有机缓蚀剂的种类繁多,主要包括三嗪,咪唑,吡啶和曼尼希等缓蚀剂,咪唑啉含有较多的活性位点且具有易被分解,无污染的特点,因此成为研究的热点之一[14~16]。程玉山等[17]合成的水溶性咪唑啉酰胺缓蚀剂分子能够在1.00 mol/L HCl发挥优异的缓蚀性能,当浓度为15 mg/L,腐蚀速率仅有1.025 mm/a,缓蚀率高达96.8%,并通过量子化学揭示其缓蚀机理,咪唑啉酰胺缓蚀剂的能隙(ΔE)值均非常小,表明其活性非常强。因此,无论是给金属空d轨道提供电子,生成共价键,还是接受金属空轨道已有电子,生成反馈π键,都非常容易,综合的证明了其缓蚀剂的缓蚀能力。阳清正等[18]以油酸、羟乙基乙二胺和1, 6-二氯己烷为原料合成了双子型咪唑啉季铵盐,研究表明,当缓蚀剂的加入量为100 mg/L时,在40℃,5%NaCl饱和CO2水溶液中的缓蚀率达90.74%,电化学测试其缓蚀率达88%。陆原等[19]利用丙炔醇对硫脲基咪唑啉的侧链氨基进行改性,以提高咪唑啉抗CO2和H2S腐蚀的性能,结果表明硫脲基咪唑啉TAI和DPFTAI在不含H2S的条件下,两者的缓蚀效率均高于93%,当含有2000 mg/L H2S后,DPFTAI的缓蚀效率仍高达91.96%,且比TAI高出18.22%。李俊莉等[20]将2-氨基吡啶和肉桂醛合成席夫碱基吡啶,席夫碱基吡啶再与2-溴乙基磺酸钠合成席夫碱基吡啶季铵盐,在160℃和20%HCl的条件下,4% Shif-PyQA的腐蚀速率为63.91 g/(m2·h),均达到SY/T 5405—2019中相关指标要求,说明席夫碱基吡啶季铵盐具有较好的缓蚀作用。上述研究者对咪唑啉衍生物和咪唑啉季铵盐缓蚀剂进行了大量研究,在不同工况下也能发挥优异的缓蚀性能,特别是李俊莉合成席夫碱基吡啶,能够在高温强酸的条件下发挥优异的性能。因此,在此基础上将油酸咪唑啉季铵化后再与肉桂醛反应合成咪唑希夫碱缓蚀剂,并研究了其在1.00 mol/L HCl溶液中的缓蚀性能和缓蚀效率。
本实验从分子结构设计出发,综合了多种高效缓蚀剂的单体,设计合成了一种新型高效咪唑希夫碱缓蚀剂,通过FT-IR和NMR证实了其结构的合理性,通过失重实验,电化学实验和理论计算系统的讨论了MIX在1 mol/L HCl溶液中的缓蚀效果和缓蚀机理。
1 实验方法
失重和电化学所用的试样均为Q235钢,其化学成分为(质量分数,%):C≤0.17、 Mn≤1.4、 Si≤0.35、 S≤0.035、 P≤0.035,剩余为Fe。电化学实验试样规格为10 mm × 10 mm × 30.0 mm(工作面:100.00 mm2),失重实验试样规格为12 mm × 12 mm × 2 mm(工作面:144 mm2),试样各面用金相砂纸打磨至1200#,试样的工作面继续打磨至2000#,抛光后非工作面用环氧树脂包裹,工作面用无水乙醇清洗干净后,25℃干燥以备用[21]。所用试剂:将浓盐酸稀释至1.00 mol/L,再将MIX缓蚀剂分别配置成浓度为0.00、0.20、0.50、1.00和2.00 mmol/L的缓蚀溶液。
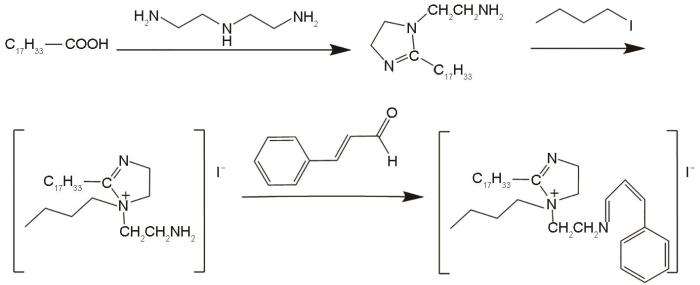
MIX缓蚀剂分子的合成原料主要包含油酸(AR)、二乙烯三胺(AR,99%)、二甲苯(AR,98%)、碘代正丁烷(99%)、肉桂醛(98%)。其合成路线如图1所示,将油酸(0.1 mol,28.24 g)加入三口烧瓶中,再加入二甲苯(40.00 mL),氮气排空气约10 min,缓慢加热至120℃,将二乙烯三胺(0.11 mol,11.34 g)至于恒压滴液漏斗中缓慢滴加(约20 min),滴加完毕后将温度升温至140℃反应2 h,进行酰胺化反应,再将温度升高至200℃左右进行环化、脱水,此过程使二甲苯在分水器中持续回流2 h,二乙烯三胺和水充分与产物相分离。待温度降低至140℃,将碘代正丁烷缓慢滴加进反应体系,温度维持约2 h。待温度降低至80℃,缓慢滴加肉桂醛(约15 min),反应2 h后,将产品直接进行减压精馏。
图1
