本研究采用绿色、简便的水热法从可再生的荔枝叶中制备了生物质CDs,并详细研究了其在HCl溶液中的腐蚀防护性能。研究表明,所制备的CDs含有丰富的含氧和含氮官能团,在HCl溶液中呈现出高达97.70%的缓蚀率。此外,我们通过吸附等温线和腐蚀形貌分析,揭示了其缓蚀机理。本研究证明了生物质基CDs在腐蚀防护中具有良好的缓蚀性能,为推动绿色高效缓蚀剂的开发提供了新的思路。
1 实验方法
碳钢是工程和日常生活应用中最广泛使用的金属之一,具有低成本、高强度和耐磨等优点。本文采用Q235钢,其含量(质量分数,%)为:C 0.18,Si 0.3,Mn 0.6,Cr 0.25,P 0.045,S 0.045,Cu 0.25,Ni 0.25,Fe余量。实验前,使用400至2000级不同粒度的砂纸依次打磨Q235钢试样,然后用去离子水洗涤和乙醇脱脂,最后在冷气流下干燥。使用AR级别36%~38%的盐酸稀释至1 mol/L浓度。荔枝叶从深圳大学校园收集,并在洗净、干燥和粉碎后使用。
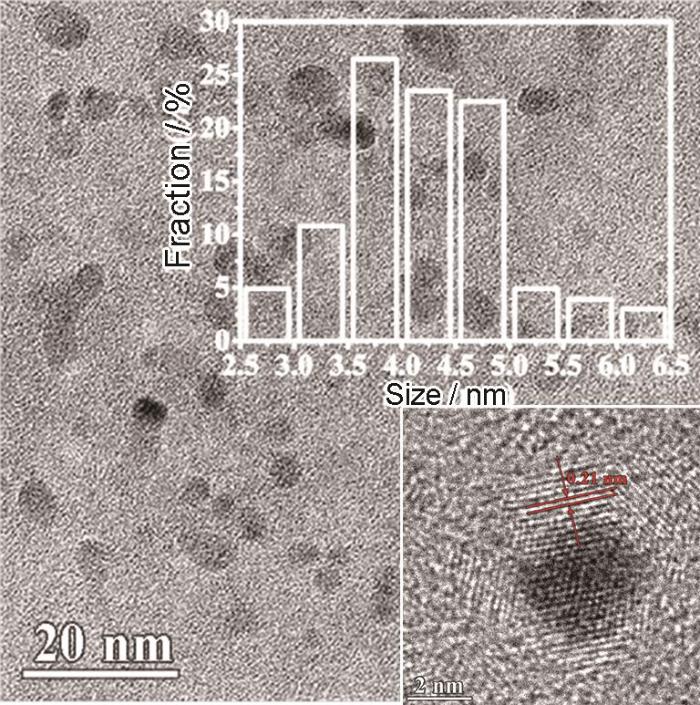
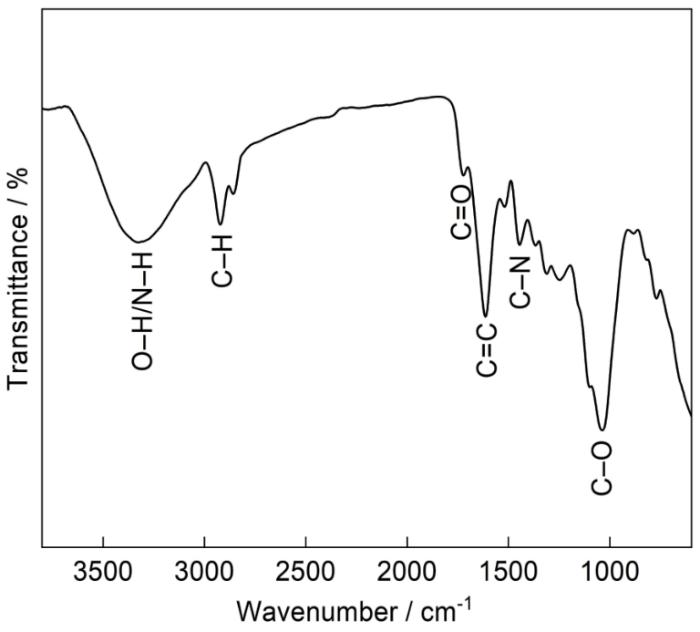
将2 g干荔枝叶和100 mL去离子水密封在150 mL聚四氟乙烯内衬的不锈钢高压釜中,加热到200℃处理12 h。自然冷却至室温后,将棕黄色混合物在10000转下离心10 min,然后通过0.2 μm的滤膜去除残留的树叶大颗粒。随后,通过旋转蒸发和真空冷冻干燥,得到棕黑色的固态荔枝CDs粉末,产率约为5%。采用透射电子显微镜(TEM,FEI Talos F200S)观察所制备CDs形貌。采用Fourier变换红外光谱仪(FTIR,Thermo Scientific Nicolet6700)对CDs基团进行观测。
将15 mm × 15 mm × 3 mm的Q235钢试样浸泡在不同浓度的CDs中的1 mol/L盐酸溶液中96 h,每24 h冲洗干燥后迅速称重3次。测试前,所有试样均通过精密电子天平称重3次,精度为0.0001 g。失重实验在室温下进行。根据公式计算腐蚀速率和缓蚀效率(η):
式中,ΔW为样品3次称重的平均失重,g;A为样品的比表面积,cm2;t为浸泡时间,h;vcorr为不加CDs溶液的腐蚀速率,mg·cm-2·h-1;
