本文以海洋平台用E690钢为实验材料,通过在湛江不同周期的暴晒实验,结合电化学分析和腐蚀形貌及产物分析,研究了其在热带海洋大气环境下的初期腐蚀行为,为E690钢在海洋环境中的开发和推广应用提供一定的数据支持。
1 实验方法
实验材料为某钢铁公司生产的E690钢,其化学成分 (质量分数,%) 为:C 0.15,Si 0.21,Mn 1.40,S 0.003,P 0.009,Cr 0.5,Mo 0.45,Ni 1.1,Al 0.025,Cu 0.25,Ti 0.015,V 0.03,Fe余量。试样加工尺寸为150 mm×100 mm×3 mm。试样工作表面用100#、500#、600#的砂纸进行逐级打磨,然后用无水乙醇和丙酮清洗,经冷风吹干后备用。
实验在湛江大气腐蚀试验站进行,开始时间为2017年12月,结束时间为2018年12月,取样周期为15、30、90、180和360 d。在暴晒试验场中安装PH-2ZJ型PH自动气象站对暴晒场地的主要环境参数进行了采集。暴晒场地为典型的亚热带气候,年平均温度为24 ℃,年平均湿度RH=88%,试样表面润湿时间为5884 h/a,Cl-平均沉积速率为57.6 mg·m-2·d-1。
用单反相机拍摄试样暴晒后的宏观形貌,暴晒试样的除锈按GB/T16545-2015规定的方法进行。试样微观形貌和元素分布采用Nova NanoSEM430型扫描电子显微镜 (SEM) 及其自带的能谱仪 (EDM) 进行观察、分析。采用X Per MRD型X射线衍射仪 (XRD) 来分析试样的锈层相组成。
电化学测试采用AUTOLAB电化学工作站,实验介质为3.5% (质量分数) 的NaCl溶液,工作电极为用环氧树脂封装的 E690钢试样,其工作面积为1 cm2,辅助电极为铂电极,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极 (SCE)。当开路电位稳定后,分别对试样进行动电位极化曲线测量和电化学阻抗测试。电化学阻抗在开路电位下进行,激励电压的幅值为10 mV;动电位扫描速率为5×10-4 V/s,扫描范围为-0.015 V~0.015 V (vs OCP)。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 腐蚀动力学分析
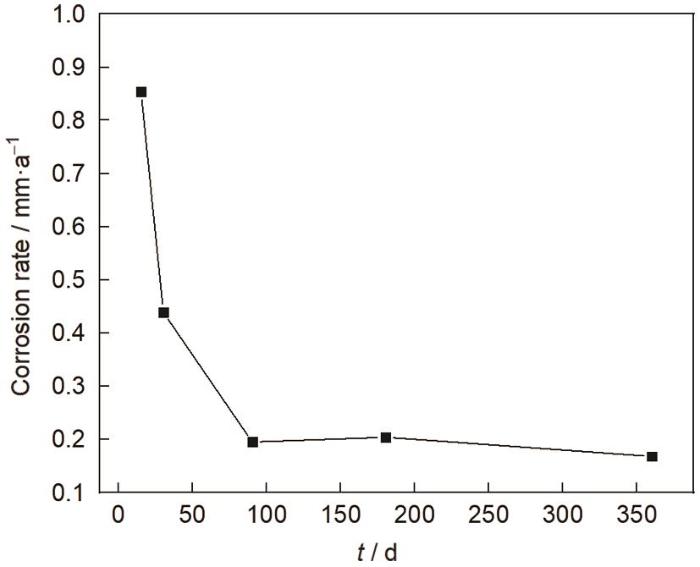
