许多传统缓蚀剂有毒性、污染环境、对生态群落产生负面影响。随着这些化学物质的积累,不仅会破坏生态环境,还会给人类带来致癌风险[3,4]。此外,一些合成的缓蚀剂虽然具有高效、环保的特点,但合成工艺复杂且成本高,限制了其在化工工业中的广泛应用。随着绿色发展重要理念的提出,国内外学者更加关注环境友好型植物缓蚀剂的开发。由于植物缓蚀剂具有无毒、无污染、成本低、提取操作简便等优势,已成为当今缓蚀剂研究领域的热点[5,6]。近年来,油菜叶提取物[7],石榴果皮水提物[8],枣椰树叶提取物[9],款冬提取物[10],金刚纂提取物[11],芦笋提取物[12],百里香(Thymus algeriensis)提取物[13]等均已被报道为价廉、高效且环境友好的Al在酸中的缓蚀剂。已有研究表明,植物提取物中一般含有不饱和结构、π键以及N、S、O等杂原子,这些结构可以与金属发生交互作用,在金属表面吸附成膜,从而起到保护金属表面不被腐蚀的作用[14]。
本课题组致力于植物缓蚀剂的研究,目前报道过HCl中的Al缓蚀剂有竹叶提取物[15]、核桃青皮提取物[16]及荞麦提取物[17]等,均具有较好的缓蚀效果。在此基础上,本研究选用滇润楠叶为原材料。滇润楠(Machilus yunnanensis)是樟科润楠属植物,分布于中国云南中部、西部至西北部[18]。该树种树龄长、冠大荫浓、树形优美、萌芽力强、耐修剪,是很好的园林绿化树种,滇润楠叶是其主要副产物之一,是一种再生速度快、可持续利用的天然资源[19]。本文采用乙醇加热回流法提取制备滇润楠叶提取物(MYLE),通过失重法、电化学法测定其缓蚀性能,并进行系列表面分析手段和溶液分析,从而探究其缓蚀作用机理。
1 实验方法
实验选用厚度为0.6 mm的Al片(Al 1060),主要成分(质量分数,%)为Fe 0.30、Si 0.15、Cu 0.024, Mg 0.0025, Ti 0.001,其余均为Al。滇润楠叶、无水乙醇、盐酸、丙酮均为分析纯。
图1为滇润楠叶的提取流程图。去泥洗净的滇润楠叶自然晾干后粉碎,称取10 g滇润楠叶粉末置于250 mL圆底烧瓶中,40%的乙醇水溶液为浸提液,浸泡2 h后再经70℃水浴回流3 h,趁热抽滤后通过旋转蒸发仪进行浓缩得到浓缩液,最后在恒温干燥箱干燥得到1.05 g固体提取物MYLE,提取率为10.5%。
图1
20 mm × 25 mm × 0.6 mm的Al片试样经60、600、1500和2000目砂纸逐步打磨至光亮后用丙酮脱脂。制备好的Al片试样准确称重后完全浸于250 mL不含和含有不同浓度MYLE的1.0 mol·L-1 HCl溶液中。2 h后取出Al片,将Al片表面冲洗干净,吹干后再次准确称重,并计算Al片在腐蚀/缓蚀前后的质量差(W)。进一步通过下式计算腐蚀速率(v)和缓蚀率(ηw)。
式中,W为Al片试样在HCl溶液中腐蚀浸泡前后的质量差(g);S为Al片试样的表面积(m2);t为腐蚀浸泡时间(h)。v0和v分别为Al片在不含和含不同浓度MYLE的HCl溶液中的腐蚀速率(g·m-2·h-1)。
