在石油天然气工业的酸化作业中,金属管道的腐蚀控制是保障开采效率与设备安全的核心问题之一。酸化处理(如盐酸酸化)通过溶解地层矿物提高储层渗透率,但强酸性环境(pH < 2)会加速碳钢(Fe基)管道的电化学腐蚀,导致管壁减薄、穿孔甚至失效[1,2]。因此,在油气田开采过程中会加入缓蚀剂,以减少金属腐蚀,而传统缓蚀剂(如炔醇类、金属盐)虽能有效抑制腐蚀,但其高毒性、难降解性及对生态系统的长期危害,与全球“双碳”目标及绿色化学理念背道而驰[3~5]。以甲醛衍生物为例,其作为常用酸化缓蚀剂[6],已被国际癌症研究机构(IARC)列为1类致癌物,欧盟等地区已逐步限制其使用。因此,开发环境友好、可再生的绿色缓蚀剂成为油气工业可持续发展的迫切需求[7]。
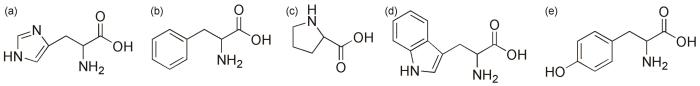
近年来,生物基缓蚀剂因其可再生性、低毒性和环境兼容性成为研究热点。植物提取物[8]、多糖(如壳聚糖)[9]及碳量子点[10]等生物基衍生物被证实具有一定缓蚀效果。例如,邓志华等[11]采用回流提取法从香根草提取到香根草提取物(VZE),评价了在1.0 mol/L HCl溶液中对碳钢的缓蚀作用,当温度为40 ℃时,缓蚀率可达91.9%。Wang等[12]合成了4种壳聚糖衍生物,在15% (质量分数) HCl中对低碳钢缓蚀效率均可达90%。氨基酸作为具有精确分子结构的天然产物,被视为传统缓蚀剂的理想替代品[13]。尤其是含环状结构的氨基酸(图1),其独特的分子构型(如吡咯环、咪唑环或苯环)赋予其更强的金属表面吸附能力和化学稳定性。研究表明,环状结构可通过π电子共轭或孤对电子与金属表面空轨道形成配位键,同时疏水环结构可增强分子在金属/溶液界面的定向排列,从而构建致密的保护膜[14]。
图1
图1
组氨酸、苯丙氨酸、脯氨酸、色氨酸以及酪氨酸的分子结构图
Fig.1
Molecular structure of histidine (a), phenylalanine (b), proline (c), tryptophan (d) and tyrosine (e)
本研究遵循Peng等[17]确立的“纯Fe(110)计算模型+工业钢材实验”的缓蚀剂研究范式。以石油天然气工业中广泛应用的Fe基材料为对象,选取如图1所示的典型含环类氨基酸(组氨酸、苯丙氨酸、脯氨酸、色氨酸、酪氨酸)为缓蚀剂,通过DFT计算解析氨基酸分子结构与其吸附性能之间的关系;结合分子动力学模拟,研究氨基酸在金属表面的作用机制,以工业标准钢材(N80钢)作为实验对象对理论计算结果进行实验验证。本研究旨在建立“分子结构-动态吸附-缓蚀性能”的构效关系,为绿色缓蚀剂的定向设计提供理论依据,同时推动计算化学在油气腐蚀防护领域的应用深化。通过融合多尺度模拟,有望突破传统试错法研发模式的局限性,加速高性能生物基缓蚀剂的工业化进程,助力油气行业向低碳化、可持续化方向转型。
1 实验模拟方法
1.1 DFT理论计算方法
采用BIOVIA Materials Studio2020软件中的DMOL3模块对氨基酸分子进行了DFT计算。BIOVIA Materials Studio2020软件提供可视化操作界面。首先,将双数值加极值化(DNP)设置为4.4,通过BLYP泛函和GGA基组对其进行结构优化。结构优化时,体系能量(Values of energy),最大力(Max. force),最大位移(Max. displacement)设为1 × 10-5 Ha,0.020 Ha/nm和0.005 Ha作为收敛准则,将收敛次数(Iterations)设置为50,以保证循环次数。自洽场容忍度(SCF tolerance)和最大值迭代次数(Max. iterations)分别为1 × 10-6和50次,以保证高精度的自洽场收敛。在结构优化成功后,计算了所有缓蚀剂分子的量子化学参数来预测结构差异并计算氨基酸分子的量子化学参数,如HOMO与LUMO轨道能量,福井函数以及它们之间的能隙(ΔE)、电离势(I)、电子亲合势(A),分子硬度(μ)、电负性(χ)以及电子转移率(ΔN),并利用软件绘制了缓蚀剂分子HOMO与LUMO轨道图,同时绘制了缓蚀剂分子的静电势分布图[18,19]。相关参数通过公式(
其中,μFe代表Fe的硬度,ΦFe代表Fe晶体的功函数,μcorr代表缓蚀剂的分子硬度,χcorr代表缓蚀剂的电负性,EHOMO代表最高占据分子轨道,ELUMO代表最低未占据分子轨道能量。
1.2 分子动力学模拟方法
其中,D为扩散系数,MSD(t)为腐蚀性粒子在一定时间间隔内位移平方的平均值,Nα 为粒子数,ri (0)和ri (t)分别表示粒子在初始时刻和t时刻的位置。
为确保计算结果的重复性和准确性,本研究采用多次独立重复实验来消除系统误差。针对分子动力学模拟,3种含环氨基酸在Fe(110)的吸附行为均经过3次独立重复计算,每次模拟均重置初始构型并随机化分子取向。量子化学计算部分,采用DFT对氨基酸分子进行3次独立几何优化与电子结构分析,每次计算均重置初始原子坐标并随机扰动键长(±0.01 nm)。最后得到的相关计算参数均为3次独立重复实验所得结果的平均值。
1.3 电化学测试方法
电化学方法所用仪器为CS310M型电化学工作站,测试系统为三电极体系,包括工作电极、对电极和参比电极。工作电极为N80碳钢,化学成分(质量分数,%)为:Cr 0.20,Mn 0.92,S 0.008,P 0.01,Si 0.19,C 0.31,Fe 98.362),作为低碳合金钢,其腐蚀活性位点集中于Fe相。N80钢中Fe相电子云分布与纯Fe(110)晶面的表面Fe原子高度一致[26]。工作电极使用之前,首先用砂纸抛光,然后用乙醇和蒸馏水进行洗涤,确保其表面光滑。对电极为铂电极,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极。在测试之前,首先要进行系统的开路电位稳定性测试,测试时间为1800 s。待其稳定后,进行电化学阻抗谱(EIS)和Tafel极化曲线测试。EIS测试频率为105~10-2 Hz,测试电压幅值为10 mV。Tafel极化曲线测试的扫描范围为相对于开路电位的±0.2 V,扫描速率0.5 mV/s。采用Zview软件和CS Analysis软件对测试结果进行分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 DFT计算结果及分析
