本文以20#钢和L245NS钢作为研究对象,通过在施加应力和动态流体的H2S/CO2环境中进行浸泡腐蚀实验,探讨了其在H2S/CO2环境中的腐蚀行为,对控制H2S/CO2环境腐蚀具有重要意义。
1 实验方法
实验所用材料为油气田地面集输常用的20#钢和L245NS钢管道用钢。20#钢的化学成分 (质量分数,%) 为:C 0.21,Si 0.28,Mn 0.43,P 0.031,S 0.029,Cr 0.24,Ni 0.24,Cu 0.15,Fe余量。L245NS钢的化学成分 (质量分数,%) 为:C 0.16,Si 0.22,Mn 0.78,P 0.005,S 0.0021,Fe余量。采用线切割切取尺寸为50 mm×10 mm×3 mm的腐蚀试样,用SiC砂纸逐级打磨至1500#,最后一道研磨沿受力方向。试样打磨完成后,用丙酮除油,再用无水乙醇进行超声清洗,最后用蒸馏水冲洗并用吹风机冷风吹干后,放入干燥皿中备用。实验前,测量试样尺寸和称量试样质量,称重精确至0.1 mg。
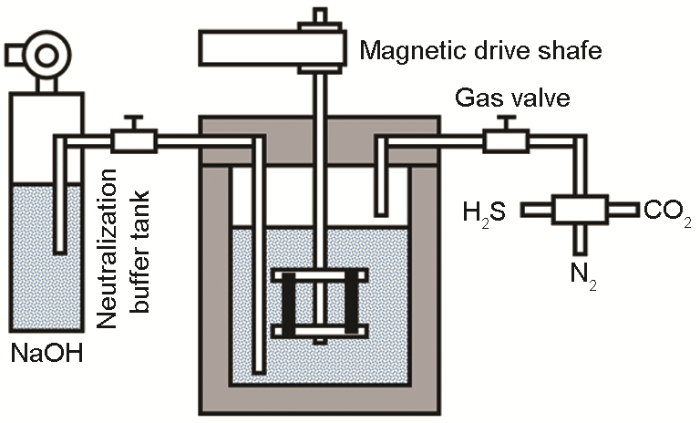
采用磁力驱动的C276高温高压腐蚀测试反应釜模拟工况条件下的腐蚀行为,反应釜结构如图1所示。腐蚀介质为塔里木油田采出水模拟液,其离子成分 (mg·L-1) 为:HCO3- 189,Cl- 128000,SO42- 430,Ca2+ 8310,Mg2+ 561,K+ 6620,Na+ 76500。浸泡温度为集输管线实际工况温度70 ℃,H2S气体分压为1578.6 Pa,CO2气体分压0.192 MPa,实验总压为6.4 MPa,浸泡时间为168 h。实验前,采用ANSYS有限元数值分析,模拟了沙丘移动导致的不同起伏倾角条件下管道的受力情况。在10°至45°倾角时,管道受到的最大拉应力约为150 MPa。采用DM-YB1820动静态应变测试系统并结合应变片传感器通过四点弯曲的方式对样品施加应力。将四点弯曲夹具安装在旋转笼上,通过磁力驱动轴实现线速度为1.5 m/s的介质流动条件。根据实验要求,将在无应力作用下静态介质中浸泡条件定义为条件1,在应力作用下静态介质中浸泡条件定义为条件2,在应力作用下动态介质中浸泡条件定义为条件3。
图1
将旋转笼固定在旋转轴上,加入除氧4 h后的腐蚀介质使试样完全浸没。将反应釜密闭后,进行试压,确定各部件正常工作后,通入N2置换出反应釜内溶液上层空气。升温至目标温度后,通入CO2和H2S气体达到实验条件并恒定,开启旋转电机使旋转轴达到流动条件后,开始计时。实验结束后,关闭旋转电机和加热,待反应釜温度降至30℃后,打开排气阀,通入氮气排出溶液和气体至中和缓冲罐,使实验溶液和气体中和吸收。取出试片后立即用清水冲洗残余腐蚀介质并用滤纸吸干,再用丙酮和无水乙醇除油除水并用冷风吹干。拍摄宏观照片,记录表面腐蚀情况。将腐蚀后的试样放入配制好的除锈液 (500 mL 盐酸+500 mL蒸馏水+20 g六次甲基四胺) 中浸泡5 min,用清水冲洗表面残酸后,放入无水乙醇中浸泡清洗,后冷风吹干,并进行称重 (精确至0.1 mg)。利用失重法测定不同条件下的腐蚀速率[9]:
其中,W0和W1分别为实验前后的样品重量,g;t为浸泡时间,h;ρ为密度,g/cm3;A为样品暴露表面积,cm3;V为腐蚀速率,mm/a。
采用Zeiss Ultra Plus场发射扫描电镜 (FE-SEM) 对腐蚀后的试样进行表面微观形貌观察。采用Smartlab 9kW高分辨X射线衍射仪 (XRD) 对腐蚀产物进行物相分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 宏观腐蚀形貌