采用PARSTAT 2273型电化学工作站测试动电位极化曲线(PDP)和电化学阻抗谱(EIS),采用传统的三电极体系,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE),辅助电极(对电极)为铂电极(Pt),用环氧树脂(固化剂为聚酰胺树脂)灌封的Al样品作为工作电极(WE)。10 mm × 10 mm的WE外露表面采用金刚砂纸逐级抛光。丙酮脱脂后,在250 mL不含和含有不同浓度MYLE的1.0 mol·L-1 HCl溶液中浸泡2 h,设置扫描范围为-250~250 mV,扫描速率为0.5 mV/s,进行PDP测试。设置频率范围为10-2~105 Hz,交流信号幅值固定为10 mV,进行EIS测试。
通过VISTA-MPX直读型电感耦合等离子发射光谱仪(ICP-OES)测定了腐蚀/缓蚀体系中Al3+浓度随MYLE浓度的变化曲线并进一步计算缓蚀率。取刚打磨好的Al片试样、1.0 mol·L-1 HCl溶液中浸泡2 h的Al片试样以及添加MYLE的1.0 mol·L-1 HCl溶液中浸泡2 h的Al片试样在10XB-PC型金相显微镜、ZEISS GeminiSEM 300型扫描电子显微镜(SEM),JC2000C1型接触角仪进行表面测试。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 静态失重法
2.1.1 MYLE的缓蚀性能
图2
图2
Al表面形貌
Fig.2
Surface morphologies of Al samples before (a) and after immersion in 1.0 mol·L-1 HCl (b) and 1.0 mol·L-1 HCl + 1000 mg·L-1 MYLE (c)
通过
图3
图3
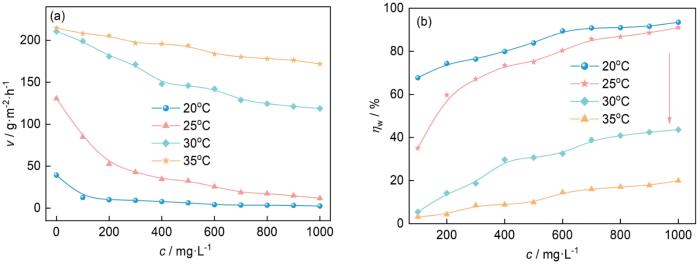
1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中腐蚀速率和缓蚀率与MYLE浓度的关系
Fig.3
Variations of corrosion rate (a) and inhibition efficiency (b) with MYLE concentration for Al in 1.0 mol·L-1 HCl
通过
2.1.2 MYLE在Al表面的吸附行为
图4
图4
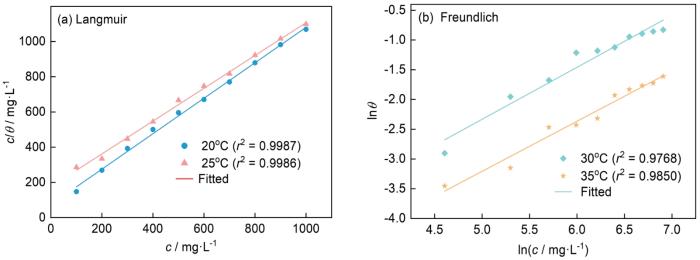
不同温度1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中MYLE在Al表面的吸附等温式
Fig.4
Adsorption isotherms of MYLE on Al surface in HCl solution at different temperatures: (a) Langmuir, (b) Freundlich
式中,c为缓蚀剂浓度(mg·L-1),θ为MYLE分子在Al表面的表面覆盖度,其值与缓蚀率(ηw)近似相等,K为吸附平衡常数(L·mg-1),n为相互作用系数。
通过
表1 线性拟合参数和吸附平衡常数
Table 1
| T / ℃ | r2 | Slope | Intercept | n | K / L·mg-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0.9987 | 1.00 | 74.22 | - | 0.0135 |