在室温下,开路电位(OCP),电化学阻抗谱(EIS),动电位极化曲线(Tafel)均在辰华CHI660e工作站上进行,电化学测试采用传统的三电极系统:饱和氯化银为参比电极,1 cm2 Pt电极为辅助电极,Q235钢为工作电极。OCP测试参数:将电极浸入缓蚀溶液中,进行3600 s稳定测试。EIS测试参数:初始电压为VOCP, 频率范围104~10-2 Hz,振幅为0.005 V。Tafel测试参数:0.001 V/s扫描速率,电位扫描范围为VOCP± 250 mV[22]。
式中,Δw为试样的质量损失,mg;CR为腐蚀速率,mg·cm-2·h-1;A为试样的表面积,cm2;t为腐蚀时间,h;CR(0)为空白组的腐蚀速率,CR(i)为含缓蚀剂分子的腐蚀速率。
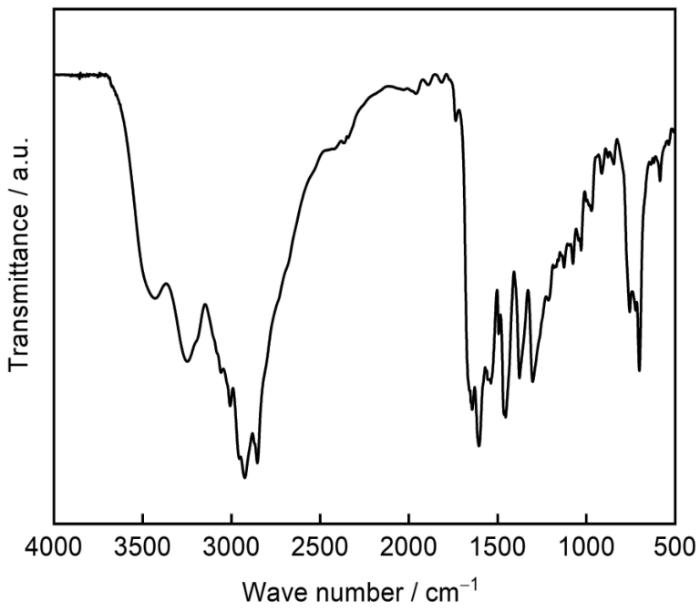
采用Spectrum One型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪对MIX分子进行表征,采用AVANCE 400核磁共振仪对MIX分子进行1H NMR和13C NMR分析。使用扫描电镜(Zeiss Evo 50 XVP model),Esprit 2.0(Germany)型扫描电子显微镜, ATR-FTIR (USA)和Thermo Fisher Scientific K-Alpha(USA)X射线光电子能谱技术在室温下对腐蚀过后的碳钢表面的吸附膜进行测定分析。
基于密度泛函理论(DFT),前线分子轨道利用Material studio 2017软件中的Dmol3模块进行计算,分子动力学(MD)则在Forcite模块中进行,先将Fe晶胞导入工作薄中并建立110面(厚度为1.2161 nm),再建立超胞,利用Adsorption Locator模块构建一个真空层厚度为3 nm并包含1个MIX分子的晶胞,先对整个体系能量优化后,再进行分子动力学优化[25]。
2 结果与分析
2.1 结构分析
图2
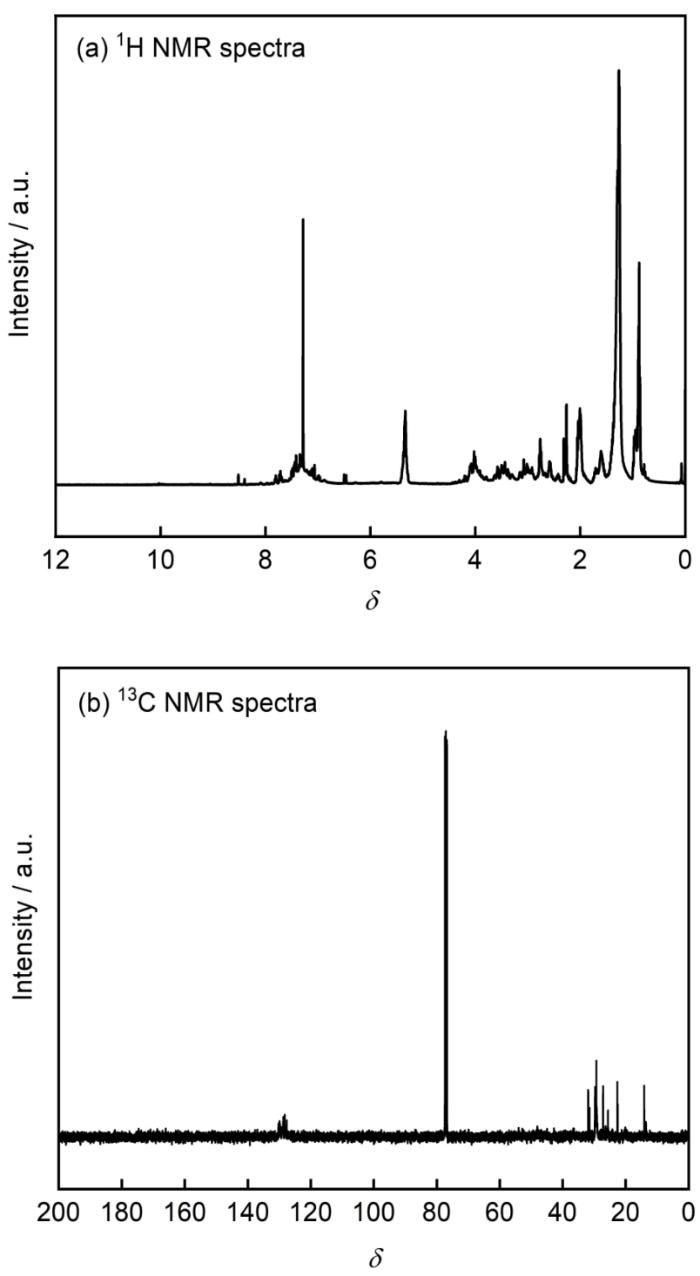
图3是MIX的NMR谱图。1H-NMR可知,δ(9.95)为-NH-的氢的特征峰,δ(3.40)和δ(3.75)为咪唑环中H的特征峰,δ(7.60)和δ(7.39)为苯的H特征峰,δ(5.32)为-C=C的H的特征峰,δ(1.29,1.33)为烷基链中H的特征峰。13C-NMR可知,其中δ(30.0)为烷基链中碳的特征峰,δ(128.6)为苯的碳特征峰,δ(128.5)为-C=C的碳特征峰。综上所述,根据MIX缓蚀剂分子和IR和NMR可知,缓蚀剂MIX已成功合成。
图3
图3
MIX在重水中NMR:1H-NMR和13C-NMR谱
Fig.3
NMR spectra of MIX in heavy water: (a) 1H-NMR, (b) 13C-NMR
2.2 电化学分析
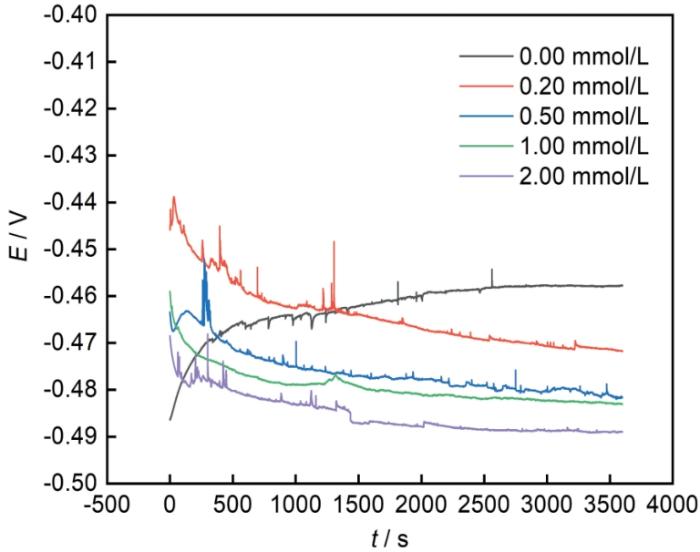
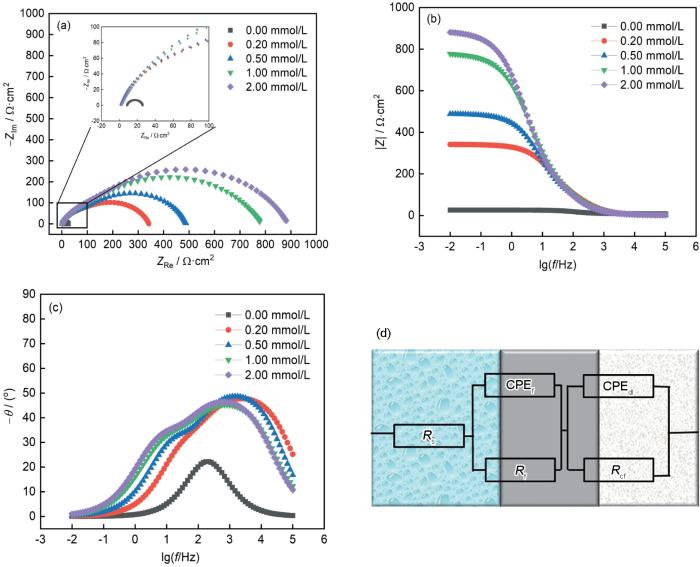
在室温下,待电化学工作站稳定以后,采用三电极系统进行不同浓度下的OCP测试,时间为3600 s,如图4所示。从图4可知,当浓度为0.00 mmol/L时,OCP约为-0.458 V,当浓度为2.00 mmol/L时,OCP约为-0.477 V。在电极浸入腐蚀溶液之初,0.00 mmol/L的OCP值快速上升,出现较大的波动,是由于Q235钢表面与腐蚀介质剧烈反应,随着MIX分子的添加,OCP值波动均变小,说明缓蚀剂分子能够吸附在Q235钢表面,形成稳定的保护膜,随着时间的延长,OCP均处于相对稳定的状态。随着MIX缓蚀剂浓度的增加,OCP均向负方向移动,且空白与腐蚀溶液的OCP值相差小于25 mV,则可证明缓蚀剂MIX分子属于混合型缓蚀剂,同时抑制反应体系的阴极和阳极反应,从而降低了整个反应体系的腐蚀速率[30]。
图4
图4
Q235钢在不同MIX浓度溶液中的开路电位
Fig.4
OCP of Q235 steel in MIX solutions with different concentrations
图5
图5
Q235钢在不同浓度MIX溶液中Nyquist图及其等效电路
Fig.5