E690钢暴晒不同时间后的腐蚀速率如图1所示。从图中可以看出,在暴晒开始,15 d后,E690钢的腐蚀速率较高,为0.854 mm·a-1,随着暴晒时间的延长,腐蚀速率不断降低,在暴晒90 d后,腐蚀速率变化较小,腐蚀趋于稳定。
图1
图1
E690钢腐蚀速率随暴晒时间的变化曲线
Fig.1
Corrosion rate curve of E690 steel with exposure time
2.2 腐蚀形貌观察
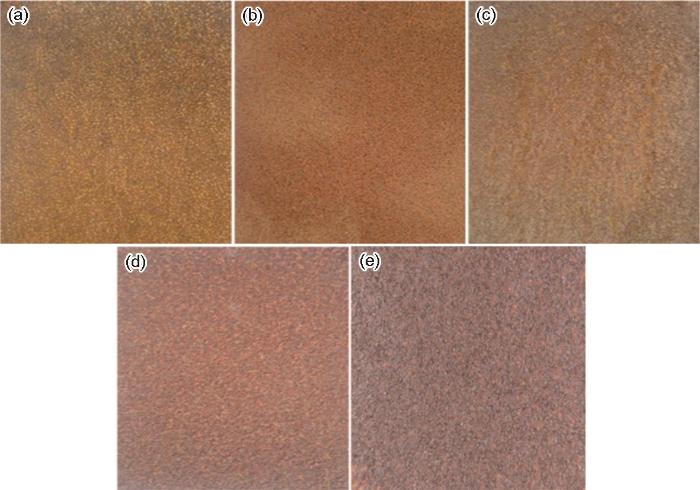
图2为E690钢暴晒不同时间后的表面宏观腐蚀形貌。从图中可知,铁锈颜色随暴晒时间的延长由红棕色逐渐转变为红褐色,试样的表面腐蚀产物不断增多,腐蚀程度逐渐加重。
图2
图2
E690钢暴晒不同时间后表面宏观形貌
Fig.2
Surface macroscopic morphologies of E690 steel after exposure to sunlight for 15 d (a), 30 d (b), 90 d (c), 180 d (d) and 360 d (e)
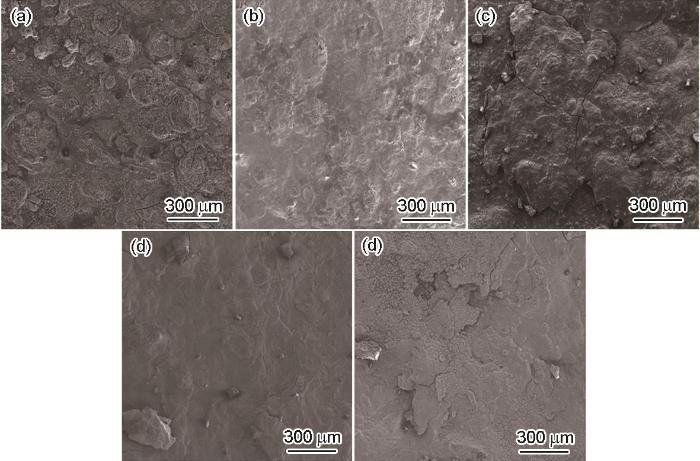
图3为E690钢暴晒不同时间后的表面微观腐蚀形貌。暴晒15 d后,试样表面完全被腐蚀产物覆盖,同时可观察到有大量的腐蚀坑存在,氯离子容易通过腐蚀坑渗透到基体表面,腐蚀速率较快。随着暴晒时间的延长,在暴晒90 d后,锈层变得比较致密,而且没有观察到腐蚀坑的存在。在暴晒360 d后,腐蚀产物有分层现象产生,内锈层比较致密,外锈层呈现疏松结构。
图3
图3
E690钢暴晒不同时间后表面微观形貌
Fig.3
Surface microscopic morphologies of E690 steel after exposure to sunlight for 15 d (a), 30 d (b), 90 d (c),180 d (d) and 360 d (e)
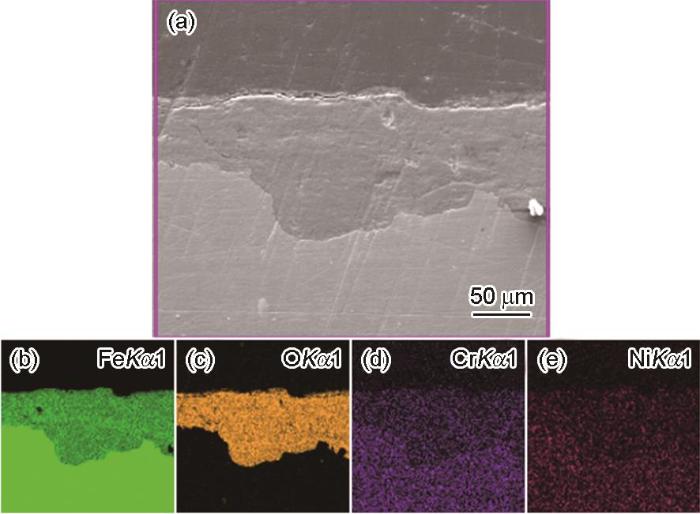
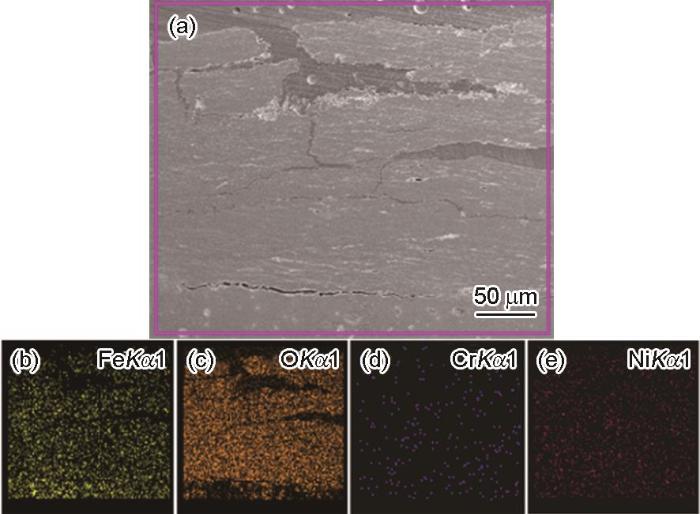
图4
图4
E690钢暴晒90 d后锈层截面腐蚀形貌和元素分布
Fig.4
