究主要集中在管体母材的耐硫酸腐蚀行为,但对焊接接头的耐硫酸腐蚀研究较少。因此,本文对工业焊管工艺下焊接接头的耐硫酸腐蚀行为进行研究,为长寿管道的选材与焊接工艺优化提供数据支撑。
1 实验方法
表1 试验材料的化学成分
Table 1
| Test material | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu | Sb | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q345NS | ≤0.1 | 0.33 | 0.77 | 0.016 | 0.004 | ≤1.0 | ≤0.4 | ≤0.6 | ≤0.15 | Bal. |
| TH550-NQ-Ⅲ | 0.09 | 0.18 | 1.44 | 0.019 | 0.006 | 0.37 | 0.28 | 0.25 | --- | Bal. |
表2 焊接工艺参数
Table 2
| Welding position | Welding current A | Arc voltage V | Welding speed mm·s-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal welding | 620±60 | 33±2 | 0.9±0.1 |
| outside welding | 750±70 | 34±2 |
参照GB/T 7901对Q345NS钢及其焊接接头进行硫酸全浸实验。实验溶液为20%硫酸,温度为20 ℃,浸泡时间为24 h。腐蚀试样尺寸为50 mm×25 mm×5 mm,每种材料取3个平行样。实验前先用丙酮和无水乙醇进行超声清洗,去除表面油污。试样清洗完毕后置于干燥器中24 h,采用精度为0.1 mg电子天平称量样品的初始质量。
采用HH-6型数显恒温水浴锅进行上述实验,实验后采用含有缓蚀剂 (六次甲基四胺) 的盐酸溶液清洗表面腐蚀产物,酸洗后用清水冲净,再依次用丙酮和无水乙醇浸泡,取出后立即用热风吹干,放入真空干燥箱中保存24 h 后对试样进行称量。
腐蚀速率 (R) 按下式进行计算:
式中,R为腐蚀速率,mm/a;m和mt为实验前后的试样质量,g;s为试样的总面积,cm2;t为实验时间,h;ρ为材料的密度,kg/m3。
相对腐蚀率=RQ345NS/RQ235B×100%。
采用Sigma 500热场发射扫描电镜 (SEM) 对Q345NS焊接接头腐蚀后各区域进行微观形貌观察,并利用其自带的能谱仪 (EDS) 分析腐蚀产物的化学成分;除锈后,利用ATOS I 350XL三维光学测试仪对Q345NS焊接接头进行3D形貌分析。
2 结果和分析
2.1 焊接接头的微观组织分析
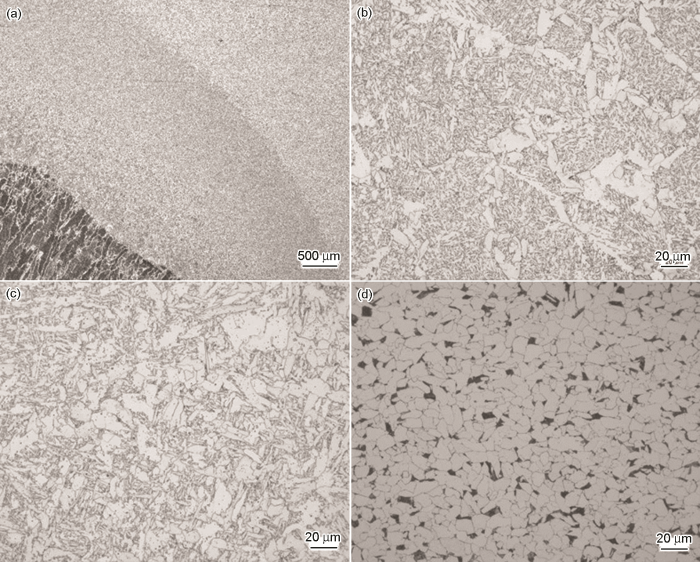
图1
图1
Q345NS钢焊接接头金相照片
Fig.1
Q345NS steel welded joint metallographic photos: (a) welded joint, (b) WM, (c) HAZ, (d) BM
2.2 焊接接头与母材腐蚀速率分析
图2
图2
Q345NS钢焊接接头与母材腐蚀速率
Fig.2
Corrosion rates of Q345NS steel and its welded joint (20 ℃, 20%H2SO4, 24 h)
2.3 焊接接头腐蚀形貌分析
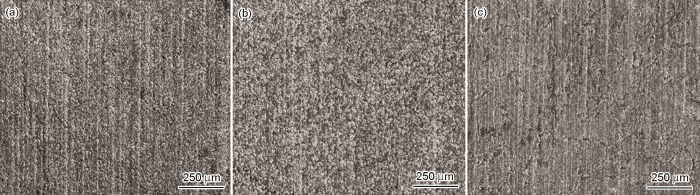