Nyquist (a), impedance module (b) and phase angle (c) plots of Q235 steel in MIX solutions with different concentrations and its equivalent circuit (d)
拟合后的电化学参数列于表1,极化阻抗RP和缓蚀效率η计算公式如下:
表1 Q235钢在MIX不同缓蚀溶液中EIS参数
Table 1
C mmol/L | Rs Ω·cm2 | Y0, f× 10-5 Ω-1·cm-2·sn | nf | Cf μF·cm2 | Rf Ω·cm2 | Y0, rct× 10-5 Ω-1·cm-2·sn | nrct | Cdl μF·cm2 | Rct Ω·cm2 | ηp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 8.59 | 2.45 | 0.99 | 10.37 | 1.48 | 12.46 | 0.81 | 33.32 | 17.14 | 0.0015 | / |
| 0.20 | 1.10 | 4.915 | 0.80 | 9.47 | 73.3 | 11.21 | 0.80 | 21.52 | 267.8 | 0.0047 | 92.04% |
| 0.50 | 1.41 | 15.26 | 0.79 | 7.87 | 411.1 | 3.66 | 0.74 | 18.72 | 76.84 | 0.0051 | 94.44% |
| 1.00 | 2.71 | 8.78 | 0.76 | 5.61 | 83.85 | 17.91 | 0.70 | 11.91 | 696.3 | 0.0038 | 96.52% |
| 2.00 | 2.46 | 19.45 | 0.72 | 3.67 | 790.3 | 8.44 | 0.71 | 8.32 | 95.37 | 0.0056 | 96.93% |
从表1可知,χ2为卡方,卡方值越小,说明拟合电路与Q235钢电极在缓蚀溶液中的机理相近或一致,表1中χ2的值均小于0.006,说明拟合电路和真实的缓蚀电路相近[33~35]。n为Q235钢表面不均匀的程度参数,nf和nrct的值均较小,说明MIX能够吸附在Q235钢表面,造成了Q235钢表面相对不均匀。随着MIX的添加,Rs的变化范围较小,可忽略不记。随着MIX浓度升高,Rf和Rst的值明显上升,这说明MIX分子能够吸附在Q235钢表面,还能降低腐蚀体系内的电荷转移速率,从而降低了Q235钢的腐蚀速率,CPE整体呈下降趋势,可能由于缓蚀剂MIX分子挤走了吸附在Q235钢表面的水分子等腐蚀介质,随MIX浓度的增加,缓蚀剂吸附在Q235钢表面的保护膜厚度增加引起的。
式中,
图6
图6
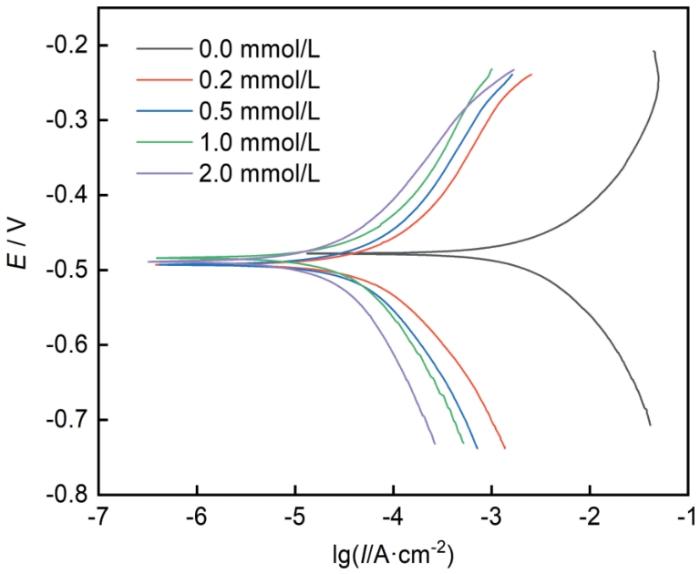
Q235钢在不同MIX缓蚀溶液中的动电位极化图
Fig.6
Potentiodynamic polarization diagram of Q235 steel in different MIX corrosion inhibition solutions
表2 极化曲线参数及缓蚀效率
Table 2
| Concentration / mmol·L-1 | -bc mV·dec-1 | ba mV·dec-1 | η | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | -0.478 | 3.5410 | 143.76 | 150.26 | / |
| 0.20 | -0.493 | 0.0827 | 147.95 | 158.05 | 97.66% |
| 0.50 | -0.484 | 0.0525 | 179.17 | 157.77 | 98.51% |
| 1.00 | -0.489 | 0.0332 | 201.65 | 145.53 | 99.06% |
| 2.00 | -0.493 | 0.0301 | 255.68 | 161.29 | 99.15% |