| 25 | 0.9986 | 0.93 | 175.84 | - | 0.0057 |
| 30 | 0.9768 | 0.87 | -6.70 | 0.87 | 0.0012 |
| 35 | 0.9850 | 0.84 | -7.41 | 0.84 | 0.0006 |
2.1.3 MYLE在Al表面的吸附热力学参数
MYLE分子在Al表面的吸附过程伴随着能量的吸收或释放,为此计算并讨论了MYLE在Al表面吸附过程的热力学参数。根据Van't Hoff方程计算出MYLE在Al表面的标准吸附焓(ΔHθ)。标准Gibbs自由能(ΔGθ)和标准吸附熵(ΔSθ)也由以下方程式计算。
式中,R为气体常数(8.314 J·K-1·mol-1),T为热力学温度(K),K为表观吸附平衡常数,csolvent为溶液中水的质量浓度,其值近似为1 × 106 mg·L-1 [24]。
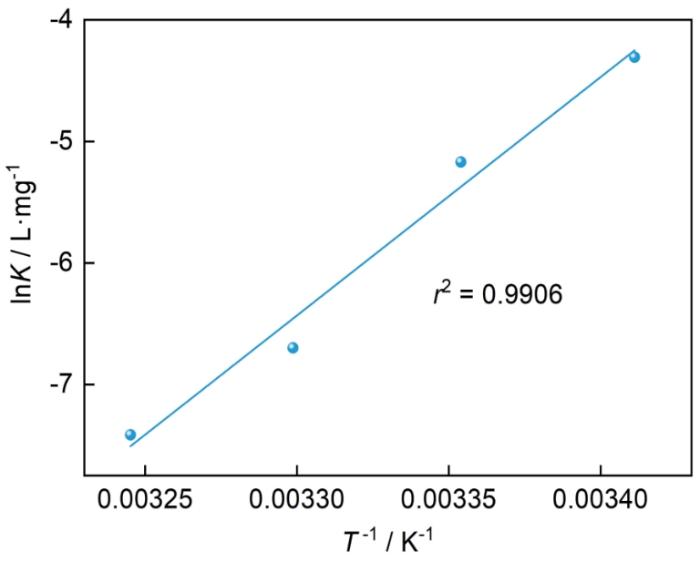
图5为lnK~1/T拟合直线,r2为0.9906,根据斜率可计算ΔHθ,并进一步根据
图5
图5
1.0 mol·L-1 HCl介质中lnK与1/T线性拟合
Fig.5
Fitted straight line of lnK versus 1/T in 1.0 mol·L-1 HCl
表2 1.0 mol·L-1 HCl溶液中MYLE在Al表面吸附的热力学参数
| T / oC | ΔHθ kJ·mol-1 | ΔGθ kJ·mol-1 | ΔSθ J·mol-1·K-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | -163.07 | -23.17 | -477.2 |
| 25 | -21.43 | -475.1 | |
| 30 | -17.93 | -478.8 | |
| 35 | -16.40 | -476.0 |
2.1.4 Al在含不同浓度MYLE的HCl中的动力学参数
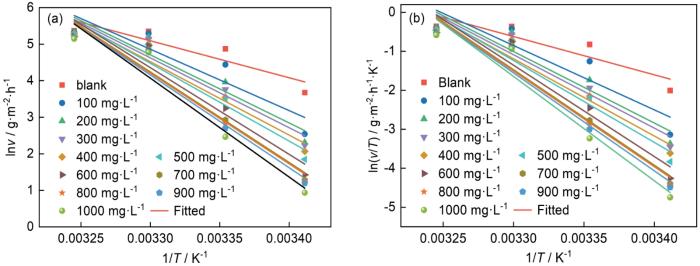
若以1/T为自变量,v为因变量进行线性拟合,其所得斜率和截距可通过
式中,NA是热学常量(数值为6.022 × 1023),h为Planck常数(数值为6.62 × 10-34 J∙s)。
图6
从图6中可以看出,lnv~1/T和ln(v/T)~1/T拟合直线均具有良好的线性关系,说明Al在添加MYLE前后的HCl中的腐蚀速率和温度的变化规律均符合Arrhenius方程和过渡态理论方程。
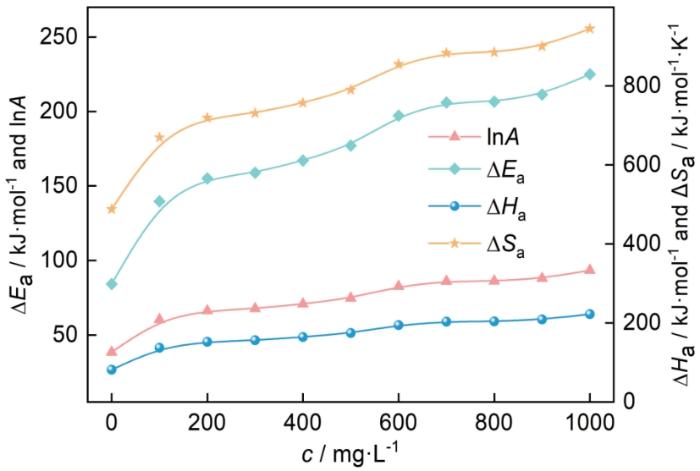
图7
图7
1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中的腐蚀动力学参数随MYLE浓度的变化曲线
Fig.7
Variation curves of corrosion kinetic parameters with MYLE concentration in 1.0 mol·L-1 HCl
2.2 Al在缓蚀体系中的动电位极化曲线
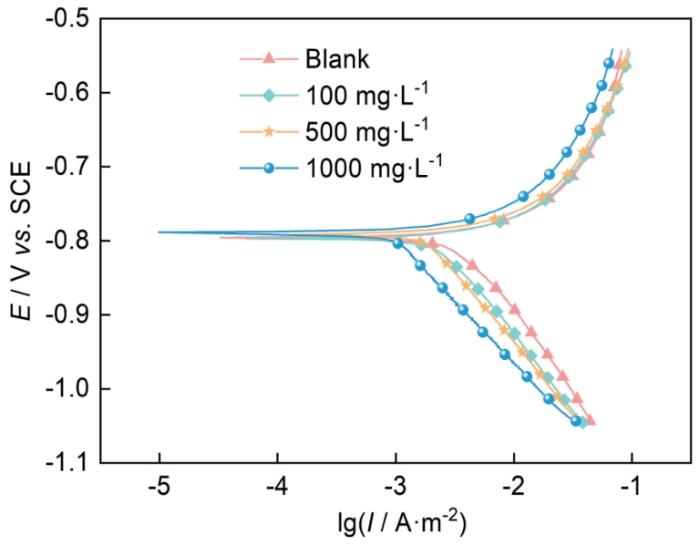