DFT理论计算,包括HOMO-LUMO能量分析,越来越多地用于预测缓蚀剂的缓蚀效率。这些计算预测了了缓蚀剂向金属表面提供电子和接受电子的能力,从而影响保护层的形成并最终影响腐蚀抑制性能。在本项工作中基于密度泛函理论来研究5种氨基酸的结构稳定性、电子性质以及反应活性。
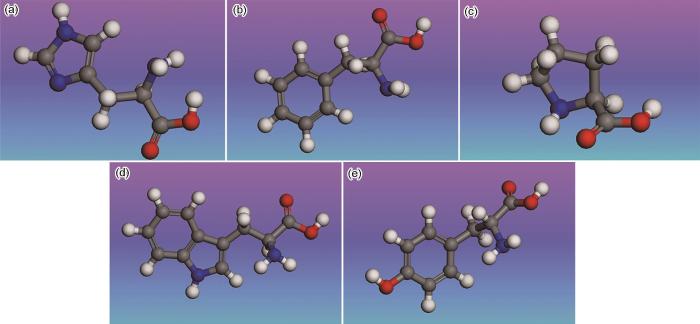
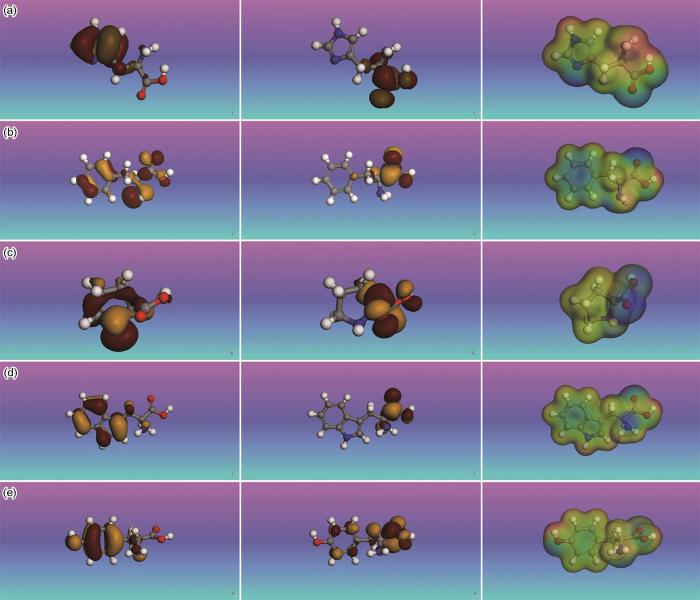
本文通过B3LYP (Becke,3-parameter,Lee-Yang-Parr)泛函中的GGA基组(Generalized gradient approximation)算法对氨基酸分子进行了结构优化,得到了其最稳定的几何构形(图2),可以看出,5种氨基酸的中心结构均基于其分子中的苯环或含氮杂环结构。图3展示了组氨酸、苯丙氨酸、脯氨酸、色氨酸和酪氨酸等5种含环氨基酸分子的HOMO和LUMO分布特征。从图中可以看出,5种氨基酸的HOMO主要分布于分子中的芳香环结构、含氮杂环以及氮原子周围区域。这一分布特征表明,氨基酸分子中的环状结构以及氮原子能够提供电子,从而与Fe原子的d-空轨道形成配位键,产生显著的吸附效应[27,28]。而LUMO则主要分布在羧基基团附近,这表明氨基酸分子中的羧基基团能够接收Fe原子的d轨道电子,形成反馈键,从而进一步增强了氨基酸分子在金属表面的吸附能力[29,30]。
图2
图2
组氨酸、苯丙氨酸、脯氨酸、色氨酸以及酪氨酸的几何优化结构
Fig.2
Geometrically optimized structures of histidine (a), phenylalanine (b), proline (c), tryptophan (d) and tyrosine (e)
图3
图3
组氨酸、苯丙氨酸、脯氨酸、色氨酸以及酪氨酸的HOMO、LUMO轨道及静电势(ESP)分布
Fig.3
HOMO (left), LUMO (middle) orbital and electrostatic potential (ESP) distribution of histidine (a), phenylalanine (b), proline (c), tryptophan (d) and tyrosine (e)
基于DFT计算结果,并结合公式(
表1 含环氨基酸量子计算相关参数值
Table 1
| Inhibitors | EHOMO / eV | ELUMO / eV | ΔE / eV | I / eV | A / eV | μ / eV | χ / eV | ΔN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histidine | -5.082 | -0.876 | 4.206 | 5.082 | 0.876 | 2.103 | 2.979 | 0.361 |
| Phenylalanine | -5.365 | -1.113 | 4.252 | 5.365 | 1.113 | 2.126 | 3.239 | 0.296 |
| Proline | -5.131 | -1.06 | 4.071 | 5.131 | 1.06 | 2.035 | 3.095 | 0.345 |
| Tryptophan | -4.586 | -0.981 | 3.605 | 4.586 | 0.981 | 1.802 | 2.783 | 0.476 |
| Tyrosine | -5.12 | -1.027 | 4.093 | 5.12 | 1.027 | 2.046 | 3.073 | 0.378 |
为了进一步分析氨基酸分子在吸附过程中的电子转移行为,以Fe作为模型金属,设定ηFe为0,Fe晶体ΦFe为4.50 eV,计算了氨基酸分子的ΔN。根据定义,当ΔN > 0时,缓蚀剂分子向金属表面提供电子;当ΔN < 0时,缓蚀剂分子从金属表面获取电子[34]。计算结果表明,5种氨基酸分子的ΔN值均大于0,说明5种氨基酸分子在吸附过程都可以将电子提供给金属表面。其中,色氨酸的ΔN值(0.456)显著高于其他4种氨基酸,表明色氨酸向金属表面提供电子的能力更为显著,从而更有利于其在金属表面的吸附。
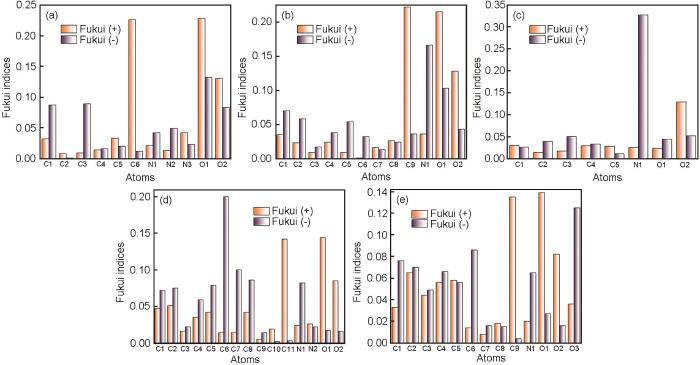
HOMO和LUMO轨道的计算结果提供了氨基酸分子全局反应性和分子轨道的信息,但无法直接确定分子中易于接受或失去电子的活性中心。通过福井函数指数计算,可以确定氨基酸分子中易于得失电子的活性中心。结合Hirshfeld布局分析,进一步研究了氨基酸分子的亲电和亲核位点,结果如图4。
图4
图4
组氨酸、苯丙氨酸、脯氨酸、色氨酸以及酪氨酸的Fukui函数指数
Fig.4
Fukui function index of histidine (a), phenylalanine (b), proline (c), tryptophan (d) and tyrosine (e)