图3为Q345NS焊接接头与母材在20 ℃、20% H2SO4、24 h除锈前后表面腐蚀形貌图片。由图可以清晰看到钢焊接接头BM、HAZ与WM的对应区域,除锈前BM呈灰黑色,HAZ呈淡黄色,WM呈土黄色;除锈后,钢焊接接头与Q345NS母材相比,整体颜色偏淡;就钢焊接接头而言,BM与WM颜色较为相近,呈淡灰色,而HAZ呈灰色。焊接接头各区域颜色的差异性表明其耐蚀性存在差异性。
图3
图3
Q345NS钢焊接接头与母材酸洗前后腐蚀形貌
Fig.3
Corrosion morphologies of Q345NS steel welded joint (a, b) and base metal (c, d) before (a, c) and after (b, d) pickling
BM、HAZ与WM腐蚀后的微观形貌如图4所示。由图可知,BM腐蚀产物较为致密,表面形成大量孔洞,形成大量条带多孔状腐蚀结构;HAZ腐蚀产物结构与BM相似,但腐蚀产物进一步增大;WM与BM腐蚀形貌相似,但出现了局部条带状腐蚀坑,同时也最不均衡。
图4
图4
Q345NS钢焊接接头微观腐蚀形貌
Fig.4
Microstructural characteristics of Q345NS steel welded joint: (a) BM, (b) HAZ, (c) WM
2.4 焊接接头元素扩散行为分析
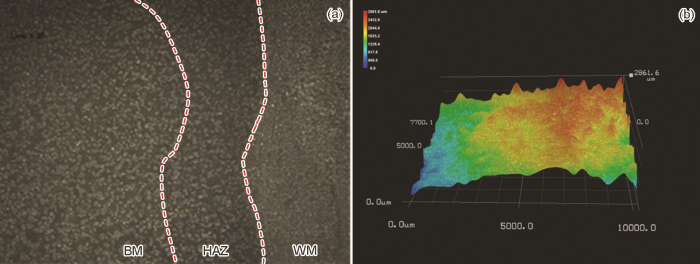
为了进一步分析钢焊接接头不同区域腐蚀差异性,对钢焊接接头腐蚀后的3D形貌进行了分析,结果如图5所示。由图可知,BM腐蚀深度跨度800~2400 μm,多集中于1600~2000 μm,平行焊缝方向腐蚀较为均匀,而垂直焊缝方向上,越靠近焊缝腐蚀深度越浅,腐蚀越轻;WM腐蚀差异性最大,不同位置腐蚀不均,腐蚀深度为400~1600 μm。HAZ腐蚀程度最轻,腐蚀深度为400~800 μm。BM与HAZ腐蚀差异性表明在焊接高温作用下,WM、HAZ内合金元素发生了显著的扩散作用。
图5
图5
Q345NS钢焊接接头3D腐蚀形貌
Fig.5
Microstructural corrosion (a) and 3D corrosion (b) morphologies of Q345NS steel welded joint
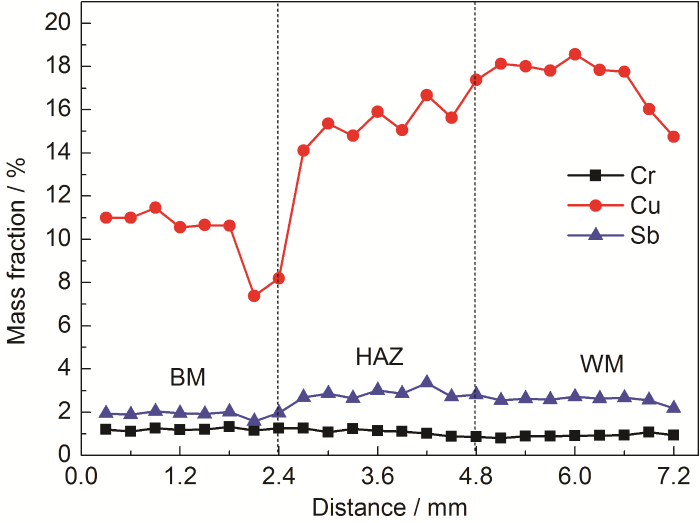
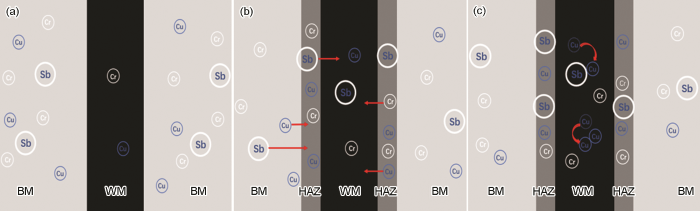
从母材至焊缝方向进行合金元素EDS点扫描,结果如图6所示。由于焊材不含Sb,可见Sb在高温与浓度差的双重作用下,发生了显著的扩散作用。Cu的扩散作用更为明显,且含量波动较大,由于WM温度可达1400 ℃,超过Cu熔点1083 ℃,较大的晶粒尺寸为Cu在晶界富集与扩散提供了有效通道,导致Cu发生显著的二次分配。
图6
图6
Q345NS钢焊接接头不同区域元素含量变化图
Fig.6
Change of element content in different areas of Q345NS steel welded joints
此外在热影响区外靠近母材一侧约600 μm的范围出现了明显的Cr、Cu、Sb元素贫瘠带,成为元素扩散行为的又一佐证。
依据上述分析,建立了腐蚀不同阶段焊接接头元素扩散模型示意图,如图7所示。
图7
图7
Q345NS钢焊接接头元素扩散模型
Fig.7