Corrosion morphologies (a) and element distribution (b-e) of the cross section of E690 steel after exposed for 90 d
图5
图5
E690钢暴晒360 d后锈层截面腐蚀形貌和元素分布
Fig.5
Corrosion morphologies (a) and element distri-bution (b-e) of the cross section of E690 steel after exposed for 360 d
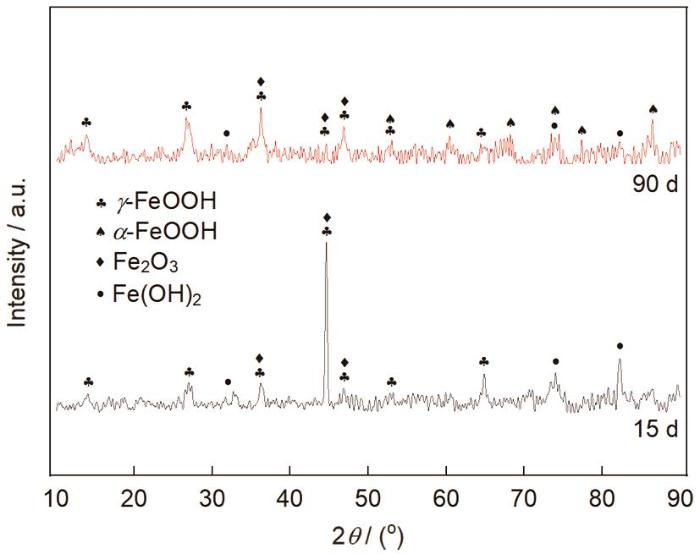
2.3 表面腐蚀产物分析
图6
图6
E690钢在不同暴晒时间后腐蚀产物的XRD谱
Fig.6
XRD spectra of rust layer of E690 steel after exposed for different time
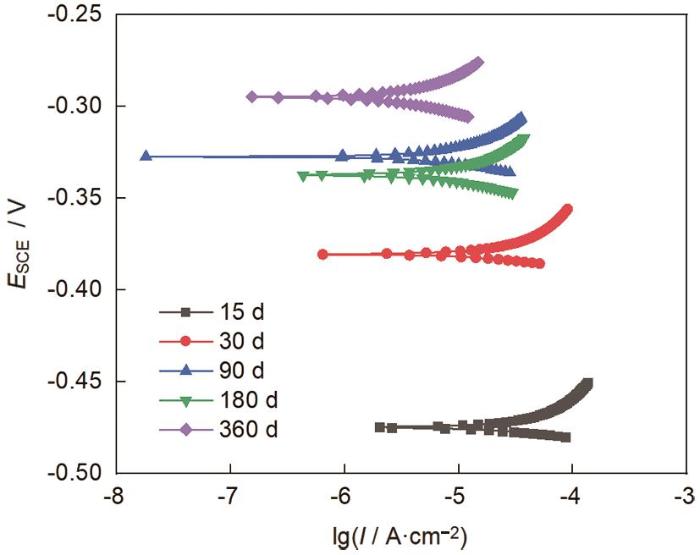
2.4 电化学分析
图7
图7
E690钢在不同暴晒周期下的极化曲线
Fig.7
Polarization curves of E690 steel after exposed for different time
表1 E690钢暴晒不同时间后的腐蚀电位和腐蚀电流
Table 1
| Exposure time / d | Ecorr / mV | Icorr / μA |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | -475.10 | 11.97 |
| 30 | -380.75 | 5.223 |
| 90 | -327.64 | 2.215 |
| 180 | -337.69 | 2.827 |
| 360 | -294.94 | 0.8578 |
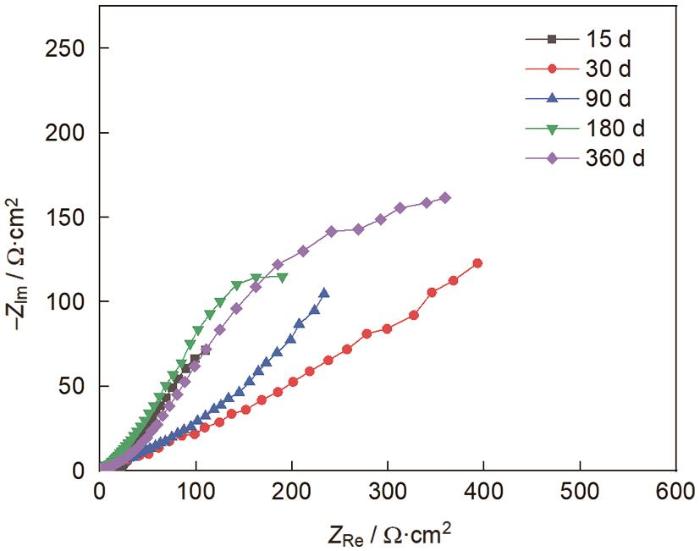
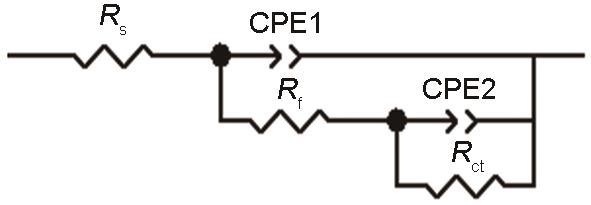