图8为Al在添加MYLE前后的1.0 mol·L-1 HCl介质中的动电位极化曲线。由图可知,添加MYLE后,PDP曲线的形状基本没有发生改变,说明MYLE没有改变Al在1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中的腐蚀机理。添加MYLE后,阴极曲线发生明显负移,阳极曲线发生正移,且随MYLE浓度的增加,阴、阳两极向腐蚀电流密度减小的方向移动更明显。这表明MYLE为混合型缓蚀剂,能够同时有效抑制阴极析氢和阳极溶解。
图8
图8
20℃时Al在不含和含不同浓度MYLE的1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中的PDP曲线
Fig.8
PDP curves for Al in 1.0 mol·L-1 HCl solutions without and with different concentrations of MYLE at 20oC
式中,Icorr和Icorr(inh)分别为不存在MYLE和存在MYLE时的腐蚀电流密度。
表3 20℃时Al在不含和含不同浓度MYLE的1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中的动电位极化参数
Table 3
c mg·L-1 | Ecorr mV vs SCE | Icorr μA·cm-2 | -bc mV·dec-1 | ba mV·dec-1 | ηP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -783 | 5219 | 281 | 18 | - |
| 100 | -794 | 1164 | 165 | 17 | 77.7% |
| 500 | -791 | 982 | 162 | 18 | 81.2% |
| 1000 | -788 | 420 | 134 | 15 | 92.0% |
2.3 电化学阻抗谱(EIS)
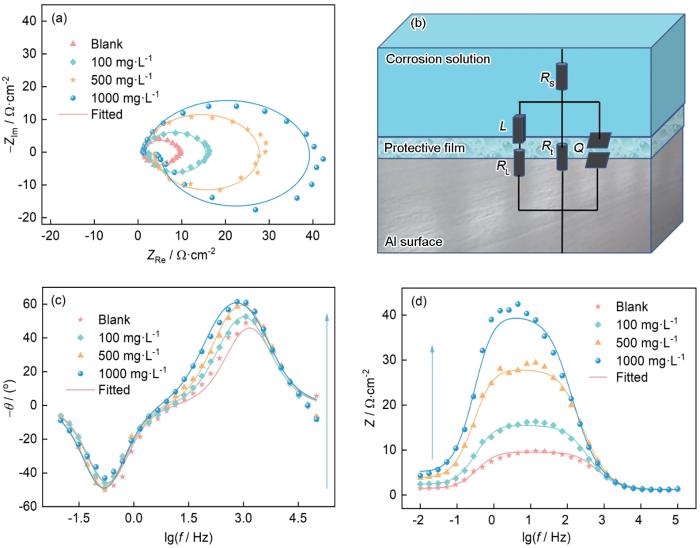
为了进一步阐明MYLE对Al腐蚀的电化学抑制行为进行了EIS测试,结果如图9所示。Al在1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中的Nyquist图(图9a)表现为高频区的容抗弧和低频区的感抗弧构成的椭圆状。高频区的容抗弧是电荷转移电阻和电极界面电容组成的阻容弛豫过程形成的,低频区的感抗弧可能是Al表面的Al2O3溶解过程形成的,或与HCl中的H+、Cl-、MYLE分子在Al表面吸脱附过程相关[31]。值得注意的是,高频区的容抗弧并不是完美的半圆状,这是电极表面不平整、吸附扩散不均匀引起的弥散效应导致的[32]。添加MYLE后Nyquist图的形状没有发生改变,仍表现为高频区的容抗弧和低频区的感抗弧构成的椭圆状。这表明MYLE的加入并没有改变Al在1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中的腐蚀机理[33]。随MYLE浓度的增大,Nyquist图半径逐渐增大。这表明电化学腐蚀反应的电阻增大,从而抑制了腐蚀反应的发生。
图9
图9
20℃时Al在不含和含不同浓度MYLE的1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中的EIS和拟合电路图