由表2可得,在浓度为0.00 mmol/L时,腐蚀电流密度为3.5410 mA·cm-2,当浓度为2.00 mmol/L时,腐蚀电流密度为0.0301 mA·cm-2,缓蚀效率可达99.15%,说明MIX能够发挥优异的缓蚀作用。随着浓度的增加,各腐蚀电流密度均大幅度减小,说明缓蚀剂分子能够有效吸附在碳钢表面,浓度越高,在Q235钢表面形成保护膜也就越稳定。MIX的各腐蚀电位与空白的腐蚀电位之差均小于85 mV,说明MIX分子是一种混合型缓蚀剂,同时抑制阴极和阳极反应。但随着MIX浓度的增加,Q235钢在缓蚀溶液中的腐蚀电位(Ecorr)向下移动,说明MIX属于抑制阴极为主的混合型缓蚀剂,从而降低了Q235钢的腐蚀速率[38~40]。
2.3 失重和吸附方程
表3 Q235钢在不同MIX缓蚀溶液中的失重参数
Table 3
| MIX, 25oC / mmol·L-1 | CR / mg·cm-2·h-1 | η |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 14.20 ± 0.0011 | / |
| 0.20 | 0.97 ± 0.0006 | 93.70% |
| 0.50 | 0.63 ± 0.0009 | 95.91% |
| 1.00 | 0.35 ± 0.0005 | 97.73% |
| 2.00 | 0.21 ± 0.0009 | 98.64% |
为进一步确定MIX在Q235钢表面的具体吸附形式,进行等温方程理论分析。相关的文献已表明缓蚀剂分子一般通过物理或化学等方式吸附在金属表面,阻碍或延缓了腐蚀介质对金属的侵蚀,从而起到了一定的缓蚀效果[43]。通过拟合Langmuir、Freundlich、Temkin、El-Awady和Flory-Huggins吸附等温式,其计算公式如下。Langmuir吸附等温方程的线性相关系数均大于其他的等温吸附方程,说明MIX在Q235钢表面的吸附形式遵循Langmuir吸附等温方程:
图7
图7
Langmuir、El-Awady、Flory-Huggins、Freundlich和Temkin等温吸附曲线
Fig.7
Langmuir (a), El-Awady (b), Flory-Huggins (c), Freundlich (d) and Temkin (e) adsorption isotherm
根据图7中拟合的方程,可求得Kads,根据下式可进一步求得Gibbs自由能ΔGm:
2.4 Q235钢表面分析
图8为不同MIX浓度下失重后Q235钢表面形貌,在浓度为0.00 mmol/L时,腐蚀程度严重,腐蚀产物堆积在Q235钢表面,Q235钢表面粗糙,沟壑纵横。随着MIX浓度的增大,Q235钢表面的腐蚀程度逐渐的降低,表面也逐渐光滑,在浓度为2.00 mmol/L时,与空白相比较,腐蚀程度已大幅度降低,Q235碳钢表面的腐蚀程度与失重和电化学数据相匹配。
图8
图8
Q235钢在不同浓度MIX缓蚀溶液中失重后的表面形貌
Fig.8
Surface morphologies of Q235 steel after mass loss in MIX corrosion inhibition solutions with a concentration of 0.00 (a), 0.20 (b), 0.50 (c), 1.00 (d) and 2.00 (e) mmol/L
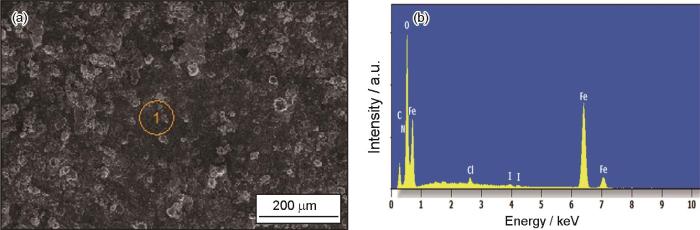
图9是Q235钢在2.0 mmol/L的缓蚀溶液中浸泡12 h后的EDS能谱,MIX缓蚀剂分子所含的元素均可在失重后的Q235钢表面检测到。其中,I的原子含量为0.33%,N的原子的含量为0.70%,证明MIX可吸附在Q235钢表面分布。
图9
图9
失重后的Q235钢表面和EDS能谱
Fig. 9
Surface morphology (a) and EDS spectrum (b) of Q235 steel after mass loss
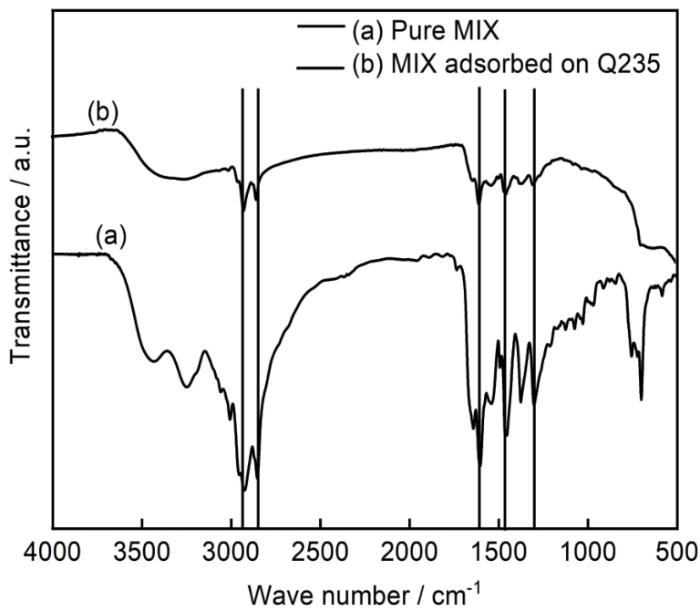
图10是失重后Q235钢表面和纯MIX的FT-IR图,在3000和1500 cm-1左右,MIX的红外特征吸收峰均可以在Q235钢表面检测到,说明MIX能够吸附在Q235钢表面并形成稳定的保护膜,从而起到了一定的缓蚀作用。
图10
图10
失重后Q235钢表面和MIX的红外图