分析结果表明,5种氨基酸分子均具有多个能够与金属表面发生相互作用的活性中心。具体而言,组氨酸分子中C(6)和O(1)处的f+值最大(分别为0.226和0.228),苯丙氨酸分子中C(9)和O(1)处的f+值最大(分别为0.222和0.215),脯氨酸分子中O(2)处的f+值最大(0.129),色氨酸分子中C(11)和O(2)处的f+值最大(分别为0.142和0.144),酪氨酸分子中C(9)和O(1)处的f+值最大(分别为0.135和0.139)。这表明5种氨基酸分子均具有较高的亲核性,能够向金属表面提供电子,增强缓蚀剂与金属表面的相互作用。此外,组氨酸分子中O(1)、C(1)、C(3)处的f-值最大(分别为0.132、0.087、0.089),苯丙氨酸分子中N(1)和O(1)处的f-值最大(分别为0.166和0.103),脯氨酸分子中N(2)处的f-值最大(0.327),色氨酸分子中C(6)和C(7)处的f-值最大(分别为0.2、0.1),酪氨酸分子中O(3)处的f-值最大(0.125)。这表明5种氨基酸分子均具有较高的亲电性,能够接纳来自金属表面的电子,有助于形成保护层,防止腐蚀[35]。
2.2 分子动力学计算结果及分析
为了更好地理解氨基酸分子与金属表面之间的吸附机理,以Fe作为金属基底进行了MD模拟以研究氨基酸分子与金属表面之间的界面接触。采用
其中,Etotal代表整个吸附体系(金属晶体、吸附的氨基酸分子和溶液)的总能量;Esurface + solution是在无氨基酸分子的情况下金属表面和溶液的总能量;EAA + solution表示氨基酸分子和溶液的总能量,而Esolution表示溶剂分子的势能。此外,结合能(Ebinding)是Eads的负值,如
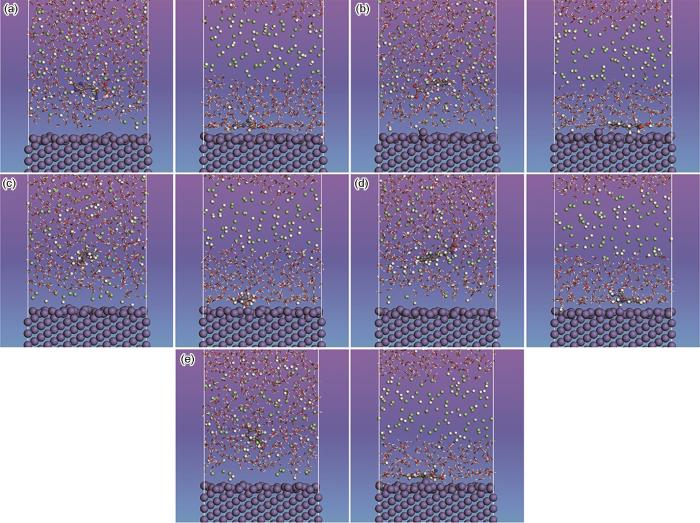
以Fe作为金属基底,在HCl溶液中研究了氨基酸分子在Fe表面的吸附行为。图5a~e展示了5种氨基酸分子在Fe表面的吸附前后的构像。吸附前(左侧),氨基酸分子以不规则形态存在于酸液中,且与金属表面保持较远距离;吸附后(右侧),氨基酸分子基于其分子中的环状结构,以平行于Fe(110)表面的方式吸附在其表面,从而在金属表面形成致密的吸附膜,有效阻止腐蚀介质与金属表面的接触。
图5
图5
组氨酸、苯丙氨酸、脯氨酸、色氨酸以及酪氨酸在Fe(110)表面吸附前、后构像
Fig.5
Conformation before (left) and after (right) adsorption on Fe(110) surface of histidine (a), phenylalanine (b), proline (c), tryptophan (d) and tyrosine (e)
表2 含环氨基酸与Fe(110)表面的相互作用吸附能和结合能
Table 2
| Inhibitors | Eads / kJ·mol-1 | Ebinding / kJ·mol-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Histidine | -307.11 | 307.11 |
| Phenylalanine | -379.01 | 379.01 |
| Proline | -288.16 | 288.16 |
| Tryptophan | -381.45 | 381.45 |
| Tyrosine | -366.40 | 366.40 |
采用MD模拟方法,研究了溶液中腐蚀性物质(H+、Cl-)在H2O相或氨基酸分子膜相中的扩散行为,从而有效评估氨基酸分子的缓蚀性能。为此,构建了腐蚀性物质(H+、Cl-)在H2O相和吸附的5种氨基酸分子膜相中扩散的三维模型。在NVT条件下,对每个扩散模型依次进行MD模拟,计算得到了腐蚀性物质(H+、Cl-)在模型中的均方位移(MSD (t))曲线,结果如图6。
图6
图6
H+和Cl-在空白H2O相和吸附氨基酸分子膜相中扩散的均方位移图
Fig.6
Mean square displacement plots of H+ (a) and Cl- (b) diffusion in the blank H2O phase and adsorbed amino acid film phase
选取扩散模型的250~501 ps时间段作为研究对象,基于
表3 腐蚀性物质(H+、Cl-)在H2O相和氨基酸分子膜相中的扩散系数
Table 3
| Solution | H+ / cm2·s-1 | Cl- / cm2·s-1 |
|---|---|---|
| H2O | 2.87 × 10-5 | 2.19 × 10-6 |
| Histidine | 2.78 × 10-6 | 2.67 × 10-7 |
| Phenylalanine | 2.02 × 10-6 | 3.54 × 10-8 |
| Proline | 1.39 × 10-6 | 9.15 × 10-9 |
| Tryptophan | 5.67 × 10-7 | 1.77 × 10-9 |
| Tyrosine | 6.46 × 10-7 | 2.52 × 10-9 |
腐蚀性物质(H+、Cl-)在氨基酸分子膜中的扩散系数显著低于空白溶液中的扩散系数,表明吸附的氨基酸分子膜能够有效阻碍腐蚀性物质向金属表面扩散。值得注意的是,色氨酸分子膜中的扩散系数最小,表明其对腐蚀性离子扩散的抑制作用最为显著,从而展现出优异的缓蚀性能[38],结果与前文关于氨基酸在Fe表面吸附能的计算结果一致。
2.3 数据重复性与误差分析
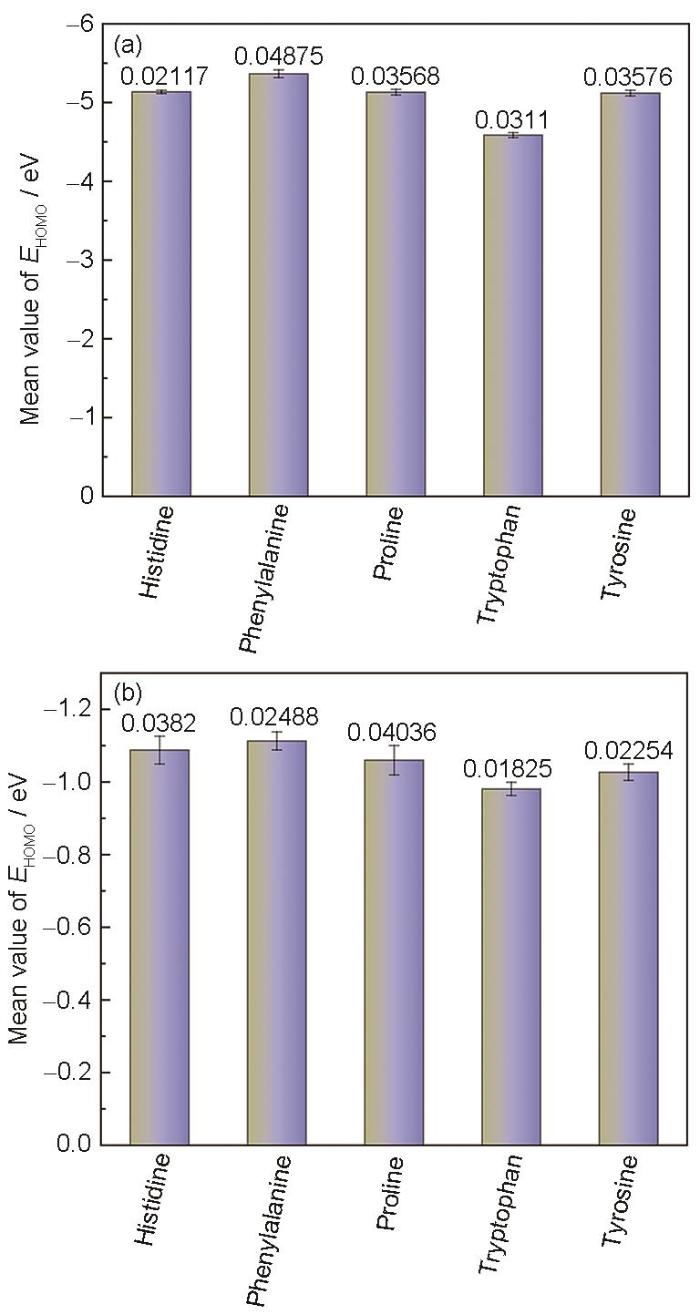
针对含环氨基酸缓蚀机制的MD模拟与DFT计算结果,通过3次独立重复计算评估计算误差及实验可重复性。对5种氨基酸分别进行3次独立DFT结构优化参数设置与收敛标准与上文一致。在结构优化成功后,计算了氨基酸分子的HOMO及LUMO轨道参数,结果如图7所示。可以看出,5种氨基酸HOMO及LUMO轨道参数标准差均小于0.05 eV,数据波动处于可接受范围。
图7
图7
氨基酸分子在HOMO及LUMO DFT模拟误差棒图
Fig.7