将CDs直接加入1 mol/L HCl中,分别形成CDs浓度为25、50、100和200 mg/L的HCl溶液。采用三电极系统(暴露面积为1 cm²的Q235钢作为工作电极(WE)、饱和甘汞电极作为参比电极(RE)、Pt片作为对电极(CE)),在PARSTAT 4000 + 电化学工作站上进行电化学阻抗谱(EIS)和动电位极化(PDP)测试。所有测试均在室温下完成。测试前,开路电位(OCP)应达到稳定状态。EIS测量范围为105~10-2 Hz,振幅为10 mV;PDP扫描电位范围为± 250 mV,速率为1 mV/s。所有电化学实验均进行3次以确保重现性。EIS数据采用ZSimDemo 3.30软件拟合和分析。
取出试样后,进行清洗和干燥,并存放于真空烘箱中进行形态观察。采用Zeiss Sigma 300型扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和自带的能谱仪(EDS)分析试样表面的二维形态和元素组成。通过FTIR获取试样表面的化学状态。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 CDs的表征分析
图1
图2
图3
图3
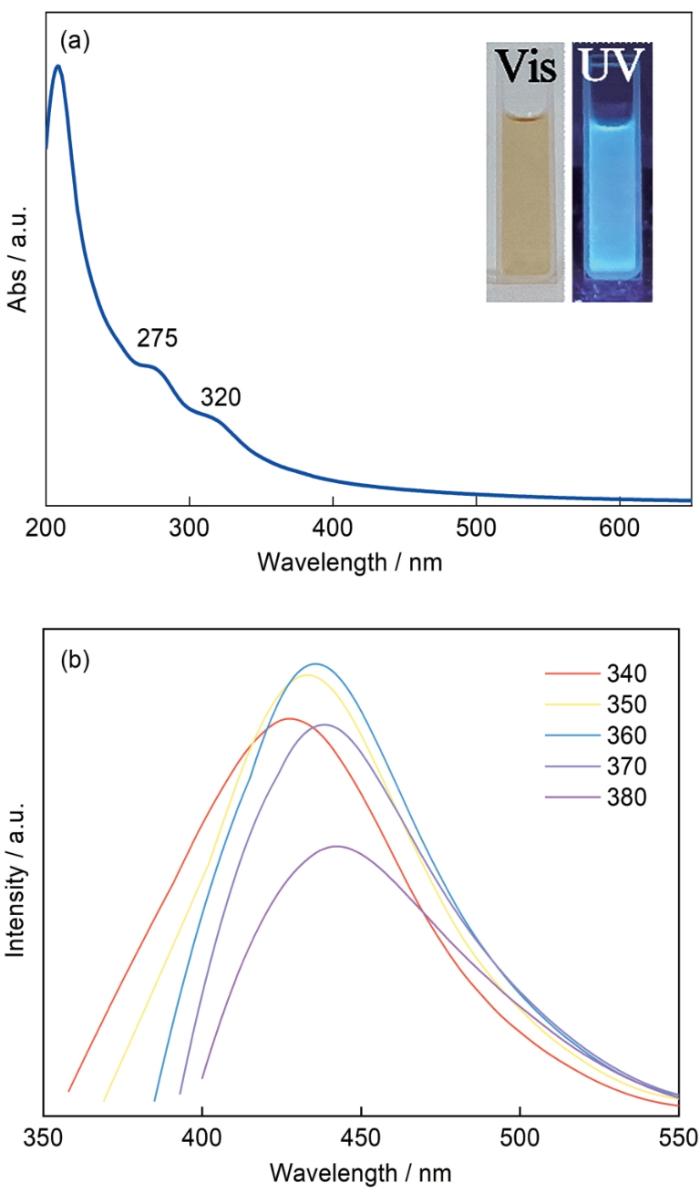
1 mg/mL的CDs水溶液UV-Vis光谱以及用不同激发波长测试得到的PL光谱
Fig.3
UV-Vis absorption spectrum (a) and PL spectra with different excitation wavelengths (b) of 1 mg/mL CDs aqueous solution. The inset photo-graphs shown in Fig.3a are 1 mg/mL CDs aque-ous solution taken under sunlight and a 365 nm UV light
2.2 CDs的缓蚀效果研究
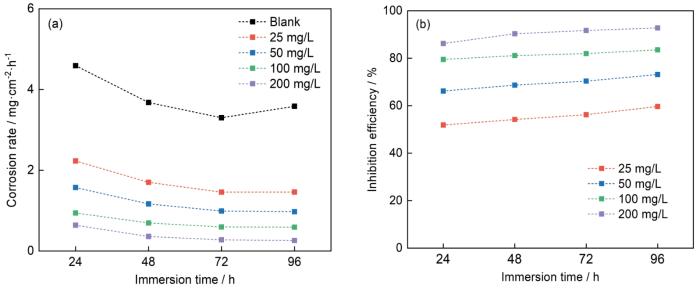
为了研究CDs作为Q235钢在1 mol/L HCl中缓蚀剂的效果,进行了失重实验、EIS和PDP测量。图4描述了不同CDs浓度下,在室温下不同浸泡时间内Q235钢在1 mol/L HCl中的腐蚀速率和CDs的缓蚀效率(η)情况。与空白溶液相比,加入CDs后,无论CDs的浓度或浸泡时间如何,腐蚀速率都大大降低。随着CDs浓度的增加,腐蚀速率呈显著下降趋势(图4a)。当CDs的含量为200 mg/L时,在24 h浸泡后,Q235钢的腐蚀速率相对于空白溶液下降了86.06%(从4.59 mg·cm-2·h-1降至0.64 mg·cm-2·h-1)。更重要的是,随着浸泡时间的延长(图4b),CDs的η从86.06%升至92.74%,表明CDs作为长期缓蚀剂具有出色的潜力。失重实验的所有结论均证明了CDs的高效缓蚀性能和长期缓蚀潜力。