20#钢和L245NS钢在模拟工况条件下浸泡实验后的宏观腐蚀形貌如图2所示。在相同H2S/CO2分压环境中,在条件1下,试样表面腐蚀轻微,仍有一定的金属光泽。在条件2下,表面腐蚀产物明显多于条件1下的,但腐蚀产物没有完全覆盖试样表面,表明应力作用促进了两种钢材的腐蚀。在条件3下,试样表面腐蚀非常严重,腐蚀产物分布比较均匀,且表面腐蚀产物呈细颗粒状,表明应力与介质流动共同作用进一步促进了腐蚀。
图2
图2
20#钢和L245NS钢在不同条件下浸泡后的宏观腐蚀形貌
Fig.2
Macroscopic feature of 20# carbon steel (a1, b1, c1) and L245NS steel (a2, b2, c2) after corrosion in static fluid under stress free (a) and applied stress (b), and in flowing fluid under applied stress (c)
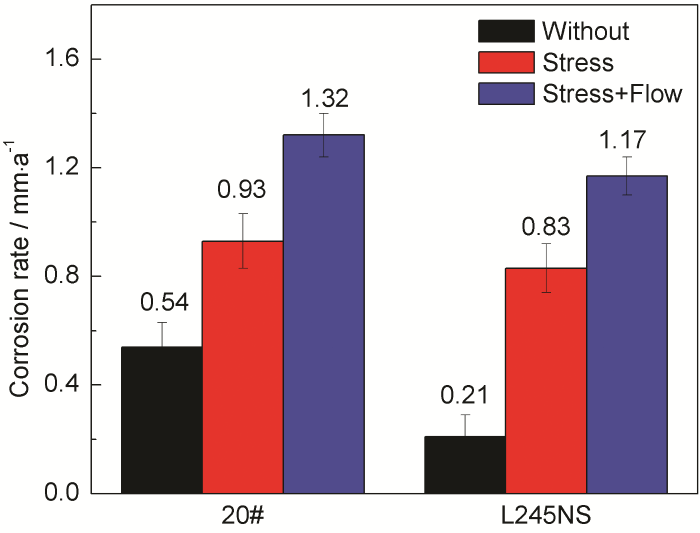
2.2 腐蚀速率分析
根据
图3
图3
20#钢和L245NS钢在各条件下浸泡时的腐蚀速率
Fig.3
Corrosion rates of 20# and L245NS steels during immersion in different conditions (static fluid/stress free, static fluid/stress, flowing fluid/stress)
2.3 腐蚀产物膜组成及微观形貌分析
图4
图4
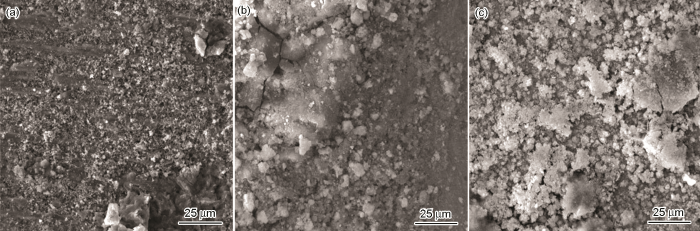
20#钢在各条件下腐蚀后的微观形貌
Fig.4
SEM images of 20# carbon steel after corrosion in static fluid under stress free (a) and applied stress (b), and in flowing fluid under applied stress (c)
图5
图5
L245NS钢在各条件下腐蚀后的微观形貌
Fig.5
SEM images of L245NS carbon steel after corrosion in static fluid under stress free (a) and applied stress (b), and in flowing fluid under applied stress (c)
图6
图6
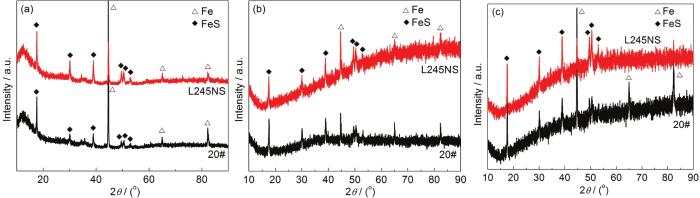
20#钢和L245NS钢在各条件下浸泡后的腐蚀产物XRD谱
Fig.6
XRD patterns of 20# carbon steel and L245NS steel after corrosion in static fluid under stress free (a) and applied stress (b), and in flowing fluid under applied stress (c)