Fig.9
Nyquist plots (a), R(QR(LR)) fitting circuit diagrams (b), Bode phase angles (c) and Bode moduli (d) of Al in 1.0 mol·L-1 HCl solutions containing different concentrations of MYLE at 20oC
表4 20℃时Al在不含和含不同浓度MYLE的1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中的EIS参数
Table 4
c mg·L-1 | Rs Ω·cm2 | Rt Ω·cm2 | RL Ω·cm2 | Rp Ω·cm2 | L H·cm2 | Q Ω·s n ·cm-2 | n | χ2 10-2 | ηR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.2 | 8.4 | 0.3 | 0.29 | 2.785 | 0.0467 | 0.9322 | 0.8 | - |
| 100 | 1.2 | 14.4 | 1.4 | 1.28 | 5.438 | 0.0559 | 0.9168 | 0.6 | 77.3% |
| 500 | 1.3 | 26.7 | 2.8 | 2.53 | 11.44 | 0.0390 | 0.9290 | 0.5 | 88.5% |
| 1000 | 1.2 | 38.6 | 4.4 | 3.95 | 16.17 | 0.0591 | 0.8944 | 1.7 | 92.7% |
通过
式中,Rp(0)和Rp(inh)分别为不存在MYLE和存在MYLE时的极化电阻。当添加MYLE浓度为1000 mg·L-1时ƞR可达92.7%,与ƞW和ƞp相近。
2.4 Al表面SEM微观形貌以及接触角测试
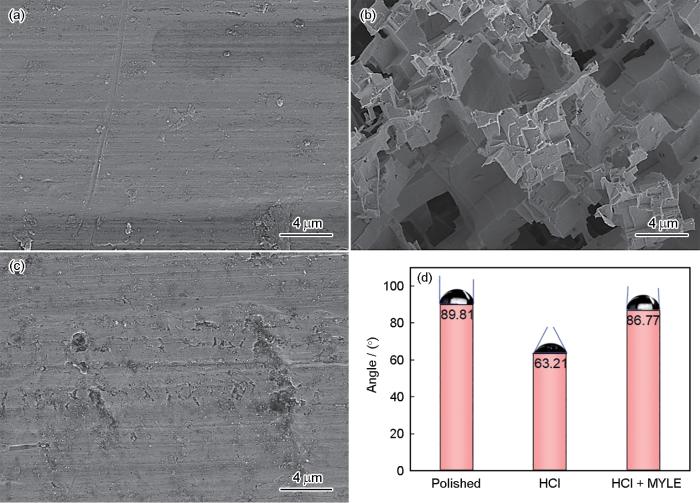
图10a为打磨好的Al表面的微观形貌,表面较为平整,可以看到砂纸打磨的痕迹。此时Al表面的接触角数值为89.81°。图10b为20℃条件下在1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中浸泡2 h的Al表面形貌,可以明显看出Al表面腐蚀严重,且腐蚀产物层具有较大空隙,随着时间的推移,腐蚀介质可以通过这些空隙进入Al基体,从而造成更严重的损害。被HCl腐蚀的Al表面的接触角降至63.21°,此时Al表面亲水性增强,意味着Al很容易与HCl发生持续的腐蚀反应。图10c为20℃条件下在添加1000 mg·L-1 MYLE的1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中浸泡2 h的Al表面形貌,可以看出添加MYLE后,Al表面腐蚀程度大大降低且较为平整,说明MYLE分子吸附在Al表面,从而减缓了HCl对Al的腐蚀。添加缓蚀剂后,Al表面接触角增大至86.77°,这表明添加MYLE后Al表面的疏水性增强。这是由于MYLE分子吸附在Al表面,从而减缓了HCl对Al的腐蚀。
图10
图10