图4
图4
Q235钢在含不同浓度CDs的1 mol/L HCl溶液中浸泡不同时间的腐蚀速率和缓蚀率随时间的变化曲线
Fig.4
Variations of corrosion rate (a) and inhibition efficiency (b) vs immersion time of Q235 steel in 1 mol/L HCl solution with different contents of CDs
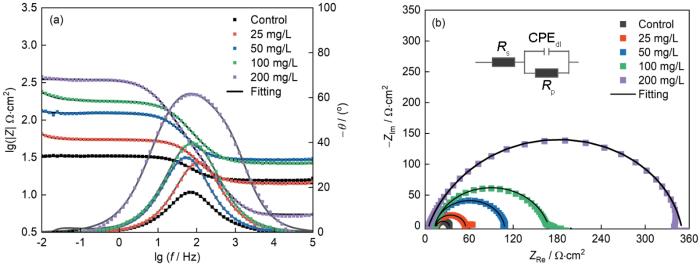
如图5a所示,在最低频率(0.01 Hz)处的阻抗模量与碳钢电极的腐蚀速率成反比,随着CDs浓度的增加呈现上升趋势,表明其对Q235钢表面的防腐性能逐渐增强[25,26]。值得注意的是,在200 mg/L CDs的HCl溶液中,|Z|0.01 Hz值达到353.22 Ω·cm2,比空白溶液高出95.51%。无论CDs浓度如何,所有Bode相位角曲线均呈现出单个峰值,对应一个时间常数。但是,随着CDs含量的增加,峰值逐渐上移,揭示了碳钢/溶液界面的电容响应增强,这归因于CDs的吸附[27]。正如图5b所示,典型Nyquist图中出现了抑制性的电容半圆,其直径随着CDs的加入而显著增大,表明CDs能够在低至25 mg/L的浓度下在碳钢表面形成有效的保护膜[14],而CDs浓度的增加则提高了保护膜的致密性。此外,所有电容半圆形状均相似,表明CDs未能改变Q235钢电极的电化学特性[28],与Bode图的结果相一致。
图5
图5
Q235钢在含不同浓度CDs的1 mol/L HCl中进行电化学测试结果
Fig.5
Bode (a) and Nyquist (b) plots of Q235 steel in 1 mol/L HCl solution and its equivalent circuit shown in Fig.5b
表1 Q235钢浸泡在不同溶液中的等效电路拟合参数
Table 1
C mg·L-1 | Rs Ω·cm2 | Rp Ω·cm2 | CPEdl μF·cm-2 | χ | γ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 1.65 | 15.83 | 193.850 | 0.04042 | - |
| 25 | 1.513 | 39.69 | 76.892 | 0.06159 | 59.41% |
| 50 | 1.796 | 94.81 | 71.187 | 0.04857 | 83.30% |