DFT simulation error bar graph of amino acid molecules in HOMO (a) and LUMO (b)
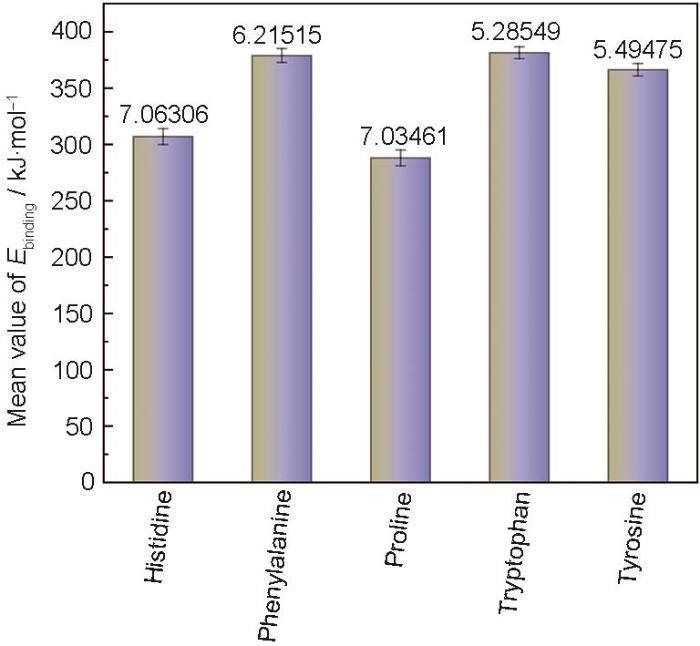
同样,对5种氨基酸分别进行3次独立MD模拟,采用相同力场与参数设置。参考
图8
图8
氨基酸分子在Fe(110)表面MD模拟误差图
Fig.8
MD simulation error bar chart of amino acid molecules on Fe(110) surface
2.4 实验验证
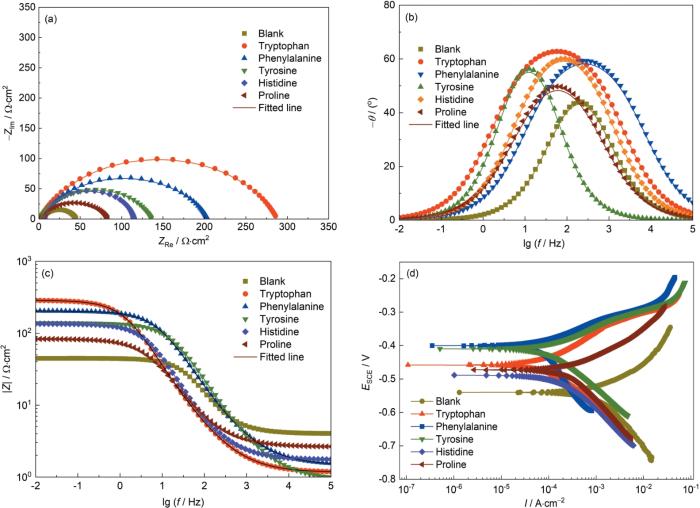
对5种氨基酸在20% (质量分数) HCl溶液中的缓蚀性能进行测试(添加量为0.1 mmol/L),结果如图9所示。图9a展示了5种氨基酸在该酸溶液中的Nyquist图。图中所有Nyquist曲线均呈扁状半圆形,其容抗弧直径显著大于纵向尺寸。添加氨基酸后,Nyquist曲线均表现出高频区电容电弧和低频区感应电弧的特征,且与未添加氨基酸时相比,曲线形状未发生明显改变。这表明氨基酸的加入虽然改变了N80钢表面的吸附行为并提高了缓蚀效率,但并未改变其在酸液中的腐蚀机理[39]。加入氨基酸后,容抗弧直径均增大,说明酸液与N80钢表面之间的电荷转移过程受到抑制[40]。图9b和c为相应的Bode图,从中可见,添加氨基酸后体系的阻抗模值和相角值均升高,表明氨基酸在N80钢表面吸附形成了保护层[41]。
图9
图9
N80钢在含和不含氨基酸的20%HCl溶液中的电化学测试结果
Fig.9
Electrochemical results of N80 steel in 20%HCl solution with and without amino acids: (a) Nyquist plots, (b) Bode plots, (c) Bode phase diagram, (d) potentiodynamic polarization curves
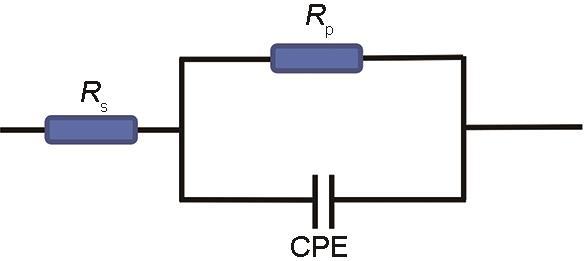
其中,R0代表未加氨基酸时的极化电阻,Rp代表加入氨基酸后的极化电阻。
图10
表4 N80碳钢在20%HCl中含不同氨基酸时的阻抗参数
Table 4
| Inhibitors | Rs/ Ω·cm2 | Rp/ Ω·cm2 | CPE-T/ µF·cm-2 | CPE-P | ηE/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 4.009 | 50.75 | 233.81 | 0.82 | - |
| Histidine | 1.738 | 108.40 | 62.08 | 0.79 | 53.18 |
| Phenylalanine | 1.477 | 202.63 | 41.19 | 0.75 | 74.95 |
| Proline | 2.629 | 90.79 | 82.93 | 0.74 | 44.10 |
| Tryptophan | 1.668 | 276.54 | 36.80 | 0.58 | 81.65 |
| Tyrosine | 1.690 | 133.93 | 54.91 | 0.90 | 62.11 |
图9d为5种氨基酸在20%HCl溶液中的动电位极化曲线图。加入氨基酸后,动电位极化曲线(PDP)的总体趋势并未发生明显变化,氨基酸的加入并未改变金属在酸液中的腐蚀机制,这与EIS测试结果相吻合。此外,氨基酸加入后,PDP曲线向左移动,说明其腐蚀发生的程度降低。极化曲线的腐蚀电位整体上移,说明氨基酸主要通过抑制阳极金属溶解反应(Fe→Fe²⁺ + 2e-)发挥作用。这与上文中的理论计算结果相吻合,氨基酸分子中含有富电子基团(如氨基-NH2)可在金属表面形成强化学吸附,阻断了Fe原子电离的活性位点。同时,5种氨基酸分子的ΔN值均大于0,表明氨基酸分子向金属表面提供电子,在阳极区形成致密吸附层,抑制阳极溶解反应的发生[44]。分子动力学模拟表明,氨基酸分子骨架中的刚性环状结构可以在表面形成三维空间屏障,这种致密排列通过空间位阻效应物理阻隔H⁺/Cl-侵蚀,抑制金属溶解反应(Fe→Fe²⁺ + 2e-)的发生,从动力学上延缓阳极溶解[45]。
其中,I0代表未添加氨基酸时的腐蚀电流密度,I代表添加氨基酸后的腐蚀电流密度。
表5 未添加和添加不氨基酸的N80碳钢在20%HCl中的PDP参数
Table 5
| Inhibitor | ba / mV·dec-1 | bc / mV·dec-1 | I / mA·cm-2 | ηE / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 94.455 | 185.50 | 1.09 | - |
| Histidine | 96.44 | 129.77 | 0.26 | 61.35 |
| Phenylalanine | 65.227 | 259.74 | 0.17 | 75.82 |
| Proline | 99.185 | 133.41 | 0.49 | 55.32 |
| Tryptophan | 96.886 | 119.31 | 0.17 | 83.93 |
| Tyrosine | 67.825 | 130.82 | 0.29 | 73.15 |
从表5可以看出,加入氨基酸后,I均明显降低,并且当加入色氨酸时,I为0.17 mA/cm2最低,缓蚀效率达83.93%。这和上文中阻抗测试保持一致。根据电化学测试结果可知,5种含环氨基酸中色氨酸拥有最佳的缓蚀性能,这与上文中理论计算部分结果保持一致,验证了理论计算结果的可靠性。
3 结论