20#钢和L245NS钢在条件2 (图4b和5b) 浸泡后,试样表面腐蚀产物增多,且有明显裂纹。通过XRD确认这层腐蚀产物膜为FeS。与条件1下形成的FeS膜相比,在条件2下形成的腐蚀产物膜具有规则的晶体颗粒外形,颗粒尺寸较大,颗粒间存在较大的空隙,形成大量的微观通道,对金属基体的保护性较弱,不能抑制腐蚀过程。这可能是由于应力作用下,腐蚀产物难以形成致密且连续的膜层,导致腐蚀介质通过空隙渗透到碳钢基体表面,腐蚀速率加快,腐蚀产物更多。相比较于20#钢,L245NS钢的腐蚀产物膜空隙较少,腐蚀产物膜致密性较高,相应地保护性较好。
20#钢和L245NS钢在条件3下 (图4c和5c) 浸泡后,试样表面腐蚀产物较少,无明显裂纹。通过XRD确认这层腐蚀产物膜为FeS。与条件2下形成的FeS膜相比,在条件3下形成的腐蚀产物膜具有不规则絮状物和大量晶体颗粒。根据腐蚀速率分析发现,两种材料在条件3浸泡后的腐蚀速率最大。这一现象可能是由于应力的作用为腐蚀介质接触基体提供通道,液体流动加速了Fe2+向溶液中扩散和腐蚀性物质接触金属基体。同时,附着力差的FeS腐蚀产物被流体冲刷而带走,难以在金属表面沉积形成腐蚀产物膜。两者共同作用下,虽然腐蚀产物膜很致密,但溶解的金属更多,沉积的腐蚀产物更少,导致更严重的腐蚀行为。相比较于20#钢,L245NS钢的腐蚀产物膜更致密。上述所有观察结果与腐蚀速率测试结果均一致。
2.4 腐蚀机理分析
分析碳钢在H2S/CO2共存环境中的腐蚀行为时,往往首先需要区分腐蚀过程中的主导作用。目前以CO2和H2S的分压比值
阳极反应为Fe的溶解:
因此,在H2S溶液中金属表面会形成FeS腐蚀产物膜:
20#钢和L245NS钢在H2S/CO2环境中的不同条件下的腐蚀机理如图7所示。图7a为无应力作用下静态介质中的腐蚀机理。在本研究的腐蚀环境中,H2S起主导作用,在金属表面覆盖一层具有保护性的FeS腐蚀产物膜[16-18],抑制了腐蚀的进一步发生,降低了腐蚀速率。图7b为只有应力作用下静态介质中的腐蚀机理。应力作用下难以形成致密的FeS腐蚀产物膜[19],腐蚀产物膜存在大量的空隙,形成微观通道,为腐蚀介质接触金属基体提供条件,进一步加速了腐蚀过程,腐蚀速率增大。图7c为在应力作用下流动介质中的腐蚀机理。流体流动促进了腐蚀性物质向金属基体的扩散过程[20],加速了金属的溶解,形成更多的Fe2+。同时,附着力差的FeS腐蚀产物被流体冲刷带走,导致金属表面难以形成更厚的腐蚀产物膜,进一步加速了腐蚀过程,腐蚀速率最大。
图7
图7
碳钢在H2S/CO2环境中不同条件下的腐蚀机理
Fig.7
Corrosion mechanisms of carbon steel in H2S/CO2 containing static fluid under stress free (a) and applied stress (b) and in flowing fluid under applied stress (c)
3 结论
(1) 在H2S/CO2共存环境中的不同条件下,20#钢的平均腐蚀速率均高于L245NS钢的。在无应力作用下的静态介质中,L245NS钢的腐蚀程度轻微,表明L245NS钢比20#钢更适合在H2S/CO2共存环境中使用。
(2) 在施加应力和介质流动条件下,两种材料的腐蚀速率均增大,且比仅施加应力条件下的腐蚀速率高。
(3) H2S在腐蚀过程中起主导作用,生成了具有保护性的FeS腐蚀产物。应力会导致腐蚀产物膜存在大量微观通道,促进了腐蚀过程的进行。在介质流动条件下的腐蚀产物膜虽然致密,但流体冲刷加速了金属溶解和腐蚀性物质的扩散,表现出最大的腐蚀速率。
参考文献
Corrosion behavior of 80SS pipeline steel in tarim gas field
[J].