| 100 | 1.912 | 161.37 | 41.835 | 0.0634 | 90.19% |
| 200 | 5.451 | 353.22 | 37.127 | 0.00697 | 95.51% |
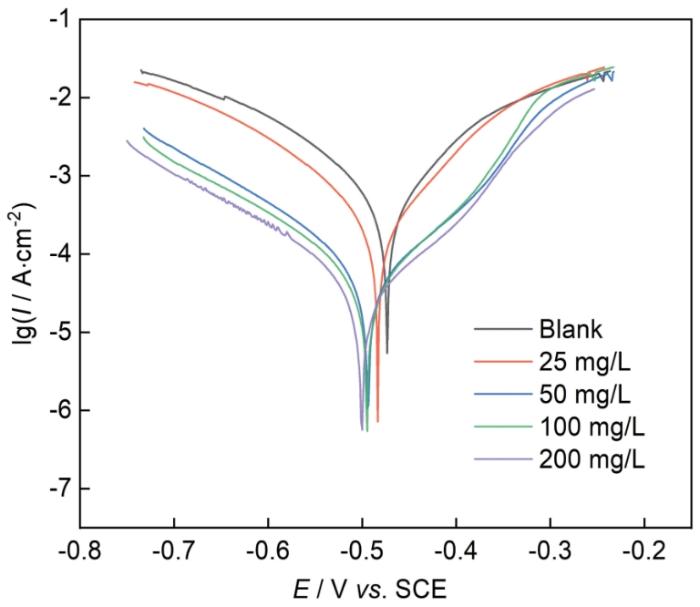
图6
图6
Q235钢在含不同浓度CDs的1 mol/L HCl中的PDP曲线
Fig.6
PDP curves of Q235 steel in 1 mol/L HCl solution with different concentrations of CDs
其中,I0corr和Icorr分别为无和有缓蚀剂的腐蚀电流密度。随着CDs浓度的增加,βa和βc均减小,同时阴极和阳极区域的Icorr均向更低值移动,说明对阴极反应和阳极反应都有抑制作用,表明CDs是作为一种混合型缓蚀剂发挥作用。同时,Icorr值随着CDs浓度的增加呈现出下降趋,且IE值呈上升趋势。当CDs含量为200 mg/L时,IE值达到最大值97.70%。上述结果与失重实验和EIS分析结果一致。
表2 PDP测试所得电化学参数
Table 2
C mg·L-1 | Ecorr mV/SCE | Icorr μA·cm-2 | -βc mV·dec-1 | βa mV·dec-1 | IE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | -468 | 891.10 | 168 | 179 | - |
| 25 | -479 | 254.21 | 147 | 152 | 71.47% |
| 50 | -491 | 154.21 | 124 | 130 | 82.69% |
| 100 | -494 | 31.28 | 106 | 129 | 96.49% |
| 200 | -496 | 20.47 | 104 | 111 | 97.70% |
失重实验、EIS和PDP测试结果表明,生物质基CDs具有高效的缓蚀性能和潜在的长期缓蚀潜力,这可能归因于CDs吸附在Q235钢表面形成的有效保护膜。相应缓蚀机理将在下文中进一步分析。
2.3 吸附等温分析
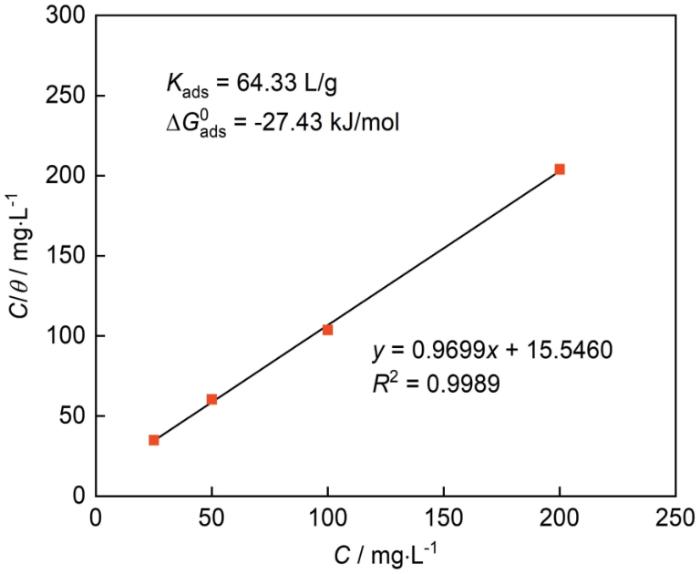
图7所示的吸附等温线可以提供关于CDs和Q235钢表面相互作用的关键信息,以探究其缓蚀机理。根据以下方程:
其中,θ为表2所示IE对应的表面覆盖度,Kads和Cinh分别为吸附平衡常数和缓蚀剂浓度,拟合结果的线性相关值R2为0.9989。结果表明,CDs缓蚀剂的吸附过程符合Langmuir吸附等温线。此外,通过以下方程确定吸附自由能(ΔG