图8为E690钢暴晒不同时间后的电化学阻抗谱,从图中可看出,随着暴晒时间的延长,E690钢的容抗弧在逐渐增大,这表明E690钢的耐蚀性随着暴晒时间的延长逐渐提高。采用图9所示的等效电路图对Nyquist图进行拟合,其中Rs、Rf、Rct分别代表溶液电阻、腐蚀产物膜电阻以及电荷转移电阻,CPE1和CPE2分别代表表面腐蚀产物膜电容和不同界面间的双电层电容。表2为等效电路图中各等效电子元件的拟合数值。从拟合数值可知,E690钢的Rf和Rct在暴晒开始都比较小,腐蚀速率较快,随着暴晒时间的延长,二者不断增大,腐蚀速率降低,在暴晒90 d后变化较小,腐蚀趋于稳定,Cr和Ni的存在提高了金属的耐腐蚀性。
图8
图8
E690钢暴晒不同时间后的Nyquist图
Fig.8
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and equivalent circuit of E690 steel at different exposure periods
图9
表2 电化学阻抗的数值拟合结果
Table 2
| Exposure time / d | Rs Ω·cm2 | Rf Ω·cm2 | Rct Ω·cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 8.33 | 26.7 | 465 |
| 30 | 7.96 | 31.2 | 874 |
| 90 | 7.14 | 59.6 | 2766 |
| 180 | 7.27 | 60.1 | 2998 |
| 360 | 7.01 | 57.2 | 2831 |
3 结论
(1) E690钢在暴晒开始时,腐蚀速率较高,随着暴晒时间的延长,腐蚀速率不断降低,在暴晒90 d后,腐蚀速率变化较小,腐蚀趋于稳定。
(2) 在暴晒15 d后,E690钢的表面可观察到腐蚀坑的存在,随着暴晒时间的延长,腐蚀产物变的比较致密,暴晒360 d后,腐蚀出现分层,外锈层呈现疏松结构。
(3) 在暴晒90 d后,Cr已经扩散到锈层中,提高了锈层的致密性,Ni促进了γ-FeOOH向α-FeOOH相的转化,提高了E690钢的耐腐蚀性,腐蚀速率降低。
(4) 在暴晒前期,E690钢的电荷转移电阻较小,腐蚀电流密度较大,腐蚀速率较高;在暴晒时间90 d时,锈层中α-FeOOH含量增加,锈层对基体的保护作用增强,腐蚀电位正移,电荷转移电阻增大,腐蚀电流密度变小。
参考文献
Comparison research on corrosion behavior of E36 and E690 steel in simulated seawater
[J].