Q345NS steel welded joint element diffusion model: (a) initial stage, (b) intermediate stage, (c) final stage
2.5 焊接接头腐蚀机理分析
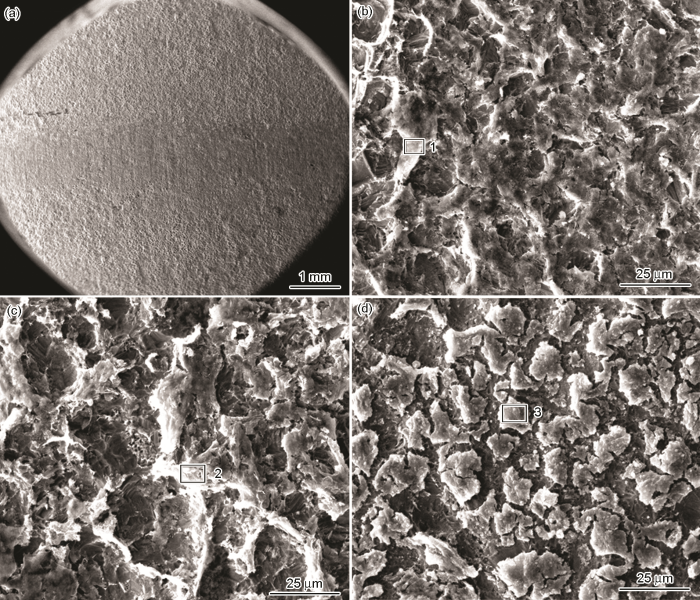
焊接接头在20%H2SO4溶液中腐蚀24 h后腐蚀产物形貌如图8所示。可以看出,BM表面存在大量孔洞,腐蚀产物较为致密,形成多孔状结构形貌。HAZ腐蚀产物结构与BM基本一致,但多孔结构尺寸更大。WM腐蚀程度介于BM与HAZ之间,腐蚀层结构呈破碎的形貌。
图8
图8
Q345NS钢焊接接头在20%H2SO4溶液中腐蚀24 h后腐蚀产物
Fig.8
Q345NS steel corrosion products on the surface of electrodes immersed in 20%H2SO4 solution for 24 h: (a) welded joint, (b) BM, (c) HAZ, (d) WM
表3为焊接接头腐蚀产物的EDS分析,可以判断腐蚀产物主要由Fe的硫酸盐、Cu、Sb化合物及氧化物组成。HAZ中Cu是基体的81倍,Sb同样高达64倍。Sb对含Cu化合物的生成起到了促进作用。
表3 Q345NS焊接接头腐蚀产物的EDS分析
Table 3
| Point | O | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu | Sb | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.26 | 0.72 | 1.09 | 0.50 | 0.68 | 1.51 | 1.02 | 15.27 | 2.13 | 68.34 |
| 2 | 11.68 | / | 0.73 | 1.04 | 0.75 | 1.18 | 1.64 | 25.81 | 4.49 | 50.73 |
| 3 | 26.13 | 0.95 | 4.79 | 0.98 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 1.60 | 23.56 | 4.02 | 32.82 |
3 结论
(1) 硫酸浸泡实验表明,焊接对母材耐蚀性产生了不利影响,Q345NS钢焊接接头的腐蚀速率较母材上升了3.3%,因此焊接时,应选择耐蚀性优于或者与母材相近的焊材。
(2) 焊接过程中,母材与焊材之间的元素浓度差导致了母材中Cr、Cu、Sb等合金元素向焊缝内扩散富集,同时,焊接过程中的高温会促进该进程,导致热影响区靠近母材一侧形成了合金元素贫瘠带;焊缝处高温导致Cu、Sb的二次分配,腐蚀差异性进一步扩大。
(3) Cu、Sb在腐蚀层大量富集,促进腐蚀层致密化,提升了材料耐硫酸腐蚀性能。
参考文献
Overview on rapid corrosion of gas pipe with dry-type blast furnace gas dedusting technology
[A].
干法除尘高炉煤气管道的腐蚀问题综述
[A].
Discussion on rapid corrosion of gas piping occurring in application of dry-type blast furnace gas dedusting technology
[J].
高炉煤气干法除尘中煤气管道快速腐蚀问题探讨