Fig.10
FTIR spectra of Q235 steel surface and MIX after mass loss
为探究Q235钢表面吸附膜的组成,对失重后的Q235钢进行XPS分析,从图11中的总谱可以看出,MIX缓蚀剂中所含元素都能够在Q235钢表面检测到,说明MIX能够吸附在其表面。从Fe能谱图中可以看出Q235钢在1.00 mol/L盐酸溶液被腐蚀,Fe基体形成Fe2+和Fe3+,MIX中的N元素可与Fe基体形成Fe-N键,说明MIX可与Q235钢发生络合反应。在C的谱图中,MIX分子中所携带的C-C/C=C均可以被检测到。在N能谱中,C-N和C=N的存在可进一步说明MIX中咪唑环能够吸附在碳钢表面。在O能谱中,Q235钢被腐蚀后,形成了Fe2+和Fe3+并吸附在Q235钢表面。
图11
图11
失重后的Q235钢表面的XPS能谱
Fig.11
XPS spectra of Q235 steel surface after mass loss: (a) XPS survey, (b) Fe 2p3/2, (c) C 1s, (d) N 1s, (e) O 1s
2.5 量子化学分析
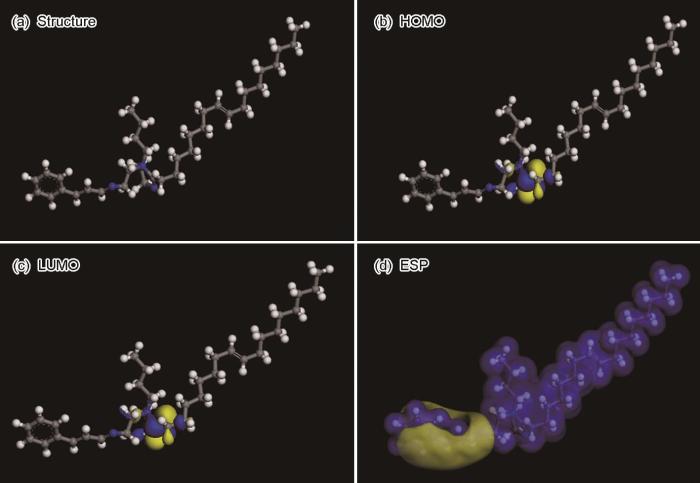
分子轨道理论与缓蚀剂分子的缓蚀能力具有一定的相关性,对其缓蚀机理具有较大的研究意义[47]。图12为MIX分子经过结构优化和能量优化的结构图,图12a~d分别为分子结构,最高占据分子轨道(HOMO),最低空分子轨道(LUMO)和电子静态电势(ESP)。根据相关文献研究表明,EHOMO表明供电子能力,其值越大,越可能与Fe的3d轨道相结合;ELUMO表明接受电子的能力,其值越小,分子越容易接受电子。ΔE = ELUMO- EHOMO,ΔE代表缓蚀剂分子的反应活性,值越小,越容易发生相互作用[48]。从图12可知,MIX分子的供电子区域主要位于咪唑环环上的C-N键和C=N双键,除此之外,苯环即是供电子区和吸电子区,MIX分子即能与Fe的3d轨道作用,从而使缓蚀剂分子在金属表面能更有效地吸附[49]。ELUMO- EHOMO,Fe=4.883 eV的值大于ELUMO,Fe- EHOMO = 2.804 eV的值,MIX分子得电子能力与Fe作用能力强于其供电子与Fe作用能力,ΔE = ELUMO- EHOMO = -2.927 - (-3.054) = 0.127 eV,表明MIX分子活性高,可以与Fe发生较强的相互作用,具有优异的缓蚀效果。
图12
图12
MIX分子的分子结构、HOMO、 LUMO和ESP
Fig.12
Molecular structure (a), HOMO (b), LUMO (c) and ESP (d) of MIX molecule
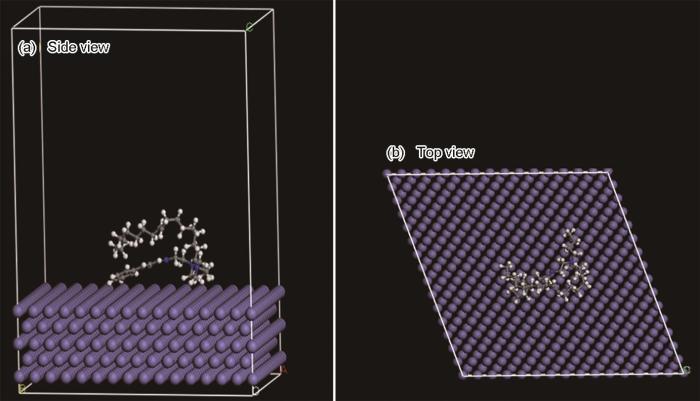
图13
图13
MIX在Fe(110)上的最佳吸附形态
Fig.13
Optimal adsorption morphology of MIX on Fe (110): (a) side view, (b) top view
相关文献研究表明[52],缓蚀剂分子与Fe基的吸附能是判定该缓蚀剂是否具有良好缓蚀性能的重要参数,MIX与Fe(110)的吸附能的关系如下:
其中,
3 结论
(1) 通过分子设计合成了一种新型高效咪唑希夫碱缓蚀剂,并通过红外光谱和核磁共振证实了MIX缓蚀剂结构的合理性。
(2) MIX分子在1 mol/L HCl溶液中能够发挥优异的缓蚀作用,在浓度为2.0 mmol/L时,失重实验,EIS,极化曲线方法测得的缓蚀效率分别为98.64%,96.93%和99.15%。
(3) MIX分子是一种抑制阴极为主的混合型缓蚀剂且能够自发地吸附在Q235钢表面。
(4) DFT和MD证明了MIX分子能够稳定的吸附在Q235钢表面,MIX的活性位点主要包括:苯基大Π键、咪唑环上的C=N双键和阳离子N+。
参考文献
A novel green reinforcement corrosion inhibitor extracted from waste Platanus acerifolia leaves
[J].