(1) 理论模拟表明,5种氨基酸均可通过吸附作用抑制金属腐蚀,其中色氨酸展现出显著优于其他氨基酸的缓蚀性能。分子动力学结果揭示,色氨酸在金属表面形成致密有序的吸附层,其独特的吲哚环取向构建了高效疏水屏障,有效阻隔H⁺/Cl-侵蚀。密度泛函理论进一步阐明其微观作用机制:色氨酸的HOMO轨道主要分布于吲哚环与氨基,可向金属空d轨道提供电子,形成反馈键;LUMO轨道则集中于杂环结构及羧酸,通过接受金属表面电子增强吸附稳定性。其全局反应性参数远高于其他氨基酸,证实色氨酸具有更强的电荷转移能力,利于构建稳定的缓蚀界面,这种特性使其能协同抑制阳极金属溶解与阴极析氢反应。
(2) 电化学测试结果表明,5种氨基酸的缓蚀效率排序与理论预测完全一致:色氨酸在Fe表面的缓蚀效率达83.93%,色氨酸的缓蚀性能源于以下协同机制;化学吸附可形成致密物理覆盖层。HOMO轨道的电子转移可降低金属表面氧化活性,削弱阳极溶解反应的驱动力,同时阻碍阴极析氢反应的发生。分子结构中的非极性芳香结构的疏水效应可有效阻隔水分子及腐蚀性离子的界面接触,从而降低金属/溶液界面的双电层反应活性。三者协同形成防护体系,共同提升缓蚀效率。
参考文献
Research, development and performance evaluation of XAI-180, a new acid corrosion inhibitor with high temperature resistance
[J].
新型耐高温酸化缓蚀剂XAI-180的研发与性能评价
[J].
Performance of two new surfactants as acidizing inhibitors for oil and gas fields
[J].
新型表面活性剂作为油气田酸化缓蚀剂的制备及其性能研究
[J].利用芥酸和油酸两种绿色原材料合成了新型的表面活性剂缓蚀剂,并对两种缓蚀剂在15%(质量分数) 盐酸溶液中进行了一系列性能测试。结果表明,两种缓蚀剂在90 ℃条件下具有良好的缓蚀效果,可以作为油气田酸化有效的缓蚀剂;通过电化学测试从电化学机理上揭示了缓蚀剂的性能;通过扫描Kelvin探针 (SKP) 和扫描电子显微镜 (SEM) 从表面形貌角度研究了其微观腐蚀情况,相比于空白组,实验组表面形貌保持较好的状态,说明两种缓蚀剂具有良好的效果;最后通过量子化学计算,从分子计算角度证实合成的缓蚀剂具有有效的作用,同时也展示出实验和理论结果的相关性。
Role of organic and eco-friendly inhibitors on the corrosion mitigation of steel in acidic environments—A state-of-art review
[J].Steel has versatile application in chemical, structure and construction industries owing to its mechanical properties. However, it is susceptible to corrosion in acid environments. Thus, it requires to protect the steel from corrosion. Different types of corrosion resistance steel, coatings and inhibitors are developed to mitigate the corrosion, but, inhibitor is the best remedies to control the corrosion of steel in acid condition. Moreover, organic and green inhibitors used in acid condition for descaling, acid pickling, pipelines, boiler tubes and oil-wells. Organic inhibitors reduce the dissolution of steel in acid but, it is hazardous, expensive and needs expertise to synthesize the inhibitor. Therefore, there is utmost required to study and compile the latest research about the eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors, which showed more than 90% corrosion inhibition efficiency. In the present study, I have reviewed the state-of-arts, and compile the latest development in organic and eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor used in acid environment as well as suggested about the future scope and role of green inhibitor for sustainable society, which is economical, less hazardous and readily available from the natural sources.
Understanding the impact of N-Arylpyridinium ions on the selectivity of CO2 reduction at the Cu/electrolyte interface
[J].