E36和E690钢在模拟海水中的腐蚀行为对比研究
[J].
Trail on high strength marine structure steel grade E690
[J].
E690级海洋结构特厚高强度钢板的试制
[J].
Comparative study of stress corrosion cracking behaviors of typical microstructures of weld heat-affected zones of E690 high-strength low-alloy steel in SO2-containing marine environment
[J].
E690高强低合金钢焊接热影响区典型组织在含SO2海洋环境中的应力腐蚀行为对比研究
[J].
Effect of SO2 content on corrosion behavior of high-strength steel E690 in polluted marine atmosphere
[J].
SO2质量分数对污染海洋大气环境中高强钢E690腐蚀行为的影响
[J].采用干湿交替腐蚀试验方法,结合电化学测试、锈层截面和腐蚀产物X射线衍射(X-ray diffraction,XRD)分析,研究SO<sub>2</sub>质量分数对E690钢在模拟污染海洋大气环境中腐蚀行为的影响。结果表明,海洋大气环境中的SO<sub>2</sub>改变了E690钢海洋大气腐蚀的电化学机制,使得极化曲线的阳极分支由弱钝化特征转变为活性溶解特征,阴极分支由氧扩散过程控制转变为氧扩散和析氢反应共同控制,因而大大促进了阳极和阴极的电化学反应过程。同时,SO<sub>2</sub>又显著促进α-FeOOH的生成和Ni、Cr合金元素在内锈层中的富集,大大促进锈层的致密化,使均匀腐蚀速率逐渐减低,并促进锈层底部点蚀坑的生长。随着模拟溶液中NaHSO<sub>3</sub>浓度的增加,E690钢在60 d内的平均腐蚀速率逐渐增加,当NaHSO<sub>3</sub>浓度达到0.03 mol/L时,又出现一定程度的降低;同时,锈层底部的点蚀坑随NaHSO<sub>3</sub>浓度的增加显著长大。
Corrosion behavior of Q690qE steel in a simulated coastal-industrial environment
[J].
Q690qE桥梁钢在模拟滨海工业环境中的腐蚀行为研究
[J].
Corrosion behavior of 690 MPa weathering bridge steel in simulated industrial atmosphere
[J].
690 MPa级耐候桥梁钢在模拟工业大气环境下的腐蚀行为研究
[J].
Corrosion resistance of E690 platform steel in simulation marine atmosphere
[J].
E690平台用钢耐海洋大气腐蚀模拟
[J].
Internal friction analysis on austenitizing process of E690 steel
[J].
E690钢奥氏体化过程的内耗分析
[J].
Oxygen-concentration cell induced corrosion of E690 steel for ocean platform
[J].In order to investigate the corrosion resistance of ocean platform steel E690 in sea water, the corrosion induced by oxygen-concentration cell of E690 steel in 3.5%NaCl with oxygen concentration within a range of 0.3 to 8 mg/L was investigated by means of electrochemical measurement techniques, scanning electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy. The influence of the difference in dissolved oxygen, the ratio of cathode area to anode area and the corrosion product on the corrosion behavior of E690 steel was examined respectively. It was found that: when the ratio of cathode area to anode area was less than four (Sc/a≤4), the cathode and these ratios would be the main factor that influenced the oxygen-concentration cell corrosion; when Sc/a>4, the dissolved oxygen would be the main factor that influenced the oxygen-concentration cell corrosion; How the corrosion product influenced the oxygen-concentration cell corrosion depends on the dissloved oxygen. When the rusted metal under an oxygen-deficient condition, the rust layer would prevent the substrate from corrosion; when the rusted metal was immersed in an aerated condition, the corrosion product would participate in the cathodic reaction process, which would accelerate the anode dissolution and resulted in localized corrosion, such as pitting.
