X70钢由于其抗形变能力强,被广泛应用到天然气和石油运输管道,建筑行业等诸多领域。然而,它在服役过程中容易遭周围腐蚀介质的侵蚀。为了判断X70钢腐蚀的程度以及采取下一步的防护措施,通过酸洗的方法除去X70钢表面的腐蚀产物就显得至关重要。酸洗虽然能够有效除去X70钢表面的氧化产物,同时也会对其基材造成一定程度的腐蚀。为了抑制钢材基体在酸洗过程中的腐蚀,在酸洗液中添加缓蚀剂是一种简单易行的方法。
缓蚀剂通常包括有机和无机缓蚀剂,有机缓蚀剂一般含有O、N、S等杂原子,共轭双键或三键等[1,2]。它们可以通过自身的孤电子对或共轭双键的π电子和Fe原子的3d空轨道形成配位键从而有效的吸附在铁表面[3]。添加缓蚀剂在金属材料腐蚀防护中具有操作简单,效果显著以及成本低廉的优势,但也可能存在诸如在使用过程中会破坏生态系统、恶化工作环境等缺点。食用香料作为环境友好型绿色缓蚀剂已经引起腐蚀工作者的注意。Mo等[4]研究了两种噻唑类食用香料对Cu在氯化钠溶液中的缓蚀性能。Tan等[5]探究了二硫化合物衍生物食用香料对Cu在硫酸溶液中的缓蚀性能。本文探究了食用香料1,4-二硫-2,5-二醇 (DDD) 作为缓蚀剂对X70钢在硫酸溶液中的缓蚀机理。DDD常用作焙烤制品、肉制品、汤品以及调味香料等,因此DDD作为缓蚀剂使用时绿色环保。具体地,本文采用电化学方法研究了温度对DDD缓蚀性能的影响,通过扫描电镜对X70钢在不同实验条件下的表面形貌进行表征,此外还利用量子化学计算和分子动力学模拟方法对DDD的缓蚀机理进行了理论分析。
1 实验方法
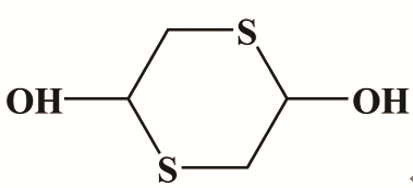
DDD购买于阿达玛斯试剂公司,纯度大于98%,使用前没有纯化,其结构式如图1所示。X70管线钢的化学组成 (质量分数,%) 为:Mn 1.7,Si 0.45,S 0.01,P 0.02,V 0.06,Mo 0.35,Ti 0.06,Nb 0.05,Fe余量。0.5 mol/L H2SO4采用高纯度浓硫酸和二次蒸馏水配制而成。DDD被稀释成0.5,1,2和5 mmol/L的待测液,0.5 mol/L H2SO4作为空白溶液。X70钢被切割成0.5 cm×0.5 cm×0.5 cm和1 cm×1 cm×0.1 cm尺寸的试样,分别用于制作工作电极和利用Quattto S型扫描电镜 (SEM) 观察观察表面腐蚀形貌。首先,将X70钢样品在400到2000目的砂纸上打磨光亮,然后浸泡在含有和不含5 mmol/L DDD的硫酸溶液中浸泡4 h。
图1
使用CHI760E电化学工作站进行电化学实验。采用三电极体系,X70钢作为工作电极,饱和甘汞电极为参比电极,铂电极为对电极。开路电位测试时,浸泡时间为1800 s,使X70钢电极表面到达一个稳定的状态。电化学阻抗谱 (EIS) 测试的频率为105~10-2 Hz,使用5 mV的正弦电压作为激励信号。最后,进行动电位极化曲线测试,测试的电位区间为Eocp±250 mV,扫描速率为1 mV·s-1。
使用Gaussian 09软件采用密度泛函理论 (DFT)中的B3LYP方法来计算DDD的量子化学参数,首先在6-311++G (d,p) 基组对DDD进行结构优化,优化后的DDD无虚频。采用Material Studio 2017软件中的Forcite模块来计算DDD分子在Fe (110) 表面的吸附,构建一个三维模拟结构 (1.985 nm×1.985 nm×3.418 nm),它具有周期性;在其中填入300个水分子,4个H3O+,2个硫酸根离子以及1个DDD分子,来模拟其吸附过程。选用COMPASS力场,模拟温度为298 K,在正则系统 (NVT) 进行模拟。时间步长为1 fs,总的模拟时间为1000 ps,在计算时固定所有Fe原子的位置。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 电化学阻抗谱分析
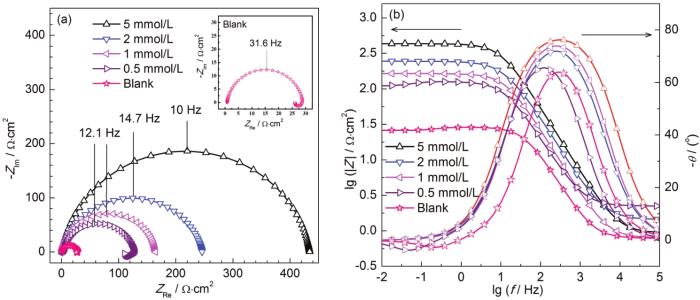
图2是X70钢电极在298 K下浸泡在含有不同浓度DDD的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的电化学阻抗谱图。如图2a所示,随着DDD浓度的增加,容抗弧半径明显增大,这表明DDD分子在X70钢表面吸附后,使得X70钢表面的电荷传递的阻力增加,从而抑制了X70钢的腐蚀。值得注意是,在空白溶液和含0.5 mmol/L DDD溶液中的Nyquist图由高频区的容抗弧和低频区的感抗弧组成,高频区的容抗弧对应了电荷转移电阻和双电层电容,低频区的感抗弧是由于吸附离子如 (H+)ads和 (SO42-)ads在X70钢表面的弛豫过程引起的[6]。可以发现,当DDD浓度为1 mmol/L时,低频区的感抗弧明显消失,这是由于DDD分子在X70钢表面形成了致密的保护膜,从而有效的阻止了吸附离子的弛豫过程。如图2b所示,随着DDD浓度的增加,阻抗模值图和相位角图明显变高变宽,这表明DDD能够展现出良好的缓蚀性能。