Application of corrosion inhibitors for steels in acidic media for the oil and gas industry: A review
[J].
Applied research of Mannich reaction in synthesis of acidifying corrosion inhibitor
[J].
Mannich反应在酸化缓蚀剂合成中的应用
[J].
Research status and development trend of inhibitors
[J].
缓蚀剂的研究现状及发展趋势
[J].
Inhibitory action of coffee skin extract on corrosion of steel in trichloroacetic acid solution
[J].
咖啡果皮提取物对钢在三氯乙酸溶液中的缓蚀性能
[J].采用失重法、电化学法、红外光谱(FTIR)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、接触角、表面张力等测试研究了农林废弃物咖啡果皮提取物(CSE)在0.10 mol·L<sup>-1</sup> 三氯乙酸(Cl<sub>3</sub>CCOOH)中的缓蚀性能。结果表明,500 mg·L<sup>-1</sup> CSE在20℃时缓蚀率高达93.7%;20和30℃下CSE在钢表面的吸附规律遵循Langmuir吸附等温式,而40和50℃下则服从Freundlich吸附等温式,标准吸附Gibbs自由能(ΔG<sup>0</sup>)在-30~-41 kJ·mol<sup>-1</sup>范围,CSE在钢表面的吸附类型为以化学吸附为主的混合吸附。CSE属于阴极抑制型缓蚀剂。添加CSE使电荷转移电阻增大,而界面双电层电容值下降。添加CSE的缓蚀钢表面的SEM微观形貌腐蚀程度和粗糙程度显著下降,但疏水性增强。FTIR表明CSE中含有大量O原子和芳香环等极性基团。随着CSE的添加,缓蚀溶液体系的表面张力逐渐降低,溶液电导率增加,钢腐蚀浸泡后,溶液表面张力较浸泡前有所增加,而溶液电导率较浸泡前有所降低。
Application and research progress of chitosan in corrosion inhibitor
[J].
壳聚糖在缓蚀剂领域的应用研究进展
[J].壳聚糖作为天然绿色高分子中第二大丰富的资源,具有无毒、可降解和成本低等优点,被广泛应用于金属的防腐蚀领域,已成为绿色缓蚀剂中性能优异的一员。综述了壳聚糖基缓蚀剂的应用研究进展,包括壳聚糖及其复配物、不同改性壳聚糖和壳聚糖复合材料三大类。总结了目前壳聚糖基缓蚀剂在金属防腐蚀缓蚀领域中存在的问题,希望深入研究壳聚糖基作为缓蚀剂的缓蚀作用机理,获得缓蚀效率更高和更加实用环保的壳聚糖基缓蚀剂。
Corrosion inhibition performance of biomass-derived carbon dots on Q235 steel
[J].
生物质碳点对Q235钢的缓蚀性能研究
[J].金属腐蚀威胁金属设施的安全性和可靠性,也加剧了环境污染和经济损失问题。然而,使用可持续、可再生且经济的原材料制备绿色缓蚀剂现阶段仍是有挑战性难题。本文以荔枝叶为原料制备了生物质基碳点(CDs),并采用失重法、电化学阻抗谱和动电位极化曲线系统研究了其在1 mol/L HCl中对Q235钢的缓蚀性能。所获得的生物质基CDs具有丰富的含氧和含氮官能团,这些官能团使CDs在1 mol/L HCl溶液中保持稳定,具有长期有效的缓蚀性能。
Corrosion inhibition of vetiver extract on steel in hydrochloric acid environment
[J].
香根草提取物对冷轧钢在盐酸溶液中的缓蚀作用
[J].采用回流提取法对香根草 (Vetiveria zizanioides) 提取得到香根草提取物 (VZE),利用失重法和电化学法研究了VZE在1.0 mol/L HCl溶液中对碳钢的缓蚀作用。结果表明:温度为40 ℃,VZE浓度为0.20 g/L时,缓蚀效果最佳,缓蚀率可达91.9%。VZE在钢表面的吸附符合Langmuir吸附等温式,吸附类型为物理吸附和化学吸附相结合的混合吸附型。动电位极化曲线表明,VZE可同时抑制阴极和阳极反应,属于混合抑制型缓蚀剂。Nyquist图谱的容抗弧随VZE浓度的增大而明显增大,碳钢的电荷转移电阻增大,腐蚀反应速率降低,从而起到缓蚀作用。
Experimental and theoretical studies of chitosan derivatives as green corrosion inhibitor for oil and gas well acid acidizing
[J].
Analysis of the protection of copper corrosion by using amino acid inhibitors
[J].
Synthesis and performance of a novel acidizing corrosion inhibitor for high temperature reservoirs
[J].In order to better slow down the corrosion of metal under high temperature acidification in oil and gas fields, a compound acidizing corrosion inhibitor with high temperature resistance and simple formula was investigated. A novel fused heterocyclic quaternary ammonium salt (BQD) was prepared by 'one-pot' reaction with quinoline and benzyl chloride as raw materials. A novel high temperature acidizing corrosion inhibitor GS-1 with simple formula was obtained by weight loss method optimization of single factor analysis with synthetic BQD as the main agent, adding formic acid, urotropine and other compound agents. At the same time, its inhibition performance was studied by electrochemical test, surface morphology analysis and quantum chemical calculation. And the inhibition mechanism of BQD was studied by molecular simulation. The results showed that when the dosage of GS-1 corrosion inhibitor was 3%, the corrosion rates of N80 steel sheets in hydrochloric acid and mud acid at 160℃ were 41.63g/(m2·h) and 31.94g/(m2·h), respectively, which were better than the requirements of industry standards. The high temperature inhibitor GS-1 could form an adsorption protective film on the surface of N80 steel sheets, which could inhibit the mixed corrosion inhibitor of anode and cathode reaction at the same time. Quantum chemical calculations and molecular dynamics simulations indicated that the corrosion inhibition activity of BQD was better than that of the common benzylquinoline quaternary ammonium salt corrosion inhibitor (BQC). At the same time, the BQD molecule was based on the conjugated plane and was adsorbed on the interface at an angle parallel to the metal substrate, which had more better inhibition performance.
新型高温酸化缓蚀剂的制备及性能评价
[J].为了更好地减缓油气田高温酸化下金属的腐蚀,研究出一种耐高温且配方简单的复合酸化缓蚀剂。以喹啉和氯化苄为原料,采用“一锅法”制备得到了一种新型稠杂环季铵盐(BQD)缓蚀主剂。通过添加甲酸、乌洛托品等复配剂,经过单因素失重法优选,得到一种配方简单的新型高温酸化缓蚀剂GS-1,通过电化学测试、表面形貌分析研究其缓蚀性能,采用分子模拟的方法研究BQD的缓蚀机理。结果表明,GS-1缓蚀剂在添加量为3%时,在160℃下盐酸与土酸的酸化环境中,N80钢片的腐蚀速率分别降低至41.63g/(m<sup>2</sup>·h)、31.94g/(m<sup>2</sup>·h),均可达行业标准要求;GS-1缓蚀剂可在N80钢片表面形成一层吸附保护层,属于兼具抑制阳极和阴极反应的混合型缓蚀剂;量子化学计算及分子动力学模拟表明,BQD的缓蚀活性优于常见的苄基喹啉季铵盐缓蚀剂(BQC),同时BQD分子是以共轭平面为基准,与金属基底平行的角度被吸附于界面上,具有更加高效的缓蚀性能。
Application of quantum chemistry method in the performance evaluation and mechanism study of corrosion inhibitors
[J].