图7
图7
依据电化学测试数据计算所得的Langmuir吸附曲线
Fig.7
Langmuir adsorption isotherm of CDs on the surface of Q235 steel
2.4 腐蚀形貌分析
为了更好地了解CDs的缓蚀机理,采用SEM、EDS和FTIR对Q235钢在1 mol/L HCl中浸泡96 h时的腐蚀形貌进行了综合分析。如图8所示,原始Q235钢表面非常光滑,有少量微弱的划痕和可忽略的凹坑,而在1 mol/L HCl中浸泡96 h后,Q235钢表面表现出严重的损伤,表面有明显的大坑和小裂纹。加入200 mg/L的CDs后,腐蚀明显减轻,小裂纹和大坑消失,这可能是由于CDs在钢表面形成了吸附膜。为了验证这一假设,用EDS和FTIR分别测量了相应的表面元素组成和化学状态[34]。从图8的EDS能谱中看出,在钢的表面检测出多种元素。其中,抛光后的Q235钢各元素所占的质量比例分别为C (26.29%)、O (3.82%)和Fe (69.77%)。而在1 mol/L HCl溶液中,Q235钢表面的能谱和元素含量变化较大。由于Fe的溶解,Fe峰强度降低(42.81%)。此外,由于Q235钢表面的氧化,O的强度(39.89%)增加。然而,当200 mg/L CDs存在时,Q235钢在1 mol/L HCl溶液中的EDS谱与抛光后的不同,其Fe含量的下降幅度比1 mol/L HCl溶液中的样品稍小,为55.61%。这些数据表明,CDs的加入明显延缓了Q235钢的腐蚀[8,16]。此外,如图9所示,CDs粉末和暴露在含有200 mg/L CDs的1 mol/L HCl中的Q235钢表面具有多个相同的特征峰,如C-H,O-H/N-H,C-N,C=O和C-O。与此同时,这些峰的强度有很大的变化,并且它们的峰值有所偏移,CDs的C=C峰无法在Q235钢表面上观察到,这归因于CDs与Q235钢表面形成了配位键[35],这进一步提供了CDs吸附在Q235钢表面的有力证据。
图8
图8
Q235钢的SEM和EDS图像
Fig.8
SEM (a-c) and EDS (d-f) images of Q235 steel samples: (a, d) original state, (b, e) immersion in 1 mol/L HCl without CDs for 96 h, (c, f) immersion in 1 mol/L HCl with 200 mg/L CDs for 96 h
图9
图9