图2
图2
X70钢浸泡在0.5 mol/L硫酸溶液中在温度为298 K时含有不同浓度DDD时电化学阻抗谱图
Fig.2
Nyquist (a) and Bode (b) plots of X70 steel immersed at 298 K in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solutions with different concentrations of DDD
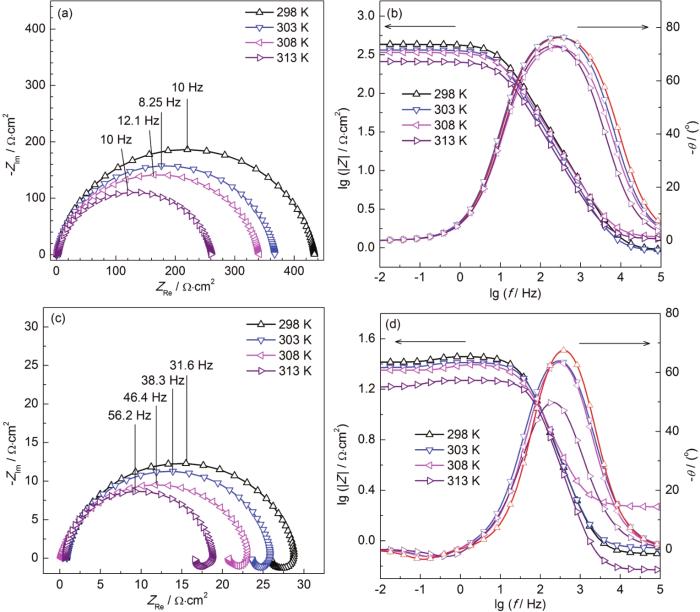
图3
图3
X70钢在298~313 K温度下浸泡在空白和含有5 mmol/L DDD的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的电化学阻抗谱
Fig.3
Nyquist (a, c) and Bode (b, d) plots of X70 steel immersed at 298~313 K in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solutions with (a, b) and without (c, d) 5 mmol/L DDD
式中,Y0代表CPE的值,j为虚数单位,ω代表角频率。n代表偏离指数,可以反映电极表面的不均一性,它的值介于-1~1。Cdl的值可以由如下公式求得[9]:
表1 X70钢在298 K下含有不同浓度DDD的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中浸泡时的EIS拟合参数
Table 1
| C / mmol·L-1 | Rs / Ω·cm2 | Y0×10-6 / S·sn·cm-2 | n | Cdl / μF·cm-2 | Rct / Ω·cm2 | L / Ω·cm2 | RL / Ω·cm2 | η / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank DDD | 0.78 | 227.2 | 0.91 | 141.1 | 28.3 | 161.2 | 233.5 | --- |
| 0.5 | 2.24 | 163.2 | 0.89 | 101.3 | 125.1 | 155.3 | 179.2 | 77.4 |
| 1 | 0.78 | 107.4 | 0.91 | 72.7 | 163.7 | --- | --- | 82.7 |
| 2 | 1.43 | 96.4 | 0.87 | 53.5 | 243.5 | --- | --- | 88.4 |
| 5 | 0.93 | 53.7 | 0.90 | 34.5 | 443.4 | --- | --- | 93.6 |
表2 X70钢在不同温度下浸泡在含有不同浓度DDD的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中EIS的拟合参数
Table 2
| T / K | C / mmol·L-1 | Rs / Ω·cm2 | Y0×10-6 / S·sn·cm-2 | n | Cdl / μF·cm-2 | Rct / Ω·cm2 | L / Ω·cm2 | RL / Ω·cm2 | η / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 0 | 0.78 | 227.2 | 0.91 | 141.1 | 28.3 | 161.2 | 233.5 | --- |
| 5 | 0.93 | 53.7 | 0.90 | 34.5 | 443.4 | --- | --- | 93.6 | |
| 303 | 0 | 0.88 | 193.6 | 0.93 | 100.3 | 25.1 | 215 | 235.6 | --- |
| 5 | 0.92 | 68.5 | 0.91 | 47.2 | 365.7 | --- | --- | 93.1 | |
| 308 | 0 | 1.85 | 316.5 | 0.87 | 155.2 | 23.5 | 51.1 | 169.5 | --- |
| 5 | 1.36 | 67.1 | 0.88 | 40.8 | 338.1 | --- | --- | 93.0 | |
| 313 | 0 | 0.57 | 160.2 | 0.97 | 134.3 | 18.1 | 182.4 | 134.1 | --- |
| 5 | 1.30 | 84.2 | 0.90 | 55.6 | 254.8 | --- | --- | 92.8 |