Synergistic inhibition effect between 2-mercaptobenzothiazole and chloride ion in sulfuric acid solution
[J].
硫酸溶液中2-巯基苯并噻唑与氯离子的协同缓蚀作用
[J].
Corrosion protection of imidazoline corrosion inhibitors with different carbon chain lengths in CO2 driving oil environment
[J].
不同碳链长度咪唑啉缓蚀剂在CO2驱采油环境中的腐蚀防护作用
[J].
Electrochemical behaviour of N80 steel in CO2 environment at high temperature and pressure conditions
[J].
Research progress on corrosion behavior of metallic materials in acetic acid environment
[J].
醋酸环境下金属材料腐蚀行为的研究进展
[J].以醋酸环境下金属部件的腐蚀失效案例为导向,总结了金属材料在醋酸环境下的腐蚀机理、影响因素 (如醋酸温度、浓度、杂质等) 及防护措施,旨在为醋酸环境用金属材料的选择以及制定合理的防腐方案提供一定指导。
Effects of corrosion inhibitor and functional components on the electrochemical and mechanical properties of concrete subject to chloride environment
[J].
Comparative corrosion behavior of five different microstructures of rebar steels in simulated concrete pore solution with and without chloride addition
[J].The present work discusses the effect of five different microstructures, coarse, fine and very fine ferrite-pearlite, martensite and tempered martensite, made by furnace cooling, air cooling, forced air-cooling, water quenching and tempering, respectively, of a rebar steel on its corrosion performance in freely aerated with and without chloride-contaminated simulated concrete pore solution using the dynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The corrosion performance of the steels with five different microstructures relates to the polarization resistance, protective ability of rusts and the extent of the galvanic attack. The corrosion rate of the steels has been found to be comparable in the simulated concrete pore (SCP) solution. However, in chloride-containing SCP solution, corrosion rate has been found to increase in the following sequence: forced air-cooled-air-cooled-quenched-furnace-cooled-tempered steels.
Anticorrosive ability of cycloheximide on mild steel corrosion in 0.5M H2SO4 Solution
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic media by 5′-Phenyl-2′,4′-dihydrospiro [indole-3,3′-pyrazol]-2(1H)-one
[J].
Chemical, electrochemical, quantum, and surface analysis evaluation on the inhibition performance of novel imidazo [4,5-b] pyridine derivatives against mild steel corrosion
[J].
Synthesis, characterization and physicochemical properties of new chiral quinuclidinol quaternary ammonium salts
[J].
Three indazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors of copper in a neutral chloride solution
[J].
Research progress of corrosion inhibitor for Mg-alloy
[J].
镁合金缓蚀剂研究进展
[J].镁化学性质活泼,在水溶液环境中腐蚀速度较快,很大程度上制约了镁合金的大规模应用。缓蚀剂是目前腐蚀与防护领域应用最广泛的一种技术,具备高效、成本低等特点,可在工业应用中大幅度提高镁合金的耐蚀性能。本文依据缓蚀剂的化学组成进行分类,概述无机、有机缓蚀剂以及复配缓蚀剂的研究进展,通过总结缓蚀机理对镁合金缓蚀剂未来的研究方向提出了展望。
Corrosion inhibition properties of propylenediamine-type double mannich base acidizing corrosion inhibitor
[J].
丙二胺型双曼尼希碱酸化缓蚀剂的缓蚀性能
[J].
Research on synthesis and application of quaternary ammonium salt amphoteric Gemini surfactants
[J].
季铵盐型两性双子表面活性剂的合成及应用研究进展
[J].综述了近年来季铵盐型两性双子表面活性剂的主要合成方法和性能,总结了季铵盐型两性双子表面活性剂在日用化工、纺织、皮革、造纸、石油开采、环境治理和金属加工防护及其他领域的应用。对新型季铵盐型两性双子表面活性剂的合成机理、合成方法和应用前景进行了总结和展望。
Synthesis of thiourido-imidazoline corrosion inhibitor and its corrosion inhibition performance
[J].
硫脲基咪唑啉缓蚀剂的合成及其缓蚀性能
[J].
Study on corrosion inhibition performance of water-soluble imidazoline amide on A3 steel
[J].
水溶性咪唑啉酰胺对A3钢的缓蚀性能研究
[J].
Preparation and inhibition mechanism of gemini imidazoline quaternary ammonium salt inhibitor
[J].
双子型咪唑啉季铵盐缓蚀剂的制备及缓蚀机理
[J].
The corrosion inhibition effect of proparynol-modified midazolin on X65 steel in CO2/H2S co-existence system
[J].
丙炔醇改性硫脲基咪唑啉在CO2/H2S共存体系中对X65钢的腐蚀抑制作用
[J].