浸泡96 h前后Q235钢表面及CDs材料的FTIR谱
Fig.9
FTIR spectra of CDs as well as Q235 steel surface before and after 96 h immersion in 1 mol/L HCl with 200 mg/L CDs
2.5 CDs的缓蚀机理
结合上述电化学实验、吸附等温线和腐蚀形貌的分析,本文对CDs的缓蚀机理给出了一个合理的解释,来说明CDs与Q235钢表面的相互作用。Q235钢在不含CDs的HCl溶液中的主要反应为:阳极反应为Fe-2e- = Fe2+,阴极反应为2H+ + 2e- =H2↑,通过引起钢的快速溶解和H+还原,从而对钢表面产生严重的腐蚀。同时,钢表面带正电荷,因此水合Cl-易于通过静电相互作用附着在钢表面上[36]。而在掺入CDs后,它们立即在HCl溶液中质子化;其次,所附的水合Cl-起到相互连接桥的作用,以促进质子化CDs在金属表面上通过静电相互作用的物理吸附,从而与H+形成竞争关系[37]。吸附等温线研究表明,除物理吸附外,化学吸附也起着重要作用。由FTIR(图2)所表征的CDs含有丰富的含氧和含氮官能团,可以通过O与N原子的孤对电子与Fe原子的未占据3d轨道之间形成配位键化学吸附在钢表面。最终,通过电化学表征、EDS (图8)和FTIR(图9)证实了CDs成功地在钢表面形成保护膜。在保护膜的作用下,可有效避免腐蚀介质与金属的直接接触,从而同时抑制阴极析氢过程和阳极金属溶解过程。此外,随着CDs含量的增加,CDs可以更有效地吸附在钢片表面,形成更致密的保护膜,进一步减轻HCl的侵蚀。综上所述,CDs在钢表面形成的保护膜,主要依赖于化学和物理吸附机制,这一过程是其发挥缓蚀作用的主要原因。
3 结论
(1) 以荔枝叶为原料,采用绿色、简便、一步水热法制备CDs,避免了有害元素的使用和有毒气体的产生。所制备的以sp2 C为核,表面含O、N官能团的环保型CDs在HCl溶液中具有良好的长期分散稳定性,为其作为酸性缓蚀剂的应用奠定了坚实的基础。
(2) 当CDs浓度为200 mg/L时,其缓蚀率高达97.70%,是一种有效的碳钢缓蚀剂。
(3) 本文研究结果有助于提高人们对生物质基CDs优异的缓蚀性能的认识,并为制备绿色高效的缓蚀剂开辟了新的途径。
参考文献
Functionalization of citric acid-based carbon dots by imidazole toward novel green corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel
[J].