其中,ε0和ε分别为空气介电常数和双电层的局部介电常数,S为X70钢的面积,d为双电层的厚度。DDD在X70钢表面的吸附是取代表面水分子的过程,因此,DDD取代的水分子越多,Cdl的值下降越明显,DDD在X70钢表面形成的吸附膜越致密。
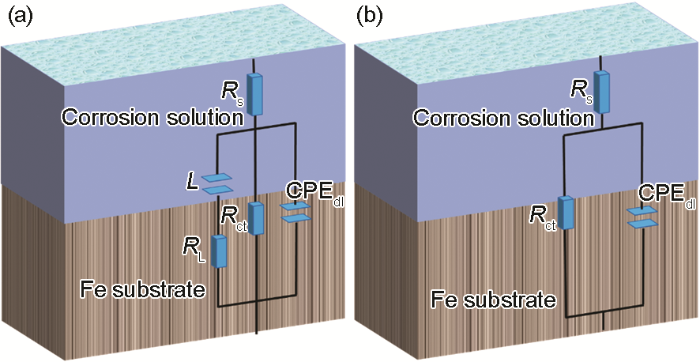
图4
图4
用于拟合电化学阻抗谱数据的等效电路
Fig.4
Equivalent circuit diagrams for fitting EIS of X70 steel in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solutions with (a) and without (b) inductance
2.2 动电位极化曲线分析
图5
图5
X70钢在不同条件下的动电位极化曲线
Fig.5
Polarization curves of X70 steel in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solutions with different concentrations of DDD at 298 K (a), with (b) and without (c) 5 mmol/L DDD at different temperatures
表3 X70钢浸泡在含有不同浓度DDD的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的极化曲线拟合参数
Table 3
| C / mmol·L-1 | Ecorr / V/SCE | Icorr / μA·cm-2 | βc / mV·dec-1 | βa / mV·dec-1 | η / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank DDD | -0.468 | 520.7 | -146.7 | 44.9 | --- |
| 0.5 | -0.473 | 107.6 | -98.3 | 60.4 | 79.3 |
| 1 | -0.473 | 81.2 | -99.5 | 45.6 | 84.4 |
| 2 | -0.490 | 53.6 | -106.8 | 79.6 | 89.7 |
| 5 | -0.503 | 30.2 | -114.0 | 87.9 | 94.2 |
表4 X70钢在不同温度下浸泡在未含DDD的0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中的极化曲线拟合参数
Table 4
| T / K | C / mmol·L-1 | Ecorr / V/SCE | Icorr / μA·cm-2 | βc / mV·dec-1 | βa / mV·dec-1 | η / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 0 | -0.468 | 520.7 | -146.7 | 44.9 | --- |
| 5 | -0.503 | 30.2 | -114.0 | 87.9 | 94.2 | |
| 303 | 0 | -0.474 | 543.2 | -148.2 | 56.2 | --- |
| 5 | -0.483 | 35.8 | -104.6 | 92.1 | 93.4 | |
| 308 | 0 | -0.475 | 552.9 | -140.4 | 55.4 | --- |
| 5 | -0.500 | 37.6 | -109.8 | 98.9 | 93.2 | |
| 313 | 0 | -0.467 | 568.1 | -138.9 | 58.9 | --- |
| 5 | -0.475 | 40.3 | -110.6 | 82.2 | 92.9 |
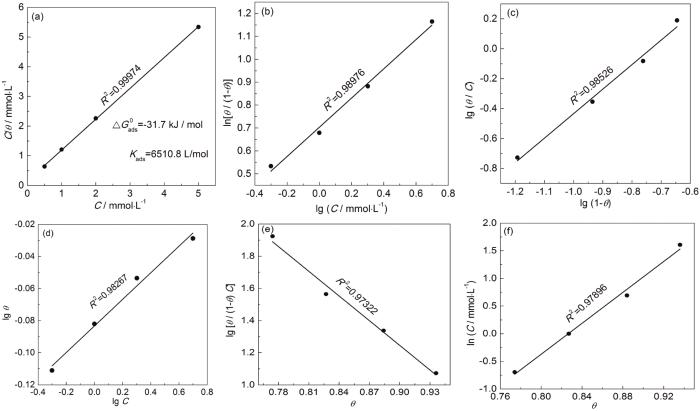
2.3 等温吸附模型研究
图6
图6
不同等温模型的拟合曲线
Fig.6
Fitting curves of Langmuir (a), El-Awady (b), Flory-Huggins (c), Freundlich (d), Frunkin (e) and Temkin (f) isothermal adsorption models
除此之外,对ΔG0ads的值进行了求解[15]:
其中,R表示理想气体常数,55.5是水的摩尔浓度,T表示热力学温度。计算后得到了Kads和ΔG0ads值,如图6a所示。ΔG0ads的值为负,表示DDD分子能够自发的吸附在X70钢/溶液界面上。ΔG0ads值的大小和吸附类型相关,ΔG0ads的值大于-20 kJ/mol时,表明带电缓蚀剂和带电金属通过静电吸引从而产生了物理吸附。ΔG0ads的值小于-40 kJ/mol时,表明缓蚀剂分子和金属表面有电荷的转移或共享形成共价键从而产生化学吸附[16]。当ΔG0ads的值介于两者之间时,说明物理吸附和化学吸附共同存在。结果表明,ΔG0ads=-31.7 kJ/mol,因此DDD在X70钢/溶液界面属于物理化学吸附共同作用。