量子化学方法在缓蚀剂性能评价和机理研究中的应用
[J].
Research progress of molecular simulation technology in the development and application of chitosan functional materials
[J].Chitosan is widely used in medicine, energy, environmental protection and other fields because of its excellent biocompatibility, renewability, biodegradability, flocculation and adsorption. With the rapid development of computer science and quantum chemistry, the application of molecular simulation to the development and application of chitosan materials has become a hot spot. In this paper, the research progress of molecular simulation technology in this field in recent years was reviewed, the basic methods and characteristics of molecular simulation were summarized, and the common modules and applications of quantum chemistry based molecular simulation software Materials Studio in chitosan research were described in detail. On this basis, the analysis and prediction of molecular structure, micro reaction mechanism and compatibility of chitosan by molecular simulation, as well as the research progress of molecular simulation of chitosan in the fields of biomedical materials, fuel cell, corrosion inhibitor and water treatment were introduced. The advantages of molecular simulation method in the development and application of chitosan functional materials and the shortcomings in the exploration of micro mechanism were summarized and analyzed. The research methods of using multi-scale simulation and combining with machine learning to improve the accuracy and calculation speed of simulation results were proposed, which provided a new idea for the design and development of new chitosan materials in the future.
分子模拟技术在壳聚糖功能材料开发和应用中的研究进展
[J].
A new exceptional imidazoline derivative corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in supercritical CO2 environment
[J].
Combined DFT and Monte Carlo simulation studies of potential corrosion inhibition properties of coumarin derivatives
[J].Corrosion, the degradation of materials due to chemical reactions with their environment presents significant challenges both economically and environmentally. It affects various industries, including construction, transportation, and manufacturing, leading to equipment failures, safety hazards, and increased maintenance costs. Coumarin derivatives have shown promise due to their inherent chemical properties and potential for biodegradability. In this study, a series of the coumarin derivatives were examined in silico to reveal their potential corrosion inhibition properties toward the Fe(110) and Cu(111) surfaces. The compounds investigated include coumarin (2H-chromen-2-one, 1), furanocoumarin (7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one, 2), dihydrofurano coumarin (2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one, 3), pyrano coumarin-linear type (8,8-dimethyl-2H,8H-pyrano[3,2-g]chromen-2-one, 4), pyrano coumarin-angular type (8,8-dimethyl-2H,8H-pyrano[2,3-f]chromen-2-one, 5), bicoumarin (3,3'-methylenebis(2H-chromen-2-one), 6), and phenyl coumarin (4-phenyl-2H-chromen-2-one, 7). The findings suggest that the bicoumarin derivative 6 exhibits the lowest adsorption energy with the Fe(110) surface, while the same energy absolute value is about two times lower for the Cu(111) surface. This is due to the formation of a planar configuration of a molecule of 6 on the metal surfaces with the participation of both coumarin fragments upon interacting with the Fe(110) surface, while one coumarin fragment interacts with the Cu(111) surface.Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were employed to study the electronic properties of the coumarin derivatives. The specific computational method used was B3LYP, a hybrid functional that combines with the 6-311 + + G(d,p) basis set. Each coumarin derivative was first subjected to a geometry optimization to find the most stable molecular structure. Electronic properties, dipole moments, and molecular electrostatic potential surfaces were calculated. The Monte Carlo simulations were used to model the adsorption behavior of the coumarin derivatives on metal surfaces, namely, Fe(110) and Cu(111). These simulations allowed to visualize interaction of the studied molecules with the metal surfaces, which is crucial for their function as corrosion inhibitors. The present study provides a comprehensive understanding of the corrosion inhibition potential of the applied coumarin derivatives. The insights gained from these methods can inform the development of effective, sustainable corrosion inhibitors that are both environmentally friendly and highly efficient.© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Inhibition of Q235 steel in 1 mol/L HCl solution by a new efficient imidazolium Schiff base corrosion inhibitor
[J].
新型高效咪唑希夫碱缓蚀剂对Q235钢在1 mol/L HCl溶液中的缓蚀作用
[J].
Mechanism analysis of highly effective imidazole-Schiff corrosion inhibitor on P110 in HCl solution
[J].
高效咪唑-席夫缓蚀剂对P110在HCl溶液中的缓蚀机理分析
[J].
Diffusion behavior of waste soybean oil rejuvenated bitumen based on molecular simulation
[J].To gain insight into the interaction and diffusion behavior of components in waste soybean oil rejuvenated bitumen from a molecular scale, the molecular models of base bitumen, aged bitumen and rejuvenated bitumen were constructed by means of molecular dynamics simulation, and the double-layer bitumen (bitumen-bitumen) models were constructed. The interaction energy and mean square displacement (MSD) were utilized to characterize the diffusion behavior of components in the rejuvenated bitumen models and the binding strength between waste soybean oil and bitumen components. The interfacial interaction energy and molecular diffusion behavior of the double-layer bitumen models were evaluated. The results showed that there was an attractive interaction between the waste soybean oil and bitumen components, and the interaction energy of 5% waste soybean oil rejuvenated bitumen was approximately 95.8% higher than that of 2% waste soybean oil rejuvenated bitumen, indicating that with the increase of the amount of waste soybean oil, the interaction energy gradually increased. By calculating the MSD, it was found that with the increase of the amount of waste soybean oil, the diffusion performance of the bitumen components in the rejuvenated bitumen model gradually increased. The waste soybean oil could effectively improve the molecular migration ability of the bitumen components in the aged bitumen model, while the component migration ability could not fully be restored to the level of base bitumen. The interfacial interaction energy of the base bitumen-aged bitumen model decreased by approximately 8.6% compared with that of base bitumen-base bitumen model, showing that the interfacial interaction ability of the virgin-aged bitumen at the molecular scale was attenuated. With the increase of the amount of waste soybean oil, the van der Waals interaction was gradually enhanced, and the interfacial interaction energy of base bitumen-8% waste soybean oil rejuvenated bitumen was basically the same as that of base bitumen-aged bitumen. The components in the base bitumen-rejuvenated bitumen model had a great diffusion rate when the content of waste soybean oil was 2%—5%. The results provided a theoretical basis for the application of waste soybean oil rejuvenated bitumen from the molecular scale.
基于分子模拟的废大豆油再生沥青扩散行为
[J].
Mechanism of temperature influence on adsorption of schiff base
[J].
温度影响席夫碱缓蚀剂吸附的机理研究
[J].研究了所合成的两种含有苯基基团的席夫碱缓蚀剂 (BB-S缓蚀剂和B-S缓蚀剂) 在不同温度下对N80钢在0.5%盐酸溶液中的缓蚀作用,探讨了温度影响席夫碱缓蚀剂的吸附机理。结果表明,BB-S缓蚀剂和B-S缓蚀剂的缓蚀效率随着温度的升高而降低,且B-S缓蚀剂的缓蚀效率在不同温度下始终大于BB-S缓蚀剂的缓蚀效率。分子动力学和量子化学计算方法表明,两种席夫碱缓蚀剂的缓蚀效率随温度的升高而降低,该现象与席夫碱缓蚀剂中苯环较大的空间位阻、分子热运动、分子吸附构型以及前线轨道能级密切相关。
Evaluation of corrosion inhibition of a bis-imidazoline corrosion inhibitor
[J].