Two amino acid derivatives as high efficient green inhibitors for the corrosion of carbon steel in CO2-saturated formation water
[J].
The choice of ionic liquid ions to mitigate corrosion impacts: the influence of superbase cations and electron-donating carboxylate anions
[J].[DBUH][CH3CH2OCH2COO] exhibited excellent corrosion inhibition for 304SS compared to imidazolium-based ILs due to the barrier effect produced by carboxylate anions containing electron-donating groups and superbase cations with a large ring.
Inhibitory effect of Gentiana olivieri extracts on the corrosion of mild steel in 0.5 M HCl: Electrochemical and phytochemical evaluation
[J].
The synthetic strategies, photoluminescence mechanisms and promising applications of carbon dots: Current state and future perspective
[J].
Facile and scalable preparation of carbon dots with Schiff base structures toward an efficient corrosion inhibitor
[J].
Insights into the newly synthesized N-doped carbon dots for Q235 steel corrosion retardation in acidizing media: A detailed multidimensional study
[J].
Novel nitrogen doped carbon dots for corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in 1 M HCl solution
[J].
One-pot hydrothermal synthesized nitrogen and sulfur codoped carbon dots for acid corrosion inhibition of Q235 steel
[J].
Understanding the adsorption and inhibitive properties of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for copper in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution
[J].
Synthesized carbon dots with high N and S content as excellent corrosion inhibitors for copper in sulfuric acid solution
[J].
Solvothermal synthesis of functionalized carbon dots from amino acid as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for copper in sulfuric acid solution
[J].
Enhanced anticorrosion performance of copper by novel N-doped carbon dots
[J].
Corrosion inhibition performance and mechanism of carbon dots as corrosion inhibitors
[J].
碳量子点缓蚀剂的缓蚀行为与机理研究
[J].
Carbon dots as effective corrosion inhibitor for 5052 aluminium alloy in 0.1 M HCl solution
[J].
Evaluation of the inhibition behavior of carbon dots on carbon steel in HCl and NaCl solutions
[J].An eco-friendly and effective corrosion inhibitor (N-CDs) was acquired by hydrothermal method in methacrylic acid and ethyl(methyl)amine precursors. Afterwards, the weight loss and electrochemistry measurement were chosen to appraise the corrosion inhibition behavior of as-prepared N-CDs for Q235 steel in Cl- contained solutions. The change rules of EIS and Tafel data displayed that the as-prepared N-CDs revealed a high-efficiency protection for steel in all test environments. Meanwhile, the inhibition efficiency of steel reached up to 93.93 % (1 M HCl) and 88.96 % (3.5 wt% NaCl) at 200 mg/L of N-CDs. Furthermore, the N-CDs could form the adsorption film on steel surface to avoid the strong attack of Cl-. By analysis, the adsorption mechanism of as-prepared N-CDs on steel surface was physicochemical interaction, which strictly complied with the Langmuir adsorption model in both solutions.