海洋用高强钢E690氧浓差腐蚀行为研究
[J].
Effect of alternating stress frequency on corrosion electrochemical behavior of E690 steel in 3.5%NaCl solution
[J].
交变应力频率对E690钢在3.5%NaCl溶液中腐蚀电化学行为的影响
[J].
Galvanic series of metals and effect of alloy compositions on corrosion resistance in Sanya seawater
[J].With the development of ocean engineering, various metallic materials have been applied to the marine environment. It is an urgent requirement to study the galvanic series and alloy composition optimization of metallic materials in the tropical marine environment. In this work, open circuit potentials (OCP) and galvanic series of 36 kinds of metallic materials in Sanya seawater were studied. By considering the response of OCP to tidal changes, the anti-corrosion effects of alloying elements were also analyzed. The results show that the OCP of metallic materials in Sanya seawater has a large range. The galvanic series order of metallic materials from high to low in Sanya seawater is: nickel alloy, duplex stainless steel, austenitic stainless steel and pure copper, ferritic stainless steel, martensitic stainless steel, copper alloy, low alloy steel, carbon steel, cast iron, aluminum alloy and aluminum anode. Low-carbon high-alloy content carbon steel and high Cr, Ni contents stainless steel have higher OCP. The potential fluctuations of carbon steel with tidal changes involves two phases: (1) under the dynamics control, the OCP of carbon steel is more negative at high tide; (2) under the diffusion control, the OCP is more positive at high tide. The potential fluctuations of metallic materials reflect the effect of the corrosion product film on the change of ionization balance, and metals with less potential fluctuations have better inhibition on ion diffusion. In Sanya seawater, the carbon steel, which has more alloying content and less carbon content, has less potential fluctuations with the tidal changes and has good oxygen diffusion resistance. The potential fluctuations of austenitic stainless steel with tidal changes are less than that of ferritic stainless steel and martensitic stainless steel. After 2700 h immersion, austenitic stainless steel and martensitic stainless steel, which have a higher content of Mo, have more stable OCP. In other words, the corrosion film gets a better corrosion resistance. The OCP of aluminum anode in Sanya seawater environment increases when the oxygen content is brought up. The OCP of Zn-containing or Ga-containing aluminum anode remains relatively stable. Al bronze and T2 copper have less potential fluctuations with tidal changes, and perform good corrosion resistance in Sanya seawater.
金属材料在三亚海水中的腐蚀电位序及合金成分对耐蚀性的影响
[J].对36种金属材料在三亚海水中的腐蚀电位序、腐蚀电位对潮汐变化的响应以及不同金属合金元素成分对耐三亚海水环境腐蚀的作用进行了研究。结果表明,三亚海水环境中金属材料腐蚀电位的稳定区间较大,腐蚀电位序从高到低为:镍基合金、双相不锈钢、奥氏体不锈钢和紫铜、铁素体不锈钢、马氏体不锈钢、铜合金、低合金钢、碳钢、铸铁、铝合金和铝阳极。碳钢电位随潮汐变化的波动在动力学控制下,高潮位时腐蚀电位较负;在扩散作用控制下,高潮位时腐蚀电位较正。金属腐蚀电位在海水中的波动体现了腐蚀产物膜对扩散控制下的腐蚀具有阻碍作用。在三亚海水环境中,低C和高合金元素含量的碳钢对氧扩散抑制作用较好。奥氏体不锈钢的腐蚀电位随潮汐变化的波动远小于铁素体不锈钢和马氏体不锈钢,浸泡2700 h后,含Mo的奥氏体不锈钢和马氏体不锈钢有较为稳定的腐蚀电位,腐蚀产物膜具有较好的保护性。铝阳极在三亚海水环境中的腐蚀电位随海水高含氧量时间的增加而上升,含Ga和高Zn含量的铝阳极材料的腐蚀电位较为稳定。Al青铜和T2紫铜在三亚海水环境中有较稳定的腐蚀电位,并且有较好的耐蚀性。
Mechanical properties and marine atmosphere corrosion behavior of E690 ocean platform steel
[J].