Study on the inhibitor of schiff base pyridine quaternary ammonium salt for anti-high temperature and high concentration hydrochloric acid
[J].
抗高温高浓盐酸席夫碱基吡啶季铵盐缓蚀剂的研究
[J].
Morinda citrifolia (Noni) leaf extract as corrosion inhibitor for steel-reinforced concrete in saline environment
[J].
Corrosion inhibition behavior of 1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid on 20SiMn steel in simulated concrete pore solution containing Cl-
[J].
羟基亚乙基二膦酸对20SiMn钢在含Cl-混凝土模拟孔隙液中的缓蚀行为
[J].采用电化学技术(动电位极化曲线、自腐蚀电位、EIS以及Mott-Schottky曲线)和表面分析方法(SEM、XPS)研究了羟基亚乙基二膦酸(HEDP)对空冷20SiMn低合金钢在含Cl<sup>-</sup>的高碱性混凝土模拟孔隙液中的缓蚀作用及机理。结果表明, HEDP对20SiMn钢在含1 mol/L NaCl饱和Ca(OH)<sub>2</sub>溶液中的缓蚀效果随HEDP浓度的升高存在极值,最佳浓度为1.441×10<sup>-4</sup> mol/L。在此浓度下HEDP将20SiMn钢的钝性保持时间从6 h延长至9 h,缓蚀效率达到46.45%~59.78%。在发生点蚀的情况下,HEDP对点蚀的发展亦有显著的抑制作用,缓蚀效率超过93%。电化学和表面分析结果表明,HEDP优先吸附在钝化膜表面,通过竞争吸附机制屏蔽了侵蚀性Cl<sup>-</sup>向钝化膜表面的附着,从而对其产生保护作用。
Corrosion inhibition effects of a novel ionic liquid with and without potassium iodide for carbon steel in 0.5 M HCl solution: An experimental study and theoretical calculation
[J].
Synergistic inhibition effect of cuscuta chinensis lam extract and potassium iodide on cold rolled steel in hydrochloric acid
[J].
菟丝子提取物与碘化钾对冷轧钢在盐酸中的缓蚀协同效应
[J].
3-Amino alkylated indoles as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 1M HCl: Experimental and theoretical studies
[J].
Synthesis of 2-imidazolines by co-grinding of N-tosylaziridines and nitriles
[J].
Synthesis and application of hydrazono-imidazoline modified cellulose for selective separation of precious metals from geological samples
[J].
Corrosion inhibition and adsorption properties of some heterocyclic derivatives on C-steel surface in HCl
[J]. J.
An exemplar imidazoline surfactant for corrosion inhibitor studies: synthesis, characterization, and physicochemical properties
[J].An optimized one-pot recipe has been developed to synthesize a surfactant molecule, referred to as OMID, consisting of an imidazoline head group and aliphatic tail, which is an exemplar corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in acidic solutions. As evidenced by gas chromatography, H-1 and C-13 nuclear magnetic resonance, and Fourier-transform infrared data, a high-purity product was achieved without the use of either a solvent or catalyst. Critical micelle concentration values and corrosion inhibition efficiencies (eta%) were determined in aqueous solutions of hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid using surface tensiometry and linear polarization resistance measurements, respectively. Hydrolysis of the imidazoline head group as a function of pH (0-11) was explored with ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy. In addition, N 1s and C 1s X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy data were acquired from both surface-adsorbed OMID and a multilayer of the imidazoline head group of OMID. These latter data are highly relevant to those attempting to understand OMID inhibition chemistry.
A critical review on the recent studies on plant biomaterials as corrosion inhibitors for industrial metals
[J].
A detailed electrochemical/theoretical exploration of the aqueous Chinese gooseberry fruit shell extract as a green and cheap corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic solution
[J].
Bis(2-aminoethyl)amine-modified graphene oxide nanoemulsion for carbon steel protection in 15% HCl: Effect of temperature and synergism with iodide ions
[J].
Influence of an imidazole-based ionic liquid as electrolyte additive on the performance of alkaline Al-air battery
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of eco-friendly nitrogen-doped carbon dots for carbon steel in acidic media: Performance and mechanism investigation
[J].
Insights into the newly synthesized N-doped carbon dots for Q235 steel corrosion retardation in acidizing media: A detailed multidimensional study
[J].
Understanding the adsorption and anticorrosive mechanism of DNA inhibitor for copper in sulfuric acid
[J].
Fabrication of environmentally friendly Losartan potassium film for corrosion inhibition of mild steel in HCl medium
[J].
Enhanced anticorrosion performance of copper by novel N-doped carbon dots
[J].
Self-assembling anchored film basing on two tetrazole derivatives for application to protect copper in sulfuric acid environment
[J].Two tetrazole compounds (BTA, BTTA) self-assembled on copper substrate and their inhibition effect toward copper corrosion in 0.5 M H2SO4 was evaluated through atomic force microscopy (AFM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), weight loss measurement along with electrochemical techniques including electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and potentiodynamic polarization. Results indicate that BTTA can provide superior inhibition performance to BTA, and the highest inhibition efficiency values of 96.3% (BTA) and 99.8% (BTTA) were achieved respectively at 2 mM. Both tetrazole inhibitor films follow Langmuir model concerning both physical and chemical adsorption, which can be verified by X-ray photoelectronic spectroscopy (XPS) analysis. Besides, the negative value of adsorption free energy infers a spontaneous adsorption process of these tetrazole compounds on Cu surface. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation reveals stronger multiple anchor adsorption of BTTA molecules than BTA because of the existence of S atom.
Synergistic inhibition effect of walnut green husk extract complex inhibitors on steel in phosphoric acid
[J].