Al表面SEM微观形貌和接触角
Fig.10
SEM surface morphologies (a-c) and contact angles (d) of Al before (a) and after immersion for 2 h in the solutions of 1.0 mol·L-1 HCl (b) and 1.0 mol·L-1 HCl + 1000 mg·L-1 MYLE (c)
2.5 ICP-OES测试
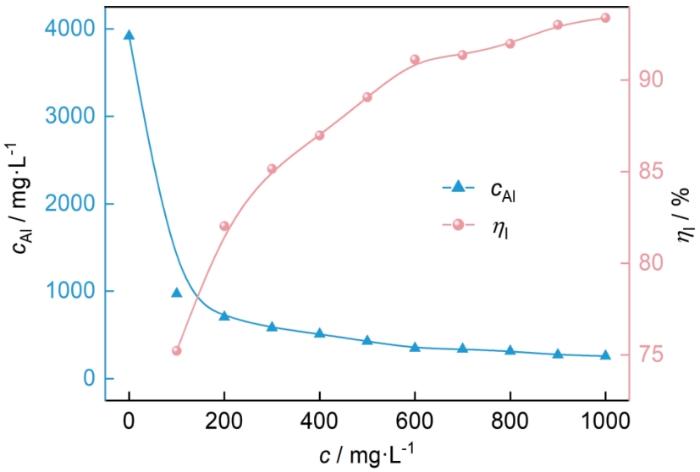
通过测定溶液中Al3+浓度进一步验证MYLE的缓蚀性能,结果如图11所示。浸泡Al 2 h后的1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中的Al3+浓度为3917.5 mg·L-1,添加MYLE后,溶液中Al3+浓度明显下降,并且MYLE浓度越大,Al3+浓度越小。这说明MYLE的添加很好的抑制了腐蚀反应的发生。当添加MYLE浓度为1000 mg·L-1时,Al3+浓度下降至258.4 mg·L-1。通过下式计算了缓蚀率(ƞI),当添加MYLE浓度为1000 mg·L-1时,ƞI为93.4%。这与失重法以及电化学结果一致,进一步印证了MYLE优异的缓蚀性能。
图11
图11
Al3+浓度和缓蚀率随MYLE浓度的变化曲线
Fig.11
Variations of Al3+ concentration and corrosion inhibition with MYLE concentration
式中,cAl(0)为1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中的Al3+浓度,cAl为添加MYLE后1.0 mol·L-1 HCl中的Al3+浓度。
2.6 腐蚀及缓蚀作用机理
Al在HCl中发生析氢腐蚀,总反应式如下:
腐蚀反应又分为阴极析氢和阳极溶解反应,阴极反应如下:
阳极反应机理如下:
图12
图12
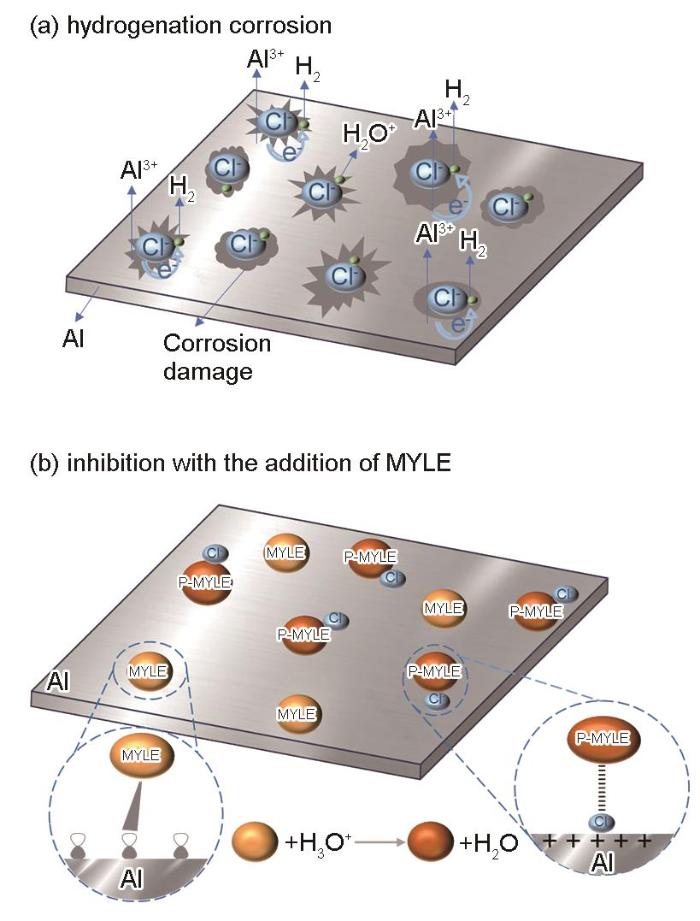
腐蚀机理和缓蚀机理示意图
Fig.12
Schematic diagrams of corrosion mechanism (a) and inhibition mechanism (b)
3 结论
(1) MYLE可作为HCl中Al的有效缓蚀剂,在20℃添加浓度为1000 mg·L-1时,最大缓蚀率可达93.5%。MYLE在Al表面的缓蚀效率随浓度增大而增大,但随温度升高而降低。
(2) MYLE在Al表面的吸附为放热反应,主要通过物理吸附的方式吸附在Al表面。20和25℃时符合Langmuir吸附等温式,而在30和35℃时符合Freundlich吸附等温式。Al在HCl中的腐蚀反应为吸热反应,Ea、A、ΔHa和ΔSa均随MYLE浓度的增大而增大。
(3) 动电位极化曲线表明MYLE是一种混合抑制型缓蚀剂,其电化学作用机理为“几何覆盖效应”。EIS表明MYLE的添加使得反应电阻增大,从而抑制了腐蚀反应的发生。
(4) 添加MYLE后,SEM表面形貌平整,接触角数值接近于打磨Al片,进一步表明MYLE吸附在Al表面从而具有优异的缓蚀性能。