[J].
Analysis of corrosion failure for gas piping conveying dry-dedusted gas and discussion about countermeasures
[J].
高炉干法除尘后煤气管道腐蚀情况分析及对策
[J].
Application of anti-acid corrosion technique in dry dusting system of blast furnace gas
[J].
干法除尘高炉煤气酸性腐蚀防控技术在莱钢的应用及探索
[J].
Causes of corrosion of blast furnace gas pipe and anticorrosive measures
[J].
高炉煤气管道的腐蚀及预防措施
[J].
Research on corrosion mechanism and anticorrosive measures of gas piping
[J].
煤气管道腐蚀机理与预防措施研究现状
[J].
Microstructure and seawater corrosion to welding joint of X70 pipeline steel
[J].
X70管线钢焊接接头组织及其海水腐蚀规律
[J].
Research progress of localized corrosion of welded joints
[J].
焊接接头局部腐蚀的研究进展
[J].
Galvanic corrosion behavior for weld joint of high strength weathering steel
[J]. J.
高强耐候钢焊接接头电偶腐蚀行为研究
[J].
Effect of heating temperature on shear strength of TA2/Q235B compound plate
[J].
加热温度对TA2/Q235B复合板剪切强度的影响
[J].
Diffusion behavior of Cu in carbon steel and its influence on corrosion resistance of carbon steel
[J].
铜在碳钢中扩散及其对碳钢耐腐蚀性的影响
[J].
Application and properties of low alloying sulfuric acid dew point corrosion—resistant steels
[J].
低合金耐硫酸露点腐蚀钢的性能和应用
[J].
Sulfuric-acid dew point corrosion-resistant steel
[J].
耐硫酸露点腐蚀用钢的研究与应用综述
[J].
Effect of antimony on the corrosion behavior of low-alloy steel for flue gas desulfurization system
[J].
Corrosion performance of a new low alloy steel Cu-Sb-Mo for resisting dew-point corrosion induced by sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid
[J].
新型耐硫酸盐酸露点腐蚀钢的性能研究
[J].