State-of-the-art on the preparation, modification, and application of biomass-derived carbon quantum dots
[J].
Synthesis of graphene quantum dots from natural polymer starch for cell imaging
[J].
State-of-the-art of biomass-derived carbon dots: Preparation, properties, and applications
[J].
Solvent-controlled synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots with a wide color gamut and narrowed emission peak widths
[J].
Kilogram-scale synthesis of carbon quantum dots for hydrogen evolution, sensing and bioimaging
[J].
Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots with superior optical properties
[J].Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) have various alluring properties and potential applications, but their large-scale applications are limited by current synthetic methods that commonly produce GQDs in small amounts. Moreover, GQDs usually exhibit polycrystalline or highly defective structures and thus poor optical properties. Here we report the gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline GQDs by a facile molecular fusion route under mild and green hydrothermal conditions. The synthesis involves the nitration of pyrene followed by hydrothermal treatment in alkaline aqueous solutions, where alkaline species play a crucial role in tuning their size, functionalization and optical properties. The single-crystalline GQDs are bestowed with excellent optical properties such as bright excitonic fluorescence, strong excitonic absorption bands extending to the visible region, large molar extinction coefficients and long-term photostability. These high-quality GQDs can find a large array of novel applications in bioimaging, biosensing, light emitting diodes, solar cells, hydrogen production, fuel cells and supercapacitors.
Carbon dots as a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of cancer-related anemia
[J].
Ethanol-derived white emissive carbon dots: the formation process investigation and multi-color/white LEDs preparation
[J].
Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism
[J].Carbon dots (CDs) with tunable photoluminescence (PL) and a quantum yield of up to 35% in water were hydrothermally synthesized in one pot and separated via silica column chromatography. These separated CDs emitted bright and stable luminescence in gradient colors from blue to red under a single-wavelength UV light. They exhibited high optical uniformity; that is, every sample showed only one peak in the PL excitation spectrum, only one peak in the excitation-independent PL emission spectrum, and similar monoexponential fluorescence lifetimes. Although these samples had similar distributions of particle size and graphite structure in their carbon cores, the surface state gradually varied among the samples, especially the degree of oxidation. Therefore, the observed red shift in their emission peaks from 440 to 625 nm was ascribed to a gradual reduction in their band gaps with the increasing incorporation of oxygen species into their surface structures. These energy bands were found to depend on the surface groups and structures but not on the particle size, not as in traditional semiconductor quantum dots. In addition, because of their excellent PL properties and low cytotoxicity, these CDs could be used to image cells in different colors under a single-wavelength light source, and the red-emitting CDs could be used to image live mice because of the strong penetration capability of their fluorescence.
Reversible polymerization of carbon dots based on dynamic covalent imine bond
[J].
Active anti-corrosion of epoxy coating by nitrite ions intercalated MgAl LDH
[J].
Carbon dots as new eco-friendly and effective corrosion inhibitor
[J].
The effect of N and S ratios in N, S co-doped carbon dot inhibitor on metal protection in 1 M HCl solution
[J].
Green synthesis, electrochemical, and DFT studies on the corrosion inhibition of steel by some novel triazole Schiff base derivatives in hydrochloric acid solution
[J].
Corrosion resistance enhancement of magnesium alloy by N-doped graphene quantum dots and polymethyltrimethoxysilane composite coating
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of mild steel by two new S-heterocyclic compounds in 1 M HCl: Experimental and computational study
[J].
Thermodynamic, electrochemical and quantum chemical investigation of some Schiff bases as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solutions
[J].
Investigation of ammonium (2,4-dimethylphenyl)-dithiocarbamate as a new, effective corrosion inhibitor for mild steel
[J].
Improved corrosion resistant performance of mild steel under acid environment by novel carbon dots as green corrosion inhibitor
[J].
Effect of chlorine ions on the corrosion behavior of reinforcing steel in concrete
[J].
氯离子对钢筋腐蚀机理的影响及其研究进展
[J].