80SS油管钢在塔里木气田中的腐蚀行为
[J].
Dynamic corrosion behavior of p110 steel in stimulated oil field CO2/H2S environment
[J].
模拟油田CO2/H2S环境中P110钢的动态腐蚀行为
[J].
Corrosion behavior of materials used for surface gathering and transportation pipeline in an oilfield
[J]. J
某油田地面集输管道用材腐蚀行为研究
[J].
Corrosion behavior of L245 steel in simulated oilfield produced water at different temperatures
[J]. J
L245钢在不同温度下的油气田模拟水中的腐蚀行为研究
[J].
Study on dynamic corrosion behaviors of tubing steels in simulated oilfield H2S/CO2 environment
[J].
油管钢的H2S/CO2动态腐蚀行为
[J].
Research progress of CO2/H2S corrosion in oil and gas pipelines and the protection techniques
[J].
油气管道CO2/H2S腐蚀及防护技术研究进展
[J].
Study on corrosion laws of pipeline steel 20# and L245NS in CO2 flooded oilfields
[J].
油田二氧化碳驱20#和L245NS管线钢腐蚀规律研究
[J].
The research of X65 pipeline steel corrosionin H2S/CO2 coexist environment
[J].
X65管线钢材在H2S/CO2共存环境中的腐蚀研究
[J].
Study of N80 steel corrosion in the oil-gas-water system containing CO2 and H2S
[J].
油气水系统中N80钢CO2/H2S共存腐蚀规律研究
[J].
Corrosion behavior of several thermal recovery well tubular steels in secondary H2S/CO2 environment
[J].
几种热采井用油管钢在次生H2S/CO2环境中的腐蚀行为
[J].
Effect of small amount H2S on CO2 corrosion behavior of oil tube steel
[J].
微量H2S对油管钢CO2腐蚀行为的影响
[J].
The effect of temperature, CO2, H2S gases and the resultant iron carbonate and iron sulfide compounds on the sour corrosion behaviour of ASTM A-106 steel for pipeline transportation
[J].
Comparison of corrosion behaviour of low-alloy pipeline steel exposed to H2S/CO2-saturated brine and vapour-saturated H2S/CO2 environments
[J].
Effect of temperature and pressure on corrosion behavior of X65 carbon steel in water-saturated CO2 transport environments mixed with H2S
[J].
Critical factors in predicting CO2/H2S corrosion in multiphase systems
[A].
Assessment and influence of temperature, NaCl and H2S on CO2 corrosion behavior of different microstructures of API 5L X52 carbon steel in aqueous environments
[J].
Corrosion behavior of P110 tubing steel in the CO2-saturated simulated oilfield formation water with element sulfur addition
[J].
Mechanism of CO2 corrosion on tubular goods and its prevention measures
[J].
油气管材CO2腐蚀机理及其防护措施
[J].
Effect of H2S partial pressure on stress corrosion cracking behavior of 13Cr stainless steel in annulus environment around CO2 injection well
[J]. J
H2S分压对13Cr不锈钢在CO2注气井环空环境中应力腐蚀行为的影响
[J].