双咪唑啉缓蚀剂的缓蚀性能评价
[J].
Design and synthesis of a novel corrosion inhibitor embedded with Quaternary ammonium, amide and amine motifs for protection of carbon steel in 1 M HCl
[J].
Comparison of the synergistic inhibition mechanism of two eco-friendly amino acids combined corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel pipelines in oil and gas production
[J].
Water-soluble chitosan salt as ecofriendly corrosion inhibitor for N80 pipeline steel in artificial sea water: experimental and theoretical approach
[J].
Oil soluble mannich base corrosion inhibitor for corrosion inhibition of copper in transformer oil
[J].
油溶性曼尼希碱缓蚀剂对紫铜在变压器油中的缓蚀行为研究
[J].通过甲醛,十二胺和乙酰丙酮合成一种油溶性曼尼希碱类缓蚀剂(OMB),采用Fourier变换红外光谱(FT-IR)表征其结构。用盐雾实验分析OMB和石油磺酸钡(T701)以25#变压器油作为基础油配置防锈油后对紫铜的缓蚀性能,使用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和原子力显微镜(AFM)进行腐蚀形貌观察,使用X射线光电子能谱(XPS)对表面进行成分分析,并结合量子化学计算和分子动力学模拟,以及Langmuir等温吸附方程式,进一步探讨了OMB对紫铜的缓蚀机理。结果表明:OMB是一种在盐雾环境下对紫铜具有优良缓蚀效果的缓蚀剂,其在紫铜表面的吸附行为为自发性吸附,符合混合吸附规律且以化学吸附为主,且平行吸附于Cu的表面。
A comparative experimental and theoretical calculation study of CaAl-LDH modified with various aromatic inhibitors for corrosion protection study in epoxy coatings
[J].
Food spices 2,5-dihydroxy-1,4-dithiane as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for X70 steel in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution
[J].
食用香料1,4-二硫-2,5-二醇环保型缓蚀剂对X70钢在0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的缓蚀性能研究
[J].使用实验和理论计算方法研究了食用香料1,4-二硫-2,5-二醇 (DDD) 对X70管线钢在0.5 mol/L硫酸溶液中的缓蚀性能。结果表明,DDD能够有效的抑制X70钢在H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>介质中的腐蚀,在温度为298 K时,DDD的缓蚀效率可以达到93.6%;随着温度的升高,DDD依然能够展现出良好的缓蚀性能。腐蚀微观形貌观察也证明了DDD能够明显抑制X70钢的腐蚀。吸附等温模型研究结果表明,DDD在X70钢表面的吸附符合Langmuir单层吸附。采用量子化学计算和分子动力学模拟从理论层面讨论了DDD在钢表面的吸附及缓蚀机理。
L-Tryptophan as green corrosion inhibitor for low carbon steel in hydrochloric acid solution
[J].
Corrosion inhibition effect of benzimidazole and two derivatives on copper in alkaline environments: experimental and theoretical analyses
[J].
Corrosion inhibition mechanism of the eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor linagliptin on copper in sulfuric acid
[J].
一种环保型缓蚀剂利拉利汀对紫铜在硫酸中的缓蚀机理研究
[J].使用电化学阻抗技术、失重法等研究了一种被用于治疗人类糖尿病且价格低廉的利拉利汀 (LNLP) 药物在0.5 mol/L硫酸溶液中对Cu的缓蚀作用和缓蚀机理。结果表明,LNLP能够有效抑制Cu在硫酸中的腐蚀,是一种绿色环保型缓蚀剂。电化学阻抗测试显示该物质能够增大Cu表面的膜电阻和电荷转移电阻,降低膜电容和双电层电容来减缓Cu在0.5 mol/L硫酸溶液中的腐蚀速率。当LNLP浓度仅为1 mmol/L时,其缓蚀效率高达99.95%。动电位极化曲线测试结果表明,LNLP是一种谦逊的混合型缓蚀剂,能够有效地抑制Cu表面的阴阳极反应。利用吸附等温曲线和理论计算探究了LNLP与Cu表面的相互作用和LNLP分子结构与缓蚀性能之间的构效关系。结果表明,LNLP在Cu表面的吸附是一种平行吸附形态,最大程度地为Cu提供了保护。LNLP分子在Cu表面的吸附主要是以分子内的氮、氧杂原子和共轭的环状官能团为活性吸附中心,通过物理和化学吸附的协同作用,在Cu表面形成了单分子层膜,隔绝了腐蚀介质与Cu表面的接触。
Synthesis of a novel fused heterocyclic Quaternary ammonium salt and its performance in ultra-low dosage as acidizing corrosion inhibitor
[J].
A comprehensive computational study of N-phenylacetamide derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for copper: Insights from DFT and molecular dynamics
[J]. J.
N, N-Bis (2,4-dihydroxy benzaldehyde) benzidine:Synthesis, characterization, DFT,and theoretical corrosion study
[J].
The Quaternary ammonium salts as corrosion inhibitors for X65 carbon steel under sour environment in NACE 1D182 solution: experimental and computational studies
[J].
Novel gossypol-indole modification as a green corrosion inhibitor for low-carbon steel in aggressive alkaline-saline solution
[J].
Gleditsia sinensic extract as green corrosion inhibitor for N80 steel in 1 M HCl
[J].
Synthesis and multifunctional application of two novel carbon quantum dots as corrosion inhibitors
[J].
Studies on pyrimidine derivative as green corrosion inhibitor in acidic environment: electrochemical and computational approach
[J].
Schiff bases as corrosion inhibitorson mild steel in acidic medium: gravimetric, electrochemical, surface morphological and computational studies
[J].
Green corrosion inhibitors for drilling operation: new derivatives of fatty acid-based inhibitors in drilling fluids for 1018 carbon steel in CO2-saturated KCl environments
[J].
New corrosion inhibitor acrylamide methyl ether for mild steel in 1 M HCl
[J].
Study on synergistic mechanism of inhibitor mixture based on electron transfer behavior
[J].Mixing is an important method to improve the performance of surfactants due to their synergistic effect. The changes in bonding interaction and adsorption structure of IM and OP molecules before and after co-adsorbed on Fe(001) surface is calculated by DFTB+ method. It is found that mixture enable the inhibitor molecules with higher E-HOMO donate more electrons while the inhibitor molecules with lower E-LUMO accept more electrons, which strengthens the bonding interaction of both inhibitor agent and inhibitor additive with metal surface. Meanwhile, water molecules in the compact layer of double electric layer are repulsed and the charge transfer resistance during the corrosion process increases. Accordingly, the correlation between the frontier orbital (E-HOMO and E-LUMO of inhibitor molecules and the Fermi level of metal) and inhibition efficiency is determined. Finally, we propose a frontier orbital matching principle for the synergistic effect of inhibitors, which is verified by electrochemical experiments. This frontier orbital matching principle provides an effective quantum chemistry calculation method for the optimal selection of inhibitor mixture.