磷酸中核桃青皮复配缓蚀剂对冷轧钢的缓蚀协同效应
[J].采用失重法、电化学法及表面分析测试研究了农林废弃物核桃青皮提取物 (WGHE) 与阴离子表面活性剂十二烷基磺酸钠 (SLS) 对冷轧钢在2.0 mol/L H<sub>3</sub>PO<sub>4</sub>介质中的缓蚀协同效应,并对WGHE中的缓蚀有效成分进行了探究。结果表明:单独的WGHE、SLS具有中等程度的缓蚀性能,50 ℃时100 mg/L的缓蚀率仅为50%左右;WGHE/SLS复配后缓蚀率不断上升,最高缓蚀率可达95.3%,两者之间存在显著的缓蚀协同效应,缓蚀协同效应系数随温度的升高而增大。WGHE/SLS复配缓蚀剂更能同时有效抑制阴极和阳极反应;Nyquist图谱呈现单一弥散容抗弧,电荷转移电阻排序为:WGHE/SLS>WGHE>SLS。WGHE中主成分芦丁、槲皮素、1-甲基萘醌与SLS之间存在缓蚀协同作用,但协同性能低于WGHE/SLS复配缓蚀剂。
Corrosion inhibition of aluminum in HCl solution by flos sophorae immaturus extract
[J].
槐米提取物对Al在HCl溶液中的缓蚀作用
[J].
Novel synthesized cationic surfactants based on natural piper nigrum as sustainable-green inhibitors for steel pipeline corrosion in CO2-3.5%NaCl: DFT, Monte Carlo simulations and experimental approaches
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of vetiver extract on steel in hydrochloric acid environment
[J].
香根草提取物对冷轧钢在盐酸溶液中的缓蚀作用
[J].采用回流提取法对香根草 (Vetiveria zizanioides) 提取得到香根草提取物 (VZE),利用失重法和电化学法研究了VZE在1.0 mol/L HCl溶液中对碳钢的缓蚀作用。结果表明:温度为40 ℃,VZE浓度为0.20 g/L时,缓蚀效果最佳,缓蚀率可达91.9%。VZE在钢表面的吸附符合Langmuir吸附等温式,吸附类型为物理吸附和化学吸附相结合的混合吸附型。动电位极化曲线表明,VZE可同时抑制阴极和阳极反应,属于混合抑制型缓蚀剂。Nyquist图谱的容抗弧随VZE浓度的增大而明显增大,碳钢的电荷转移电阻增大,腐蚀反应速率降低,从而起到缓蚀作用。
Anti-corrosion performance of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives for mild steel in acidic medium: Gravimetric, electrochemical, DFT and molecular dynamics simulation investigations
[J].
Electrochemical, density functional theory (DFT) and molecular dynamic (MD) simulations studies of synthesized three news Schiff bases as corrosion inhibitors on mild steel in the acidic environment
[J].
Corrosion performance of Schiff base derived from 2,5-dimethoxybenzyaldehyde: X-ray structure, experimental and DFT studies
[J].
Density functional theory analysis on four pyrazine corrosion inhibitors and their adsorption behavior on Cu(111) surface
[J].
4种吡嗪类缓蚀剂及其在Cu(111)面吸附行为的密度泛函理论研究
[J].
Quantum chemistry calculation of corrosion inhibition performance of oleic-acid imidazoline corrosion inhibitors
[J].
油酸基咪唑啉缓蚀剂缓蚀性能和量子化学计算
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of ionic liquids on the surface of Q235 steel in methanol/sulfuric acid medium
[J].The corrosion behavior of Q235 steel in methanol medium in the presence of sulfuric acid and the inhibition properties of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([Bmim]Cl) for Q235 steel in methanol/sulfuric acid aqueous solutions were studied in the paper. The corrosion inhibition characteristics of [Bmim]Cl for Q235 steel were evaluated by static mass loss method, polarization curve method, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The corrosion inhibition mechanism of [Bmim]Cl was analyzed by quantum chemical calculation and molecular dynamics simulation. The corrosion rates of carbon steel increased with the increase of sulfuric acid in methanol. The results of experiments showed that the corrosion inhibition efficiency increased gradually with the increase of the concentration of [Bmim]Cl in methanol solution containing 59.51 ml 0.05 mol·L-1 H2SO4 aqueous solutions. When the concentration was 0.6 mol·L-1, the corrosion inhibition efficiency can reach the optimal, that is 90.63%. And [Bmim]Cl was a mixed inhibitor, which mainly controlled by the anodic reaction. Frontier orbitals analysis and Fukui function showed that the adsorption sites of ionic liquids on the surface of carbon steel were distributed on the imidazole ring and chemisorbed with Fe. The molecular dynamics simulation results showed that the inhibitor molecules were adsorbed parallel to the metal surface by cationic [Bmim]+, and the anion Cl- diffuses in solution to achieve the inhibition effect. The theoretical calculation results are consistent with the experimental results, that is, [Bmim] Cl has a good corrosion inhibition effect on Q235 steel in a methanol / sulfuric acid aqueous solution, laying a foundation for the research and application of new ionic liquid corrosion inhibitors.
离子液体在甲醇/硫酸介质中对Q235钢表面的缓蚀性能
[J].探究硫酸存在时Q235钢在甲醇中的腐蚀行为,以及离子液体1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑氯盐([Bmim]Cl)对金属表面的缓蚀作用。通过静态失重法、电化学测试、扫描电子显微镜来测定[Bmim]Cl对Q235钢的缓蚀性能。并利用量子化学计算和分子动力学模拟分析[Bmim]Cl分子的缓蚀机理。在甲醇中随着硫酸含量的增加碳钢的腐蚀速率增加。含有59.51 ml 0.05 mol·L<sup>-1</sup> H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>的甲醇溶液作为腐蚀介质时,随着[Bmim]Cl浓度升高,缓蚀效率逐渐增大,当浓度为0.6 mol·L<sup>-1</sup>时,缓蚀效率达到最佳值,为90.63%,且[Bmim]Cl是主要控制阳极反应的混合抑制剂,SEM分析表明在含有缓蚀剂溶液中浸泡后的Q235钢表面相对于未加缓蚀剂更加平整。前线轨道分析和Fukui指数都表明,离子液体在碳钢表面的吸附位点分布在咪唑环上,与Fe发生化学吸附。分子动力学模拟结果表明缓蚀剂分子以阳离子[Bmim]<sup>+</sup>平行吸附于金属表面,阴离子Cl<sup>-</sup>扩散在溶液中的方式达到缓蚀的效果。理论计算结果与实验结果一致,即[Bmim]Cl在甲醇/硫酸水溶液中对Q235钢具有很好的缓蚀作用,为新型离子液体缓蚀剂研究应用奠定了基础。
Trifunctional epoxy polymer as corrosion inhibition material for carbon steel in 1.0 M HCl: MD simulations, DFT and complexation computations
[J].