(5) Al在缓蚀体系腐蚀浸泡后的电导率随MYLE浓度的增大而增大,这意味着H3O+的消耗降低,也就是腐蚀反应被抑制,且缓蚀体系的к值与MYLE的缓蚀效率成正比。
参考文献
Research progress on corrosion inhibition of green corrosion inhibitors for aluminium metals
[J].
绿色缓蚀剂对金属铝的缓蚀性能研究进展
[J].
Inhibition effect of orange peel extract on aluminum in hydrochloric acid solution
[J].
橙子皮提取物对HCl溶液中铝的缓蚀作用研究
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of aluminum and aluminum alloys by soluble chromates, chromate coatings, and chromate-free coatings
[J].
Reviews on corrosion inhibitors: a short view
[J].
Frontiers and advances in green and sustainable inhibitors for corrosion applications: a critical review
[J].
Plant extracts as “green” corrosion inhibitors for steel in sulphuric acid
[J].
Corrosion inhibition effect of the rape leaf extract on metal aluminum
[J].
油菜叶提取物对金属铝的缓蚀作用
[J].
Aqueous extract of Punica granatum fruit peel as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for aluminium alloy in acidic medium
[J]. J.
Computational and experimental evaluation of inhibition potential of a new ecologically friendly inhibitor leaves of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) for aluminium corrosion in an acidic media
[J].
Tussilago farfara extract (TFE) as green corrosion inhibitor for aluminum in hydrochloric acid solution
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of aluminium by alkaloid extract of aerial part of Euphorbia neriifolia linn in HCl solutions
[J].