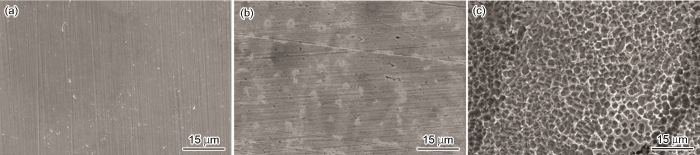
2.4 SEM分析
图7
图7
X70钢在不同条件下的SEM形貌图
Fig.7
SEM images of X70 steel before (a) and after immersion at 298 K for 4 h in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution with (b) and without (c) 5 mmol/L DDD
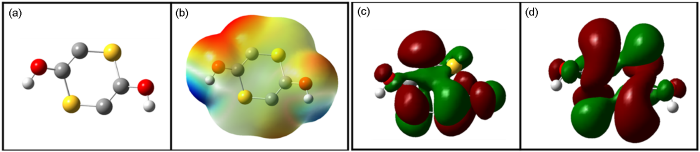
2.5 量子化学和分子动力学模拟分析
图8
图8
DDD分子优化后的构型,静电势图,HOMO和LUMO轨道的电子云分布
Fig.8
Optimized configuration (a), electrostatic potential map (b), and distributions of electron clouds of HOMO (c) and LUMO (d) orbitals of DDD molecular
另外,DDD分子的HOMO和LUMO轨道的电子云分布在整个分子上,这说明DDD能够平行的吸附在X70钢的表面去获得最大的覆盖度。DDD分子的EHOMO值为-6.58 eV,ELUMO值为-3.51 eV。HOMO轨道和LUMO轨道分别对应了DDD分子的给电子能力和得电子能力。可以通能隙值ΔE (ELUMO-EHOMO) 来判断DDD分子的反应活性。DDD的能隙值为3.07 eV,低的能隙值表明DDD能够显示出卓越的缓蚀性能。
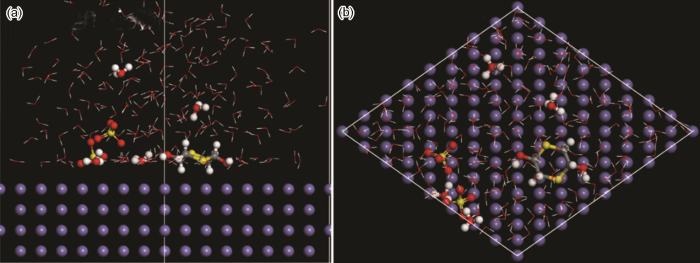
其中,Etot表示的整个模拟体系的总能量,Esubs是这个模拟体系中除了缓蚀剂分子的能量,Einh是单个DDD缓蚀剂分子的能量。通过
图9
图9
DDD分子在Fe (110) 表面的稳定吸附构型
Fig.9
Stable adsorption configuration of DDD molecule on Fe (110) surface: (a) side view, (b) top view
3 结论
(1) DDD能够有效地抑制X70管线钢在硫酸溶液中的腐蚀,极化曲线结果表明DDD属于混合型缓蚀剂。在298~313 K温度范围,DDD的缓蚀性能能够维持在90%以上。
(2) DDD在X70钢表面的吸附符合朗缪尔单层吸附模型,并且属于同时存在化学和物理共同吸附。
(3) 量子化学计算结果表明,DDD吸附活性位点集中在O和S原子上,这些杂原子能和铁原子形成配位键。分子动力学模拟表明,DDD分子能够平行的吸附在Fe (110) 表面以获得最大的覆盖度。
参考文献
Evaluation of Ginkgo leaf extract as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor of X70 steel in HCl solution
[J].
A combination of experiment and theoretical methods to study the novel and low-cost corrosion inhibitor 1-hydroxy-7-azabenzotriazole for mild steel in 1 M sulfuric acid
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of X65 steel in sulfuric acid by two food flavorants 2-isobutylthiazole and 1-(1,3-Thiazol-2-yl) ethanone as the green environmental corrosion inhibitors: Combination of experimental and theoretical researches
[J].
Study on the influences of two thiazole flavor ingredients on Cu corrosion caused by chloride ion
[J].
A combined experimental and theoretical study of the inhibition effect of three disulfide-based flavouring agents for copper corrosion in 0.5 M sulfuric acid