E690海洋平台用钢力学性能和海洋大气腐蚀行为
[J].
Study on corrosion resistance of E690 steel in industry ambient environment
[J].
E690在模拟工业大气环境下的腐蚀性能研究
[J].
Atmospheric corrosion behavior of weathering steels in initial stage
[J].
大气腐蚀下耐候钢的初期行为规律
[J].
Atmospheric corrosion of Ni-advanced weathering steels in marine atmospheres of moderate salinity
[J].
Morphology, products and corrosion mechanism analysis of Q235 carbon steel in sea-shore salty soil
[J].
Q235碳钢在滨海盐土中的腐蚀形貌、产物及机理分析
[J].
Research on bainite transformation in steels
[J].
钢中贝氏体相变机制的研究
[J].本文简要地总结了国内近年来在贝氏体相变理论研究方面的主要成果,包括以下方面:①发现钢中的贝氏体超精细结构;②贝氏体表面浮突完全由贝氏体铁素体长大过程中形变产生,单一超亚单元对应的浮突呈帐篷型;③贝氏体铁素体宽面上存在三维巨型台阶,在近NW关系下相变单元宽面接近(335)f,为扩散型界面;④发现钢中贝氏体碳化物在α/γ界面的γ侧形核并向奥氏体内生长;⑤建立了贝氏体激发形核—台阶长大模型,理论计算表明这种机制是合理的,它成功地解释了贝氏体的多层次复杂结构,以及上贝氏体、下贝氏体等不同形态的形成原因等。
Influences of Fe3C and pearlite on the electrochemical corrosion behaviors of low carbon ferrite steel
[J].The microstructure of X80 pipeline steel welding joint, consisted of Fe<sub>3</sub>C and degenerated pearlite, was simulated by carburizing treatment. The effects of Fe<sub>3</sub>C and pearlite on the electrochemical properties of bainitic ferrite steel and localized corrosion occurrence regularity in Yingtan soil simulation solution were investigated by scanning Kelvin probe (SKP), scanning vibrating probe (SVP) and local electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (LEIS), combined with immersion test. It is demonstrated that the corrosion potential of degenerated pearlite is lower than bainitic ferrite, and decreases with increasing Fe<sub>3</sub>C content. Localized corrosion occurs on the surface of the carburized sample in Yingtan soil simulation solution. The anodic oxidation process is observed to be initiated on the carburized degenerated pearlite, whereas the cathodic reaction involving dissolved H<sup>+</sup> is on bainitic ferrite, and the anodic current density increases with increasing Fe<sub>3</sub>C concentration. As the ion contents of the soil simulation solution doubled, the anodic dissolution of degenerated pearlite increases, and the local impedance of the electrode decreases.
Fe3C和珠光体对低碳铁素体钢腐蚀电化学行为的影响
[J].通过对X80管线钢进行固体渗碳模拟焊接接头区域的Fe<sub>3</sub>C和退化珠光体组织,采用扫描Kelvin探针(SKP)、扫描振动参比电极(SVP)和局部电化学交流阻抗谱(LEIS)结合浸泡实验分析了Fe<sub>3</sub>C和珠光体对铁素体钢表面电化学性能以及在鹰潭土壤模拟溶液中的局部腐蚀发生规律的影响. 结果表明, 退化珠光体组织在空气(湿度为40\%, 温度为22 ℃)中的腐蚀电位低于贝氏体铁素体, 并且随着Fe<sub>3</sub>C含量的增加, 腐蚀电位降低; 渗碳试样在鹰潭模拟溶液中发生局部腐蚀,中心铁素体区为整个材料电偶腐蚀的阴极, 退化珠光体和退化珠光体/贝氏体铁素体区为阳极, 随着Fe<sub>3</sub>C含量的增加, 阳极溶解电流密度增大;模拟溶液各离子含量成倍增加后, 退化珠光体的阳极电流密度升高, 电化学交流阻抗值降低, 局部腐蚀效应增大.