氢促进局部塑性变形理论的发展趋势
Hydrogen Enhanced Localized Plasticity: A Critical Review
氢促进局部塑性变形理论的发展趋势 |
| 张倩茹, 孙擎擎 |
|
Hydrogen Enhanced Localized Plasticity: A Critical Review |
| ZHANG Qianru, SUN Qingqing |
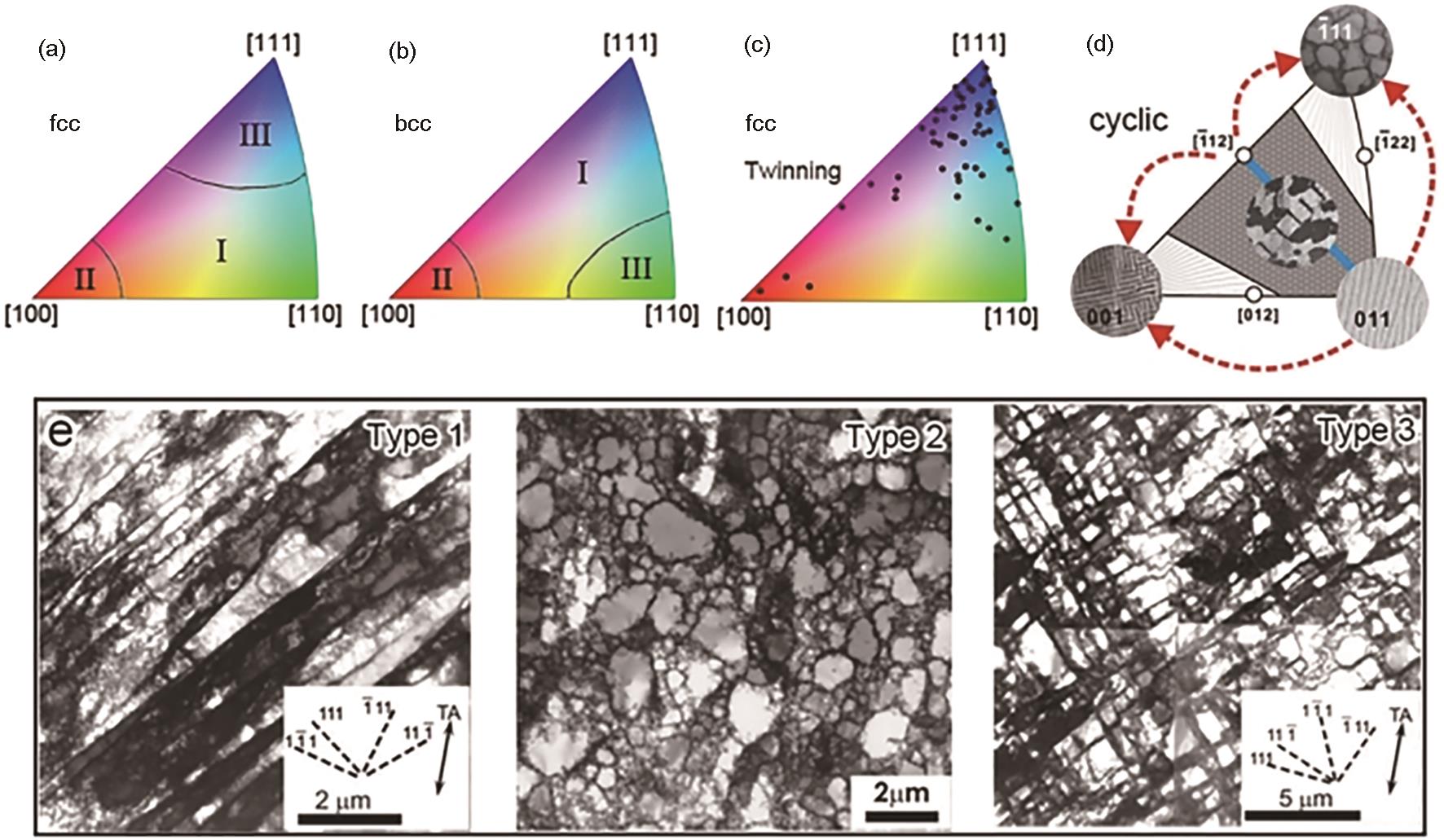
| 图4 金属变形组织的晶体取向关联性[ |
| Fig.4 Orientation dependence of deformed microstructure in metals: (a) orientation dependence of dislocation structure of fcc metals with medium to high stacking fault energy during uniaxial tension[ |

|