[J].
Experimental and theoretical studies of two imidazolium-based ionic liquids as inhibitors for mild steel in sulfuric acid solution
[J].
A novel and high-efficiency inhibitor of 5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3h-1,2-dithiole-3-thione for copper corrosion inhibition in sulfuric acid at different temperatures
[J].
Self-assembling anchored film basing on two tetrazole derivatives for application to protect copper in sulfuric acid environment
[J].
Use of Rosa canina fruit extract as a green corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 1 M HCl solution: A complementary experimental, molecular dynamics and quantum mechanics investigation
[J].
Tetrahydroacridines as corrosion inhibitor for X80 steel corrosion in simulated acidic oilfield water
[J].
Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in 1 M HCl solution by ethanolic extract of eco-friendly Mangifera indica (mango) leaves: Electrochemical, molecular dynamics, Monte Carlo and ab initio study
[J].
Insights into the inhibition mechanism of three 5-phenyltetrazole derivatives for copper corrosion in sulfuric acid medium via experimental and DFT methods
[J]. J.
Investigation of 1-butyl-3-methyl-1H-benzimidazolium iodide as inhibitor for mild steel in sulfuric acid solution
[J].
A new insight into corrosion inhibition mechanism of copper in aerated 3.5wt.%NaCl solution by eco-friendly Imidazopyrimidine Dye: Experimental and theoretical approach
[J].
Investigation of imidazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors of copper in sulfuric acid: Combination of experimental and theoretical researches
[J]. J.
A combined experimental and theoretical study of papain as a biological eco-friendly inhibitor for copper corrosion in H2SO4 medium
[J].
Magnolia grandiflora leaves extract as a novel environmentally friendly inhibitor for Q235 steel corrosion in 1 M HCl: Combining experimental and theoretical researches
[J].
Locust Bean Gum as a green and novel corrosion inhibitor for Q235 steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 medium
[J].