Shatavari (Asparagus Racemosus) as green corrosion inhibitor of aluminium in acidic medium
[J].
Thymus algeriensis extract as a new eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for 2024 aluminium alloy in 1 M HCl medium
[J].
Challenges and advantages of using plant extract as inhibitors in modern corrosion inhibition systems: recent advancements
[J].
Inhibition effect of bamboo leaf extract on the corrosion of aluminum in HCl solution
[J].
竹叶提取物对铝在HCl溶液中的缓蚀作用(英文)
[J].
Synergistic inhibition effect of walnut green husk extract and Nd(NO3)3 on aluminum in HCl solution
[J].
核桃青皮提取物与Nd(NO3)3对Al在HCl溶液中的缓蚀协同效应
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of aluminium in HCl solution by buckwheat extract
[J].
荞麦提取物对铝在HCl溶液中的缓蚀作用
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of machilus yunnanensis leaves extract for steel in H2SO4 solution
[J].
滇润楠叶提取物在H2SO4中对钢的缓蚀作用
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of machilus yunnanensis leaves extractive for steel in H3PO4
[J].
滇润楠叶提取物在H3PO4中对钢的缓蚀性能研究
[J].
The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids
[J].
Colloid and capillary chemistry (Freundlich, Herbert)
[J].
Gibbsian interpretation of Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin isotherms for adsorption in solution
[J].
Conifer Cone (Pinus resinosa) as a green corrosion inhibitor for steel rebar in chloride-contaminated synthetic concrete pore solutions
[J].
Papaya leaves extract as a novel eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for Cu in H2SO4 medium
[J].
Experimental and theoretical evaluation of two pyridinecarboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazone compounds as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution
[J].
Inhibition action of hexadecylpyridinium bromide on cold rolled steel in Cl3CCOOH solution
[J].
溴代十六烷基吡啶对冷轧钢在三氯乙酸中的缓蚀性能
[J].
Eupatorium Adenophora (Spreng.) leaves extract as a highly efficient eco-friendly inhibitor for steel corrosion in trichloroacetic acid solution
[J].
Synergistic effects of formaldehyde and alcoholic extract of plant leaves for protection of N80 steel in 15%HCl
[J].
Kapok leaves extract and synergistic iodide as novel effective corrosion inhibitors for Q235 carbon steel in H2SO4 medium
[J].
On electrochemical techniques for interface inhibitor research
[J].
Adsorption and inhibition of sodium dodecyl sulfate on aluminum surface in hydrochloric acid
[J].
盐酸中十二烷基硫酸钠在铝表面的吸附及缓蚀性能
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of aluminum in HCl solution by Flos sophorae immaturus extract
[J].
槐米提取物对Al在HCl溶液中的缓蚀作用
[J].
Inhibition effect of Brainea insignis extract against carbon steel corrosion in HCl solution
[J].
铁蕨提取物对碳钢在盐酸中的缓蚀行为研究
[J].
An efficient corrosion inhibitor of cassava starch graft copolymer for aluminum in phosphoric acid
[J].
Synergistic corrosion inhibition effects of quaternary ammonium salt cationic surfactants and thiourea on Q235 steel in sulfuric acid: experimental and theoretical research
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of vetiver extract on steel in hydrochloric acid environment
[J].
香根草提取物对冷轧钢在盐酸溶液中的缓蚀作用
[J].采用回流提取法对香根草 (Vetiveria zizanioides) 提取得到香根草提取物 (VZE),利用失重法和电化学法研究了VZE在1.0 mol/L HCl溶液中对碳钢的缓蚀作用。结果表明:温度为40 ℃,VZE浓度为0.20 g/L时,缓蚀效果最佳,缓蚀率可达91.9%。VZE在钢表面的吸附符合Langmuir吸附等温式,吸附类型为物理吸附和化学吸附相结合的混合吸附型。动电位极化曲线表明,VZE可同时抑制阴极和阳极反应,属于混合抑制型缓蚀剂。Nyquist图谱的容抗弧随VZE浓度的增大而明显增大,碳钢的电荷转移电阻增大,腐蚀反应速率降低,从而起到缓蚀作用。
Studies on the chemical constituents of two lauraceae medicinal plants
[D].
两种滇产樟科药用植物的化学成